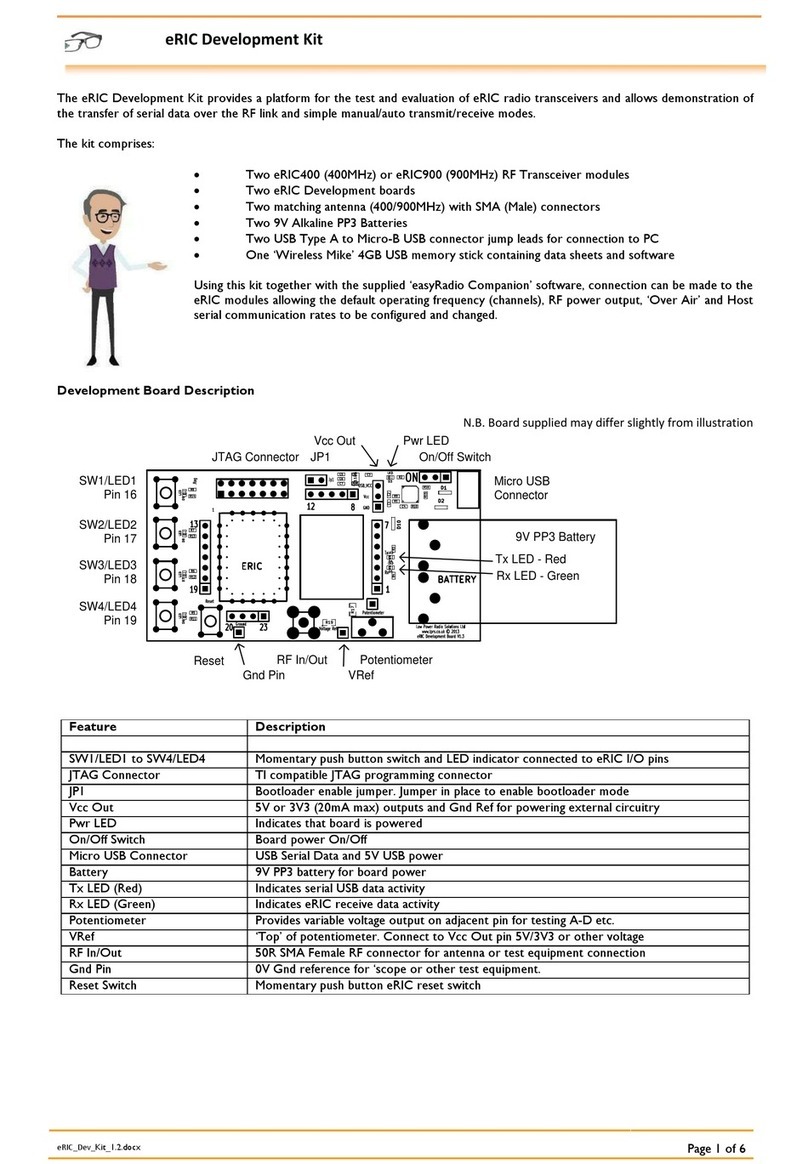
SENTRON A120-001 Quick start guide

1
ISFET pH-sensor kit
Technical guide
Contents
Description..................................................................................................................................2
Specifications..............................................................................................................................3
Electrical connections..................................................................................................................4
3.1 Analog front-end module.....................................................................................................4
3.2 AD Converter module ..........................................................................................................4
3.3 USB Interface module..........................................................................................................5
Calibration ..................................................................................................................................6
Data communication...................................................................................................................7
5.1 Protocol...............................................................................................................................7
5.2 Examples.............................................................................................................................8
5.2.1 Performing a single point calibration............................................................................8
5.2.2 Performing a multi-point calibration ............................................................................9
5.2.3 Retrieving the pH signal .............................................................................................10
5.2.4 Retrieving the temperature signal..............................................................................10
5.2.5 Retrieving the slope values ........................................................................................11
5.3 ASCII table.........................................................................................................................12
E7500347.02

