Section 16: SUSPENSION
16-5
6. Build up air pressure in system.
Note: To accelerate this operation, air reser-
voirs can be filled from an exterior air supply
connected to the accessory tank fill valve or to
the emergency fill valve.
7. Check operation of bellows, and with the pri-
mary air system at normal operating pressure
(95 - 125 psi (655 - 860 kPa)), coat the air line
connections and air spring mounting areas
with a water and soap solution. Bubbles will in-
dicate an air leak, and none is permissible.
Repair or replace defective parts.
8. Remove the hydraulic floor jack from under the
axle, then lower vehicle to ground.
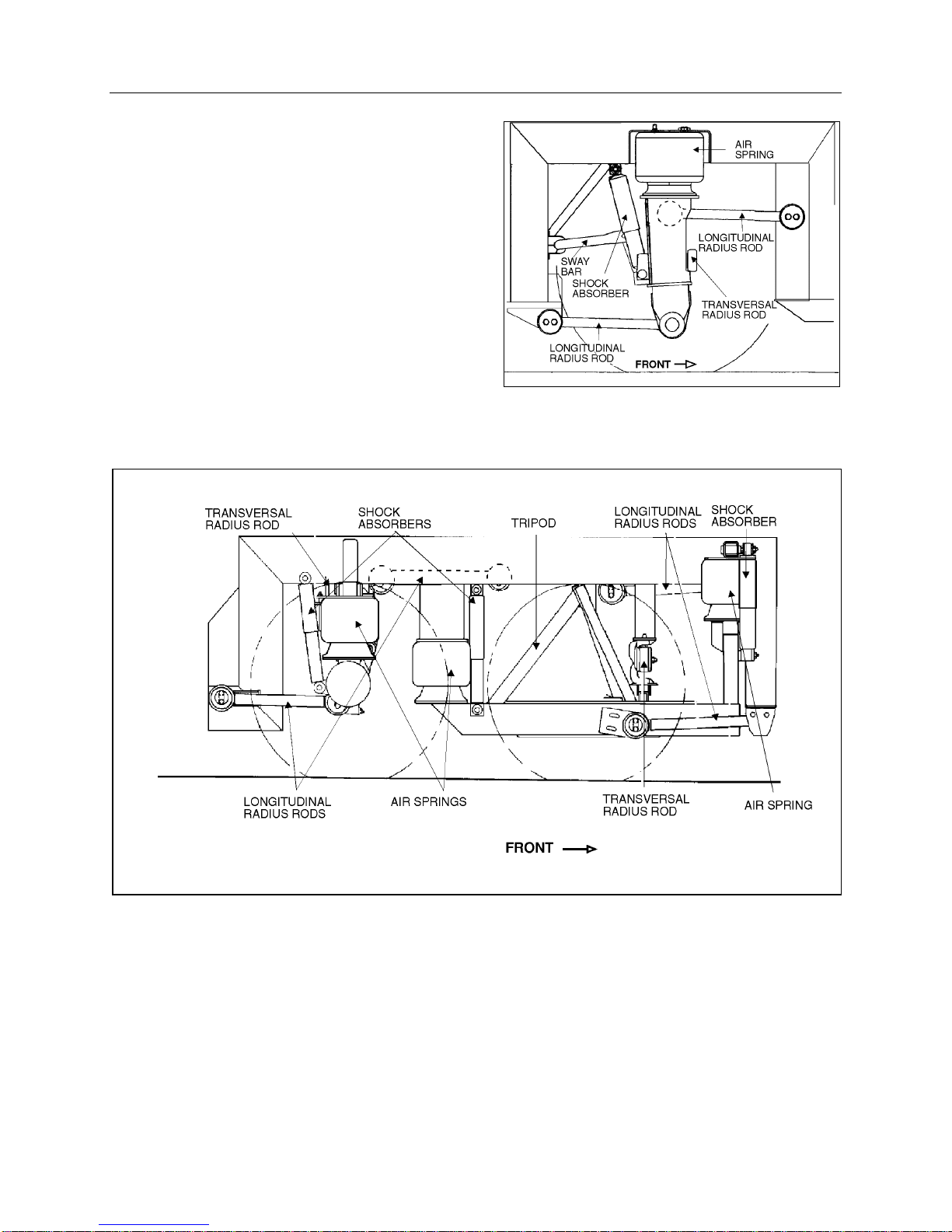
3. SHOCK ABSORBER
Double-action, telescoping-type shock absorbers
ensure a smooth ride and enhance vehicle stabil-
ity on the road. All shock absorbers are eye-type
mountings. The front and tag axles are each pro-
vided with two shock absorbers while the drive
axle is provided with four of them (Fig. 1 and 2).
