Building a Simple Voltage Source Inverter
Your Task:
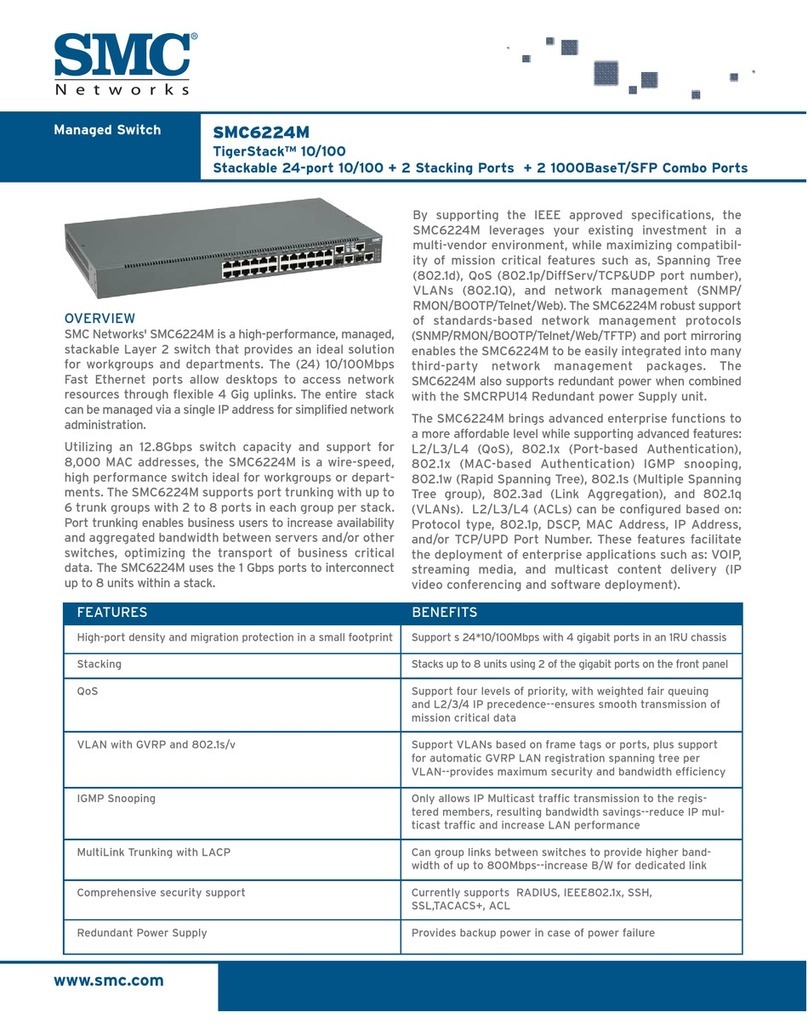
1Create a new PLECS model and build the VSI and PWM modulator given in Fig. 1. Use the Half
Bridge component from the “Electrical”, “Power Modules” section of the PLECS component library.
Use a PWM Capture block from the PLECS RT Box library and connect it to the IGBT gate inputs
as shown in the figure. Also note the difference in the Polarity setting for the two PWM Out com-
ponents.
Use the default component parameters unless noted differently in Fig. 1.