2
Description
Sentron offers a glass-free modular pH-kit designed specifically for development and testing
purposes. With this pH-kit, development engineers and researchers have a large degree of flexibility
in how they integrate our proprietary ISFET pH sensor into their applications or experimental set-ups.
Due to the modular design, the functionality can be expanded as required and components can be
replaced individually.
The pH-kit consist of a ISFET pH sensor, Reference and Analog front-end module. These modules are
always needed as a basis for pH measurement. Thanks to the small size of the ISFET pH sensor and
Reference electrode it can be used to measure small volumes or develop applications with small
form factors. The Analog Front-end module has an uncalibrated analog pH output signal with a
voltage output 0 —3.3 V of ~ 52 mV / pH and pH 7 between 500 mV and 1800 mV. The PT1000 RDT
temperature sensor in the ISFET pH sensor is wired directly to the Analog front-end module output.
The reference electrode also connects to the Analog front-end module and either the standard
reference electrode with porous PTFE diaphragm can be used or a suitable custom reference
electrode can be attached.
The AD Converter module can be attached to the Analog front-end module. This extension module
with microprocessor, AD Converter and galvanic isolation makes it well suited for use in embedded
applications. The communication with the AD Converter is based on a serial RS232 interface with a
TTL level. Using a standard serial interface it is possible to perform calibrations and read pH and
temperature values. Application of a temperature correction algorithm to the pH signal is performed
directly by the microcontroller of the AD Converter module. The galvanic isolation provides an extra
safety barrier and prevents ground loops.
With the USB Interface extension module, which connects to the AD Converter module, it is possible
to request measured pH and temperature values from a laptop or PC with a USB port. The USB
Interface extension module, with appropriate user developed software, allows the pH-kit to be used
for applications that require direct connection to a PC, such as real time monitoring of pH values in
an experiment or process.

3
Specifications

4
Electrical connections
The diagram below illustrates how the components of the pH-kit are connected together. The
modules will only function when connected in this order.
1. ISFET sensor +
Reference electrode
2. Analog front-end
3. AD Converter
(Optional)
4. USB Interface
(Optional)
Modules 1 and 2 are always needed to conduct pH measurements with the test kit. Modules
3and 4are optional.
3.1 Analog front-end module
The ISFET sensor is connected to the Analog Front-End module through an FFC connector. There are
also 7 pin connections on the module. One pin (Pin 7) is for connection of the reference electrode.
The remaining 6 serve as output pins for the Analog front-end module. They are described below:
7.
Pin 1. pH signal out ~52 mV/pH. pH 7 between 500 and 1800 mV
Pin 2. +3V3 Power +3V3 DC power power input +/- 100mV
Pin 3. AGND Analog Ground
Pin 4. PT1000 Directly wired to the PT1000
Pin 5. PT1000 Directly wired to the PT1000
Pin 6. N.C. Not used
Pin 7. Reference External reference electrode connection
3.2 AD Converter module
The 6 pin connector of the AD Converter module can be attached directly to the Analog Front-end
module. The AD Converter module also had 4 output pins, which are described below:
Pin 1. +5V +5V DC power input +/- 100mV
Pin 2. RxD Data input, TTL 5V level, 115k2, 8N1
Pin 3. TxD Data output, TTL 5V level, 115k2, 8N1
Pin 4. GND Digital GND.
The AD Converter module contains 1.5kV galvanic insulation between inputs and outputs.
1.
2.
3.
4.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
ISFET
sensor
connector
Analog
front-end
connector

5
3.3 USB Interface module
The 4 pin connector of the USB Interface module can be attached directly to the AD Converter
module. A mini USB cable can be attached to the mini USB B connector.
The USB interface provides a USB 1.1 or 2.0 connection to a computer (note the USB interface is not
USB 3.0 compatible). It is possible to connect multiple USB interface modules to one PC, up to the
current limit of your USB ports.
USB Driver Installation:
Normally Windows will recognize the USB interface as a USB to COM port converter. Windows will
install the driver automatically or download the driver from the internet. In some cases the driver
needs to be installed manually. The latest drivers can be downloaded from the FTDI website.
(http://www.ftdichip.com/Drivers/VCP.htm)
When Windows has installed the driver properly it will assign a COM port number to the USB
Interface. Through this port number the communication can be established. Look up at your device
manager to find out the assigned port number. The figure below shows an example that Windows
has assigned COM4 to the connected USB interface.
Mini USB B connector
AD
Converter
connector

6
Calibration
It is always necessary to calibrate an ISFET pH sensor before use. During prolonged use the senor
may need to recalibrated at intervals. The frequency of recalibration is dependent on the conditions
the sensor is subjected to and it is recommended to test the calibration at the end of a measurement
run to confirm the calibration is still accurate. To perform a calibration place the ISFET sensor in the
right buffer solution and communicate according the protocol of chapter 5.1.