Shock absorbers are non-adjustable and non-
repairable. Maintenance requirements involve
replacement of the rubber mounting bushings,
and tightening of all shock absorber pins at the
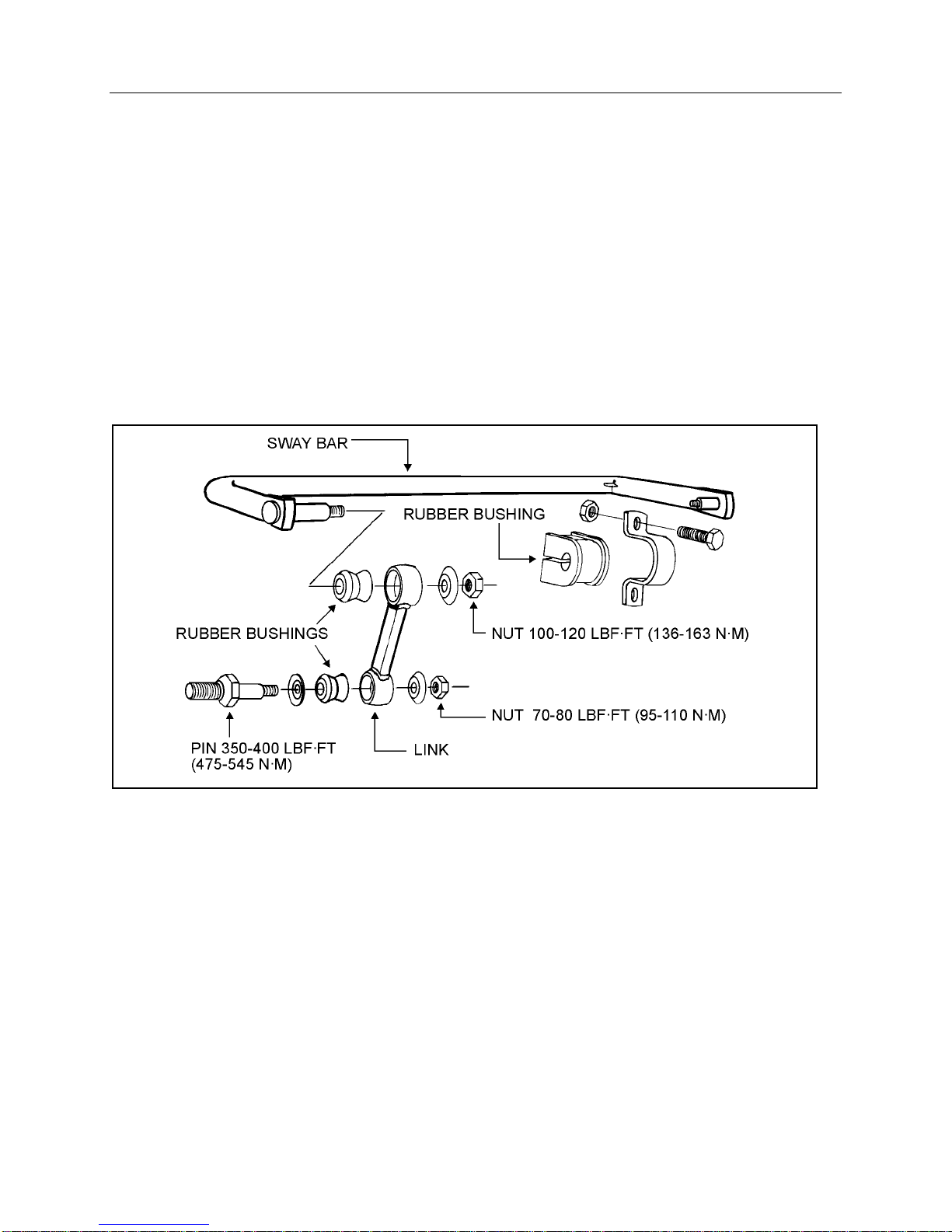
proper torque (350 - 400 lbf·ft (475 - 545 N·m))
when shock absorber replacement occurs. If a
shock absorber becomes inoperative, complete
unit must be replaced.
Caution: When a shock absorber is found
defective, always replace with a new set on
affected axle, except if there has been a recent
replacement of one unit. The following method
will help in determining if both shock absorb-
ers on the same axle have to be replaced.
3.1 Inspection
Loosen lower mounting of both shocks, then
carefully attempt to raise and lower the bottom
portion of each shock. Note the rate of effort for
distance of travel. Replace both shocks if a defi-
nite differential rate is found.
The shock must be bench checked in an upright,
vertical position. If checked in any other position,
air will enter the cylinder tube and make the shock
absorber appear defective.
Proceed as follows to check shock absorbers:
1. With the shock absorber in a vertical position
(top end up), clamp the bottom mount in a
vise.
Caution: Do not clamp the reservoir tube or
the dust tube.
2. Rotate the dust tube. Notice any binding con-
dition (may be compared with new unit). Bind-
ing condition indicates a scored rod. Units with
scored rods should be replaced.
3. Fully extend shocks and check for leaks in the
seal cover area. Shock fluid is a very thin hy-
draulic fluid that has a characteristic odor and
dark brown tint. A slight trace of shock fluid
around the seal cover area is not a cause for
replacement. The shock seal is designed to
permit a very slight seepage to lubricate the
rod. Units which leak should be replaced.
4. Visually check shock for dents that could
cause the shock to bind. Also, check for a bent
rod.
5. Extend and collapse shock to determine that it
has control (resistance) in both rebound and
compression.
6. Visually inspect the shock mountings and ve-
hicle mountings for:
a) Broken mounts;
b) Extreme bushing wear;
c) Shifted bushing or sleeve;
d) Deep cracks in bushing material (shallow
surface cracks are normal);
e) Loose shock absorber pins;
f) Presence of convex washers, and their po-
sition according to the rubber bushing.
3.2 Removal
1. Remove nuts and washers from shock ab-
sorbers on upper and lower mounting pins,
taking care to identify the inner and outer
washers to ease reinstallation. Refer to fig-
ure 4 for details.