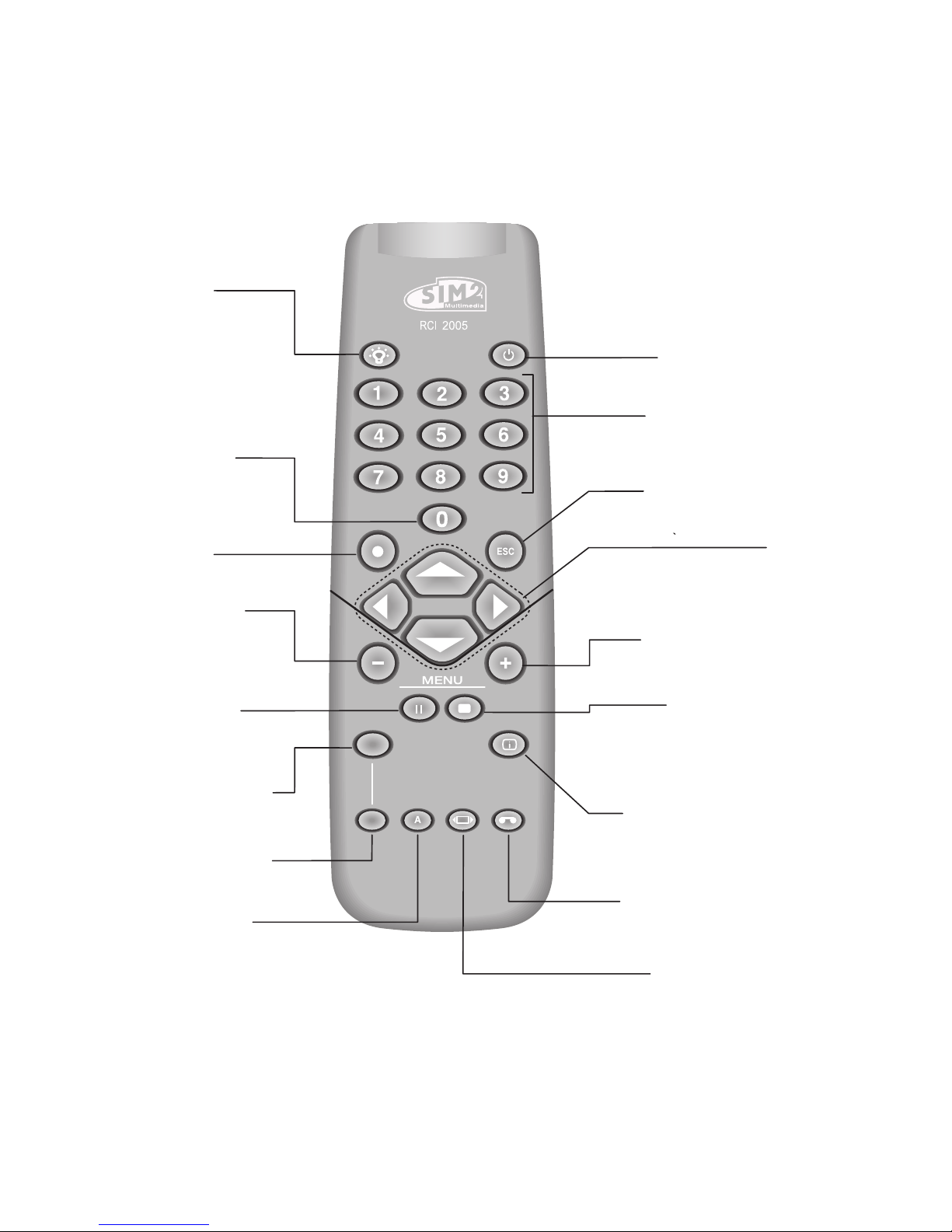
4
• Read this manual carefully and keep it in a safe
place for future consultation.
This manual contains important information on how to install
and use this equipment correctly. Before using the
equipment, read the safety prescriptions and instructions
carefully. Keep the manual for future consultation.
• Do not touch internal parts of the units.
The units contain electrical parts carrying high voltages and
operating at high temperatures. Do not remove the cover
from the units, refer to qualified service personnel for all repair
and maintenance requirements.
The warranty will be automatically invalidated if the cover is
removed from the units.
• Power supply disconnect device.
The device for disconnecting the units from the mains power
supply is constituted by the power cable plug. Ensure that
the power cable plugs and the electrical mains socket outlets
are easily accessible during installation operations. To
disconnect the units from the electric power supply, pull the
plug to remove it from the socket outlet. Do not pull the power
cable.
• Use only the specified type of mains power
supply.
Connect the units to a mains electrical supply with rated
voltage of between 100-240 VAC, 50/60 Hz and equipped
with a protective earth connection. If you are unsure of the
type of mains power supply in your home, consult a qualified
electrician.
Ensure that the power draw of the units is commensurate
with the rating of the electrical socket outlets and any
extension cables that are used.
For the DigiOptic™ Image Processor use exclusively the
power supply unit provided or an alternative power supply
unit expressly approved by SIM2.
• Beware of power supply cables.
Position the power supply cables so that they do not
constitute an obstruction.
Position the power supply cables where they cannot be
reached by children.
Install the units as close as possible to the wall electrical
socket outlet. Do not tread on the power cables, make sure
that they are not tangled or pulled; do not expose the power
cables to heat sources; make sure that the power cables do
not become knotted or kinked. If the power cables become
damaged, stop using the system and request the assistance
of an authorised technician.
• Disconnect the apparatus from the mains power
supply in the event of electrical storms and when
not in use.
To avoid damage that could be caused by lightning striking
in the vicinity of your home, disconnect the units in the event
of electrical storms or when the system will remain unused
for prolonged periods.
• Avoid contact with liquids and exposure to
humidity.
Do not use the units near water (sinks, tanks, etc.); do not
place objects containing liquids on top of or near the units
and do not expose them to rain, humidity, dripping water or
spray; do not use water or liquid detergents to clean the
units.
• Prevent the units from overheating.
Do not obstruct ventilation openings. Do not place the units
near heat sources such as heaters, radiators or other devices
that generate heat (including amplifiers). Do not position the
unitsinconfined,poorlyventilatedplaces(bookcase,shelves,
etc.).
• Do not expose the eyes to the intense light
emitted by the lamp.
Never look directly at the lamp through the ventilation
opening when the unit is switched on.
Risk of eyesight impairment. Ensure also that children do
not look directly at the lamp.
• Position the unit on a stable surface.
To avoid serious injury to persons and damage to property,
make sure the units are placed on a level, flat and stable
surface from which they cannot fall, tip over or slide. Pay
special attention if the units are placed on a trolley so that
they can be moved around. Ensure that the units are not
subjected to impact.
• Do not insert objects through the units’ openings.
Make sure that no objects are inserted inside the units. If
this should occur, disconnect the unit from the power supply
immediately and call an authorised technician.