7
Data communication
Before connecting and powering up the modules in your embedded environment or to the computer make sure the all the necessary module are connected to
each other and correct baud rate of 115k2 8N1 is set. See chapter 3 for power and data pins on the AD converter module when the USB interface is not connected
and the communication is directly to the AD converter.
5.1 Protocol
A command is sent to the device in the form of ASCII characters, and the return string is received as a series of bytes representing 6-bit binary decimals. The
return bytes will need to be decoded into a measurement value through a calculation. The method of decoding is shown in the table below.
1Dummy bytes
2Response time is depending on signal stability, maximum at 120 seconds
3 Use function after desired number of calibration points is achieved
4 Separation bytes
5Shown numbers are separate bytes, not characters.
Function
Send ASCII command
(bytes)
Decode calculation.
Multiply or add decimal
byte position value.
Units
A B C D1E1F1G1H1I1J K A*4096+B*64+C 0.001 pH
byte byte byte 000 000 000 000 000 000 013 010
A B C 1D 1E 1F G A*64+B 0.1 °F
byte byte 000 000 255 013 010
Start Calibration
CLR!<CR>
(067 076 082 033 013)
082 013 013
Calibration pH 2
111!<CR>5
(001 001 001 033 013)
001 013 010 2
Calibration pH 4
112!<CR>5
(001 001 002 033 013)
002 013 010 2
Calibration pH 7
113!<CR>5
(001 001 003 033 013)
003 013 010 2
Calibration pH 10
114!<CR>5
(001 001 004 033 013)
004 013 010 2
Calibration pH 12
115!<CR>5
(001 001 005 033 013)
005 013 010 2
End calibration 3
QIT!<CR>
(081 073 084 033 013)
084 013 010
000!<CR>
(048 048 048 033 013)
ABCDEFGHIJKLMN 013 010 A4B C D4E F G4H I J4K L M N
001 byte byte Slope pH 2-4 = B*64+C 0.1 %
002 byte byte Slope pH 4-7 = E*64+F 0.1 %
003 byte byte Slope pH 7-10 = H*64+I 0.1 %
004 byte byte 013 010 Slope pH 10-12 = K*64+L 0.1 %
Receive bytes from AD Converter or USB Interface.
Retrieve slope
Decimal bytes return
ABCDEFG 013 010
777!<CR>
(055 055 055 033 013)
Retrieve temperature
ABCDEFGHIJK 013 010
999!<CR>
(057 057 057 033 013)
Retrieve pH value

8
5.2 Examples
Below some communication examples on the various protocol functions are presented to illustrate
communication with the AD Converter and USB Interface modules.
5.2.1 Performing a single point calibration
pH7 calibration sequence:
Rinse the probe with deionized water.
Place ISFET sensor and reference in the calibration pH7 buffer solution. Initiate the
calibration process by sending the Start Calibration command: CLR!<CR>
Wait for the AD Converter or USB interface module to acknowledge, receive: 082 013 013
The AD converter or USB interface module is now ready to receive the calibration pH 7
command…
Initiate the pH7 calibration by sending the calibration pH 7 command: 113!<CR>
Allow some time for the module to stabilize (this may take up to 2 minutes maximum)…
Wait for the module to stabilize, receive bytes: 003 013 010
End the calibration process, send: QIT!<CR>
Wait for the module to confirm calibration end, receive: 084 013 010
Rinse the ISFET sensor and reference electrode with de-mineralized water…
The calibration is completed.
For performing a pH 2, 4, 10 or 12 calibration, repeat the sequence and use the appropriate
calibration command bytes. See chapter 5.1 for the command bytes of each pH buffer solution.

9
5.2.2 Performing a multi-point calibration
To rule out erroneous multi-point calibrations, the calibration can only take place for an increasing or
decreasing pH sequence.
Multi-point calibration sequence:
For example a calibration in pH 4 –7 –10 buffer.
Rinse the probe with deionized water.
Place ISFET sensor and reference in the first calibration buffer solution. In this case pH4
buffer.
Initiate the calibration process by sending the Start Calibration command: CLR!<CR>
Wait for the AD Converter or USB interface module to acknowledge, receive: 082 013 013
The AD converter or USB interface module is now ready to receive the first calibration command
bytes of the buffer sequence…
Initiate the pH4 calibration by sending the calibration pH 4 command: 112!<CR>
Allow some time for the module to stabilize (this may take up to 2 minutes maximum)…
Wait for the module to stabilize, receive bytes: 002 013 010
Rinse the probe with deionized water.
Place ISFET sensor and reference in the next calibration buffer solution, pH 7.
Initiate the pH7 calibration by sending the calibration pH 7 command bytes: 113!<CR>
Allow some time for the module to stabilize (this may take up to 2 minutes maximum)…
Wait for the module to stabilize, receive bytes: 003 013 010
Rinse the probe with deionized water.
Place ISFET sensor and reference in the next calibration buffer solution, pH 10.
Initiate the pH10 calibration by sending the calibration pH 10 command bytes: 114!<CR>
Allow some time for the module to stabilize (this may take up to 2 minutes maximum)…
Wait for the module to stabilize, receive bytes: 004 013 010
When performing even more calibration points, repeat this part for each extra desired point.
End the calibration process, send: QIT!<CR>
Wait for the module to confirm calibration end, receive: 084 013 010
The calibration is completed.
Send the “end calibration command bytes” just once after the last performed calibration point.

