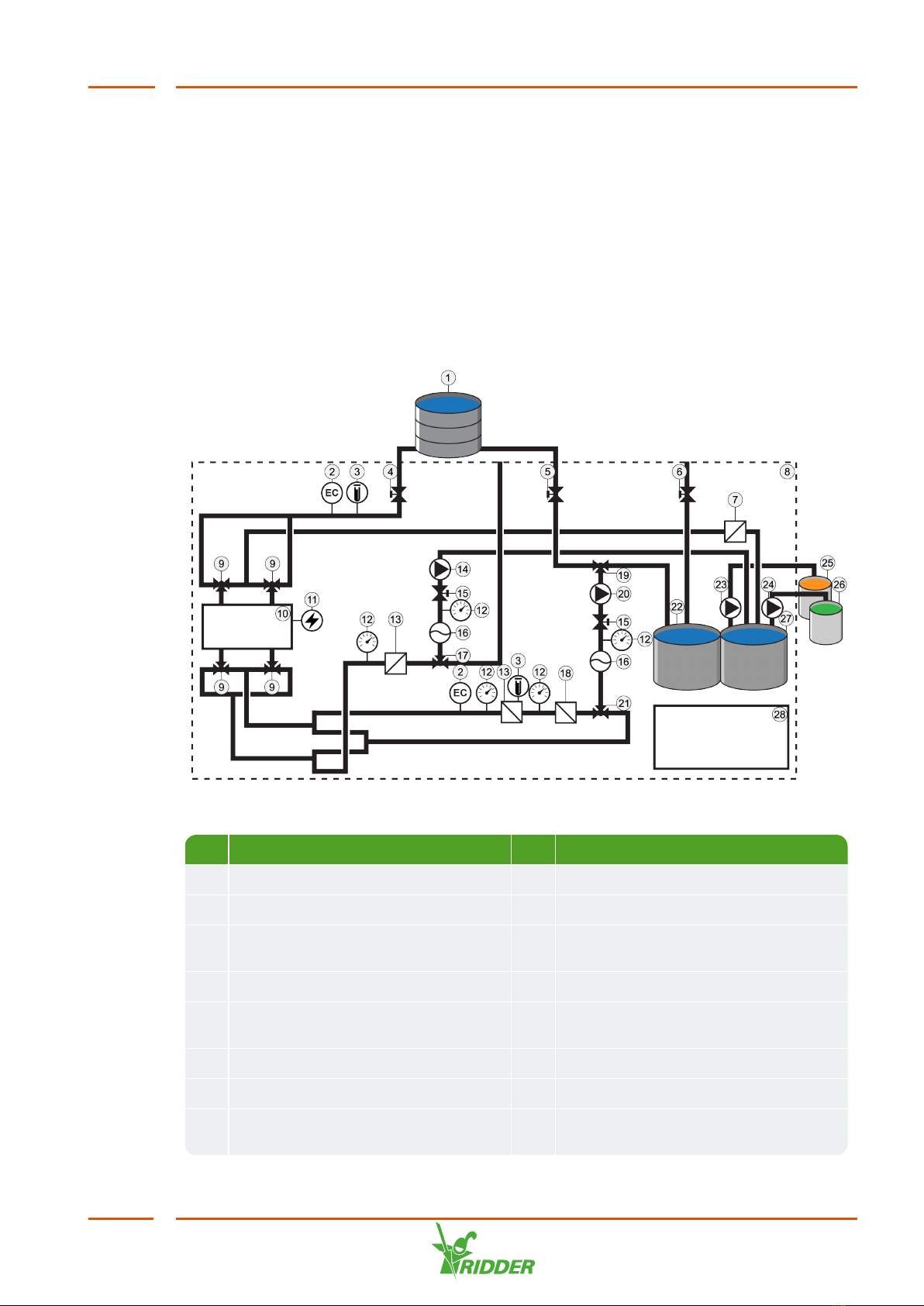
Ridder NoNa+ User manual
Popular Water Filtration System manuals by other brands

Atlantic Ultraviolet
Atlantic Ultraviolet Mighty Pure MP16A owner's manual

SunSun
SunSun CBG-500 Operation manual

Hayward
Hayward XStream Filtration Series owner's manual

Contech
Contech DownSpout StormFilter Operation and maintenance

Teka
Teka Airfilter MINI operating instructions

Wisy
Wisy LineAir 100 Installation and operating instructions

Schaffner
Schaffner Ecosine FN3446 Series User and installation manual

Pentair
Pentair FLECK 4600 SXT Installer manual

H2O International
H2O International H20-500 product manual

Renkforce
Renkforce 2306241 operating instructions

Neo-Pure
Neo-Pure TL3-A502 manual

STA-RITE
STA-RITE VERTICAL GRID DE FILTERS S7D75 owner's manual