© RFbeam Microwave GmbH |Schuppisstrasse 7 |CH-9016 St. Gallen |www.rfbeam.ch |K-MD2 Engineering Sample |user manual 07/2018 – Revision A |Page 3/23
INSTALLATION
Double-click the K-MD2_CTP-RFB-01XX_Setup.msi
file to start the installation of the control panel. Follow
the steps until installation is completed.
To use the integrated video function, the « Logitech
HD Webcam C525 » is recommended and suppor-
ted by the control panel. Please download and install
necessary drivers for the webcam from the manufac-
turer’s website.
Setup for TCP (Ethernet)
Choose this option to connect the radar via TCP. To
connect the radar with the computer via ethernet
follow these steps:
1. Plug in the delivered power supply (+12VDC) and
connect it to the K-MD2
2. Connect the ethernet cable to the K-MD2 and
your computer
3. After some seconds the LED1 starts blinking
4. Change the IPV4 connection settings on your
computer to a static setting with the following
parameters:
IP-Address: 192.168.16.1
Subnet: 255.255.255.0
5. Open the cmd console and type in:
ping 192.168.16.2 <enter>
6. The K-MD2 should now respond to this ping. If
there is no response at all, recheck your IP-ad-
dress settings. If your IP-address settings are cor-
rect, please consider the possibility your firewall is
blocking the connection.
7. Connect your webcam – wait until Windows has
installed the webcam drivers.
8. Your K-MD2 is now connected with your compu-
ter – start the control panel.
9. Now click the “Connect” button in the TCP frame
(Figure 2). If it does not connect immediately, click
again until it successfully connects your K-MD2.
10. On a system with multiple cameras, the window
Figure 3 will pop up. Select the camera you want
to use.
11. After connecting, the control panel will display the
following view of Figure 4.
Figure 2: TCP area
Figure 3: Camera selection window
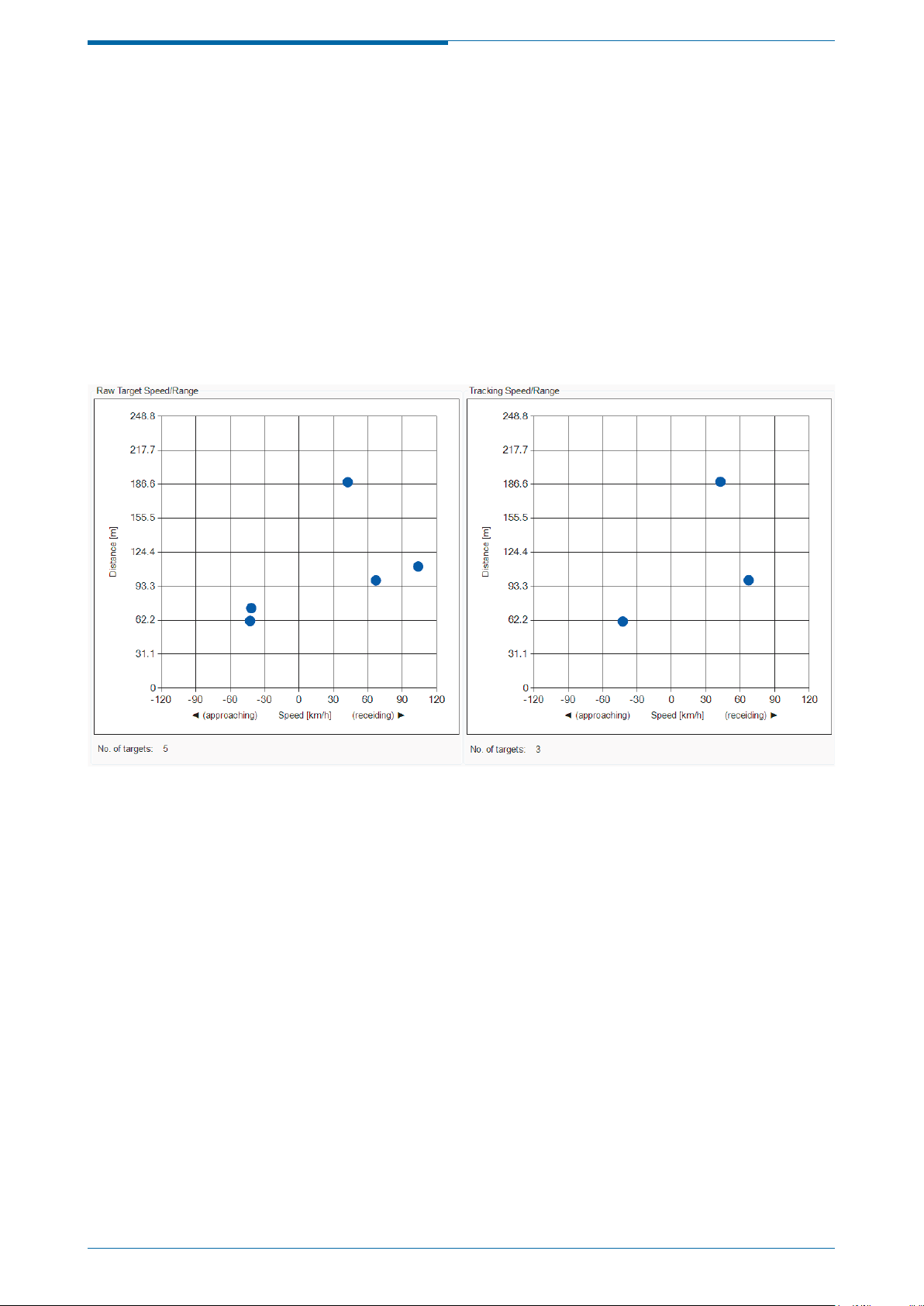
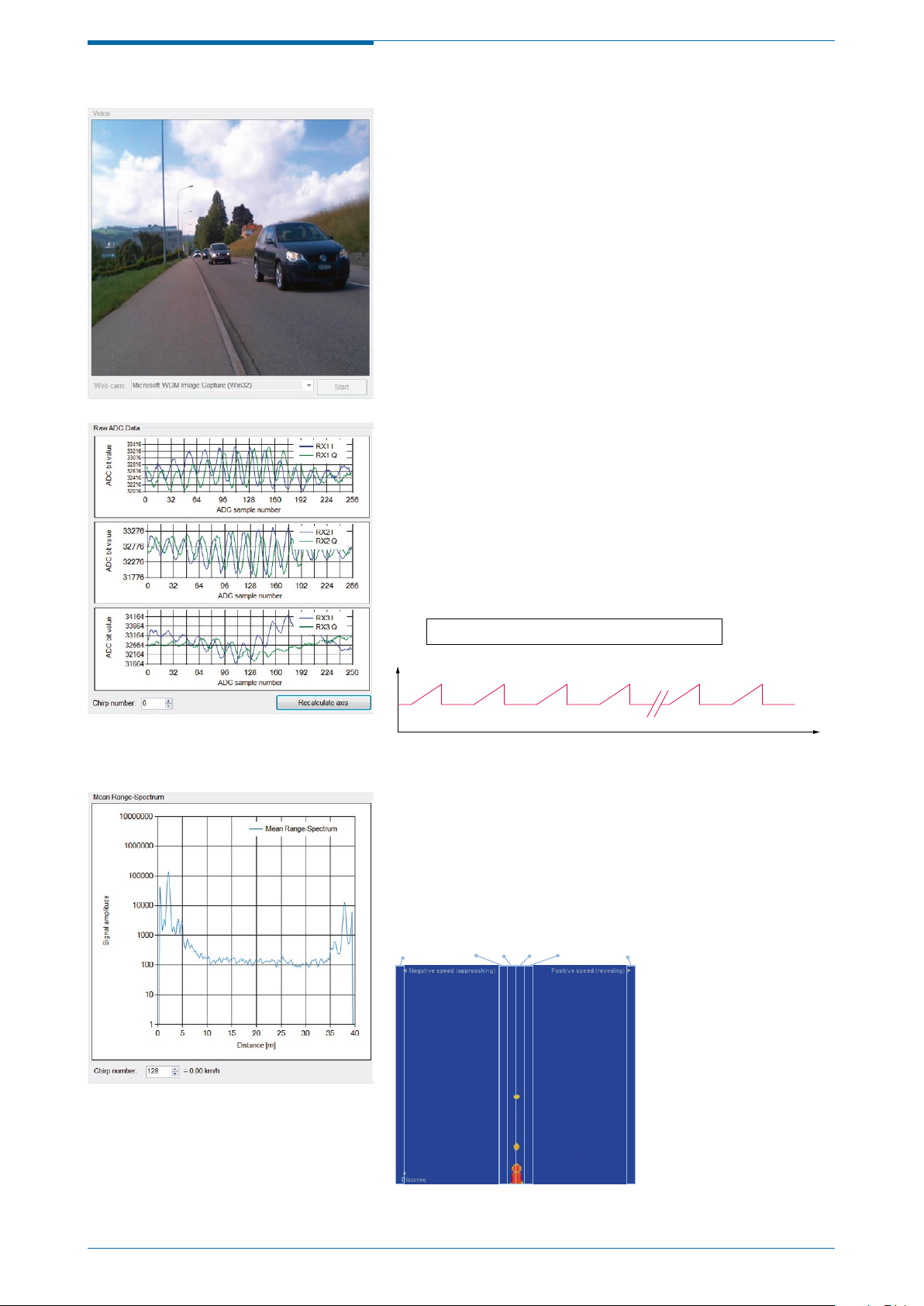
Figure 4: Default connected view