10
5.2.3 Retrieving the pH signal
After a single or multipoint calibration the AD Converter module the pH value can be read out.
Retrieve pH value
Send the command bytes: 999!<CR>
Wait for the module to return the pH value, receive bytes: ABCDEFGHIJK
Data ABCDEFGHIJK marks the byte position. Values in bytes are needed for decoding.
Byte position
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
Byte value
byte
byte
byte
000
000
000
000
000
000
013
010
Decode received sequence if e.g.:
Byte position
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
Received bytes
001
023
027
000
00
000
000
000
000
013
010
Protocol:
A = 001
B = 023
C = 027
DEFGHIJK = n/a
A*4096 + B *64 + C = 1*4096 + 23*64 + 27 = 5595
pH value = 5.595
5.2.4 Retrieving the temperature signal
Retrieve temperature value
Send the command bytes: 777!<CR>
Wait for the module to return the pH value, receive bytes: ABCDEFG
Data ABCDEFG marks the byte position. Values in bytes are needed for decoding.
Byte position
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
Byte value
byte
byte
000
000
255
013
010
Decode received sequence if e.g.:
Byte position
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
Received bytes
012
023
000
000
255
013
010
Protocol:
A = 012
B = 023
CDEFG = n/a
A*64 + B = 12*64 + 23 = 791
Temperature value = 79.1 °F

11
5.2.5 Retrieving the slope values
A slope can only be calculated between two calibration points. When retrieving a slope after only a
single point calibration the returned values will represent 0%.
Normal slopes between two consecutive pH buffer solutions should be between 105% –95%.
Slopes outside these values, can indicate a polluted or aging ISFET sensor /reference electrode.
Although calibrations and measurements can be performed the measured values may be less
accurate. In this case, if cleaning the sensor / reference electrode does not resolve the slope issue be
sure to replace the ISFET sensor and/or reference electrode.
Retrieve slope value:
Send the command bytes: 000!<CR>
Wait for the module to return the slope values, receive bytes: ABCDEFGHIJKLMN
Data ABCDEFGHIJKLMN marks the byte position. Values in bytes are needed for decoding.
Byte position
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
Byte value
001
byte
byte
002
byte
byte
003
byte
byte
004
byte
byte
013
010
Decode received sequence if e.g.:
Byte position
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
Received
bytes
001
000
000
002
015
052
003
000
000
004
000
000
013
010
Slope positions:
Protocol
Decode
Result
slope between pH 2 and pH 4
B*64+C
000*64+000
0%
slope between pH 4 and pH 7
E*64+F
015*64+052
101.2%
slope between pH 7 and pH 10
H*64+I
000*64+000
0%
slope between pH 10 and pH 12
K*64+L
000*64+000
0%
ADGJ = n/a

12
5.3 ASCII table
This manual suits for next models
4
Table of contents
Popular Microcontroller manuals by other brands

Emerson
Emerson Vission 20/20 Operation and service manual

STMicroelectronics
STMicroelectronics STM32WL5 Series Reference manual
GigaDevice Semiconductor
GigaDevice Semiconductor GD32E230F-START user guide
Silicon Laboratories
Silicon Laboratories UG338 user guide
NXP Semiconductors
NXP Semiconductors S32R27 Hardware Design Guide

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments TMS320C6000 DSP user guide
PIMORONI
PIMORONI OctoCam PIM286 Assembling

Phytec
Phytec phyCORE-LPC3250 Quick start instructions
NXP Semiconductors
NXP Semiconductors S32R274RRUEVB quick start guide

Fujitsu
Fujitsu BBF2004 Series instruction manual

Altera
Altera Arria 10 SoC user guide
Silicon Laboratories
Silicon Laboratories C8051F930-DK user guide