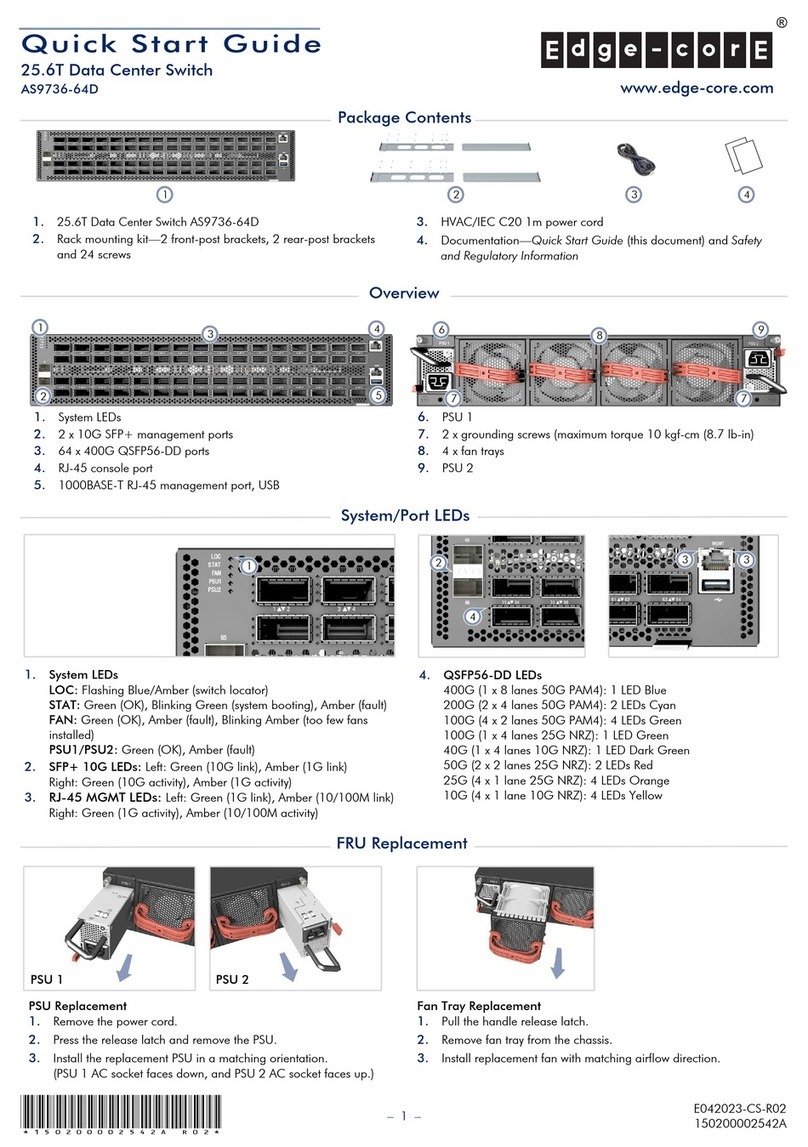
2Use a DSUB loopback cable to connect the Digital Out ports on the RT Box front panel with the
Digital In ports.
3Open the Coder options... menu and enter a discretization step size of 5e−6seconds, select your
RT Box target in the Target tab and click Build.
Connect to the External Mode and check the simulation scopes. What do you see? Is this
result reasonable?
The “PWM” Scope should show six PWM signals which are on the range of zero to one.
Right click the Scope window and select Spread signals to view all six inputs at once. The
“Current” Scope should show a balanced three-phase sinusoidal inductor current. These
results are expected based on the sinusoidal input signals to the PWM Out blocks.
What is the execution time of the model and processor loading? These performance metrics
can be accessed from the RT Box Web Interface. Can the model complexity be increased?
The average execution time of the model should be near 2.2µsand the processor loading
will be 40 % to 45 %. The model complexity can be increased since the processor loading is
well below 100 %. Alternatively, the simulation time step could be further reduced.
After completing these tasks, your model should be the same as the reference model
vsi_loopback_1.plecs.
3 Building a VSI model in PLECS with discrete components
In this section you will replace the half-bridge power modules with discrete IGBT components. This
exercise is supposed to highlight some of the limitations of conventional (discrete) switch models in
real-time applications.
Note: Always use the dedicated power modules when building up a converter topology for real-
time simulation since using discrete components can mean high loss in simulation accuracy!
To simulate a PLECS model in real-time, the model must be discretized to run at a fixed sample
time using a fixed-step solver. The ideal sample time, or discretization step size, is a compromise be-
tween system model fidelity and accuracy of the simulation results. Conventional switch model perfor-
mance in real-time applications is closely coupled to the chosen discretization step size, as the switch
state can only change once per simulation time step. This limits the number of achievable duty cycles
within a switching period.
With conventional switch models, a comparatively small step size must be chosen relative to the PWM
switching frequency to achieve acceptable model fidelity. When small time steps are chosen, there is a
www.plexim.com 2