Smartworks Smart-Net User manual

Smart-Net Gateway
Installation and User’s Manual

2
Table of Contents
Overview............................................................................................................................ 5
Features........................................................................................................................... 5
Packing Materials............................................................................................................ 5
Contact Information........................................................................................................ 5
Installation......................................................................................................................... 6
Connecting the Smart-Net Gateway ............................................................................... 6
Connecting Smart-Net Devices....................................................................................... 6
Configuring an IP Address.............................................................................................. 7
Using the IPGatewaySetup Java Utility...................................................................... 7
Using a Web Browser................................................................................................. 8
Web Interface.................................................................................................................. 11
Logging in..................................................................................................................... 11
Changing Network Settings.......................................................................................... 12
Adjusting the Date and Time........................................................................................ 13
Setting the Time Zone............................................................................................... 14
Manually Setting the Date and Time........................................................................ 14
Automatically Setting the Date and Time................................................................. 15
Rebooting the Smart-Net Gateway............................................................................... 15
Changing the System Password.................................................................................... 15
Viewing the Connected Devices History...................................................................... 16
Changing FTP Logging Settings................................................................................... 17
Changing Dial Up Networking Settings....................................................................... 17
XML-RPC........................................................................................................................ 18
Overview....................................................................................................................... 18
Accessing XML-RPC Methods .................................................................................... 18
Common Field Descriptions......................................................................................... 19
Timestamp................................................................................................................. 19
Status......................................................................................................................... 19
ROMID..................................................................................................................... 20
ParentID.................................................................................................................... 20
UserID....................................................................................................................... 20

3
Smart-Net Gateway XML-RPC Methods..................................................................... 20
SmartNet.Status ........................................................................................................ 20
SmartNet.Time.......................................................................................................... 21
SmartNet.Find........................................................................................................... 21
SmartSenseTH.Read................................................................................................. 22
SmartSenseTH.Write................................................................................................ 23
SmartWatt.Read........................................................................................................ 24
SmartWatt.Write....................................................................................................... 27
SmartPDU.Read........................................................................................................ 28
SmartPDU.Map......................................................................................................... 29
SmartPDU.Write....................................................................................................... 29
Additional Resources.................................................................................................... 30
FTP Logging.................................................................................................................... 31
Overview....................................................................................................................... 31
Configuring and Testing............................................................................................... 31
Enabling/Disabling ................................................................................................... 32
Server Host................................................................................................................ 33
Server Username/Password ...................................................................................... 33
Remote Log Directory .............................................................................................. 33
Reading and Upload Intervals................................................................................... 33
Alerting Options............................................................................................................ 33
Enabling/Disabling ................................................................................................... 33
From Address............................................................................................................ 34
To Address................................................................................................................ 34
Message Type ........................................................................................................... 34
Log File Formats........................................................................................................... 34
Common Fields......................................................................................................... 35
SmartSenseTH .......................................................................................................... 36
SmartWatt................................................................................................................. 37
SmartPDU................................................................................................................. 38U
Smart-Net.................................................................................................................. 39
Exception .................................................................................................................. 39
Test............................................................................................................................ 40

4
Intervals and Memory Usage........................................................................................ 40
Attaching a Modem/PPP............................................................................................... 40

5
Overview
Features
The Smart Works Smart-Net Gateway provides connectivity to your Smart-Net network
from TCP/IP networks via an Ethernet connection and a static IP address. This enables
you to manage and communicate with an entire Smart-Net network from a single static IP
address.
The Smart-Net Gateway currently supports the following features:
•Plug and Play self discovery of new devices
•Flexible wiring topologies up to 1000’ with Category 5 cable
•Intuitive web interface for configuration
•XML based procedure calls (XML-RPC)
•Automatic device monitoring via FTP
•(Optional) Dial Up Networking Support via an external modem
Packing Materials
The Smart-Net Gateway is shipped with the following materials:
•Smart-Net Gateway
•Power supply
•CD-ROM (which includes this users manual and additional resources)
Contact Information
If you wish to contact Smart Works, Inc., you may do so using one of the following
methods:
•E-Mail – [email protected]
•Telephone – (253) 735-0552
•Fax – (253) 735-0562
•Web – http://www.smart-works.com

6
Installation
Connecting the Smart-Net Gateway
The Smart-Net Gateway features the following connections (Figure 1):
•One Console Serial Port
•One External Serial Port
•One 5V DC, 300mA Power Input Jack
•One RJ-12 Smart-Net Device Port
•One RJ-45 Ethernet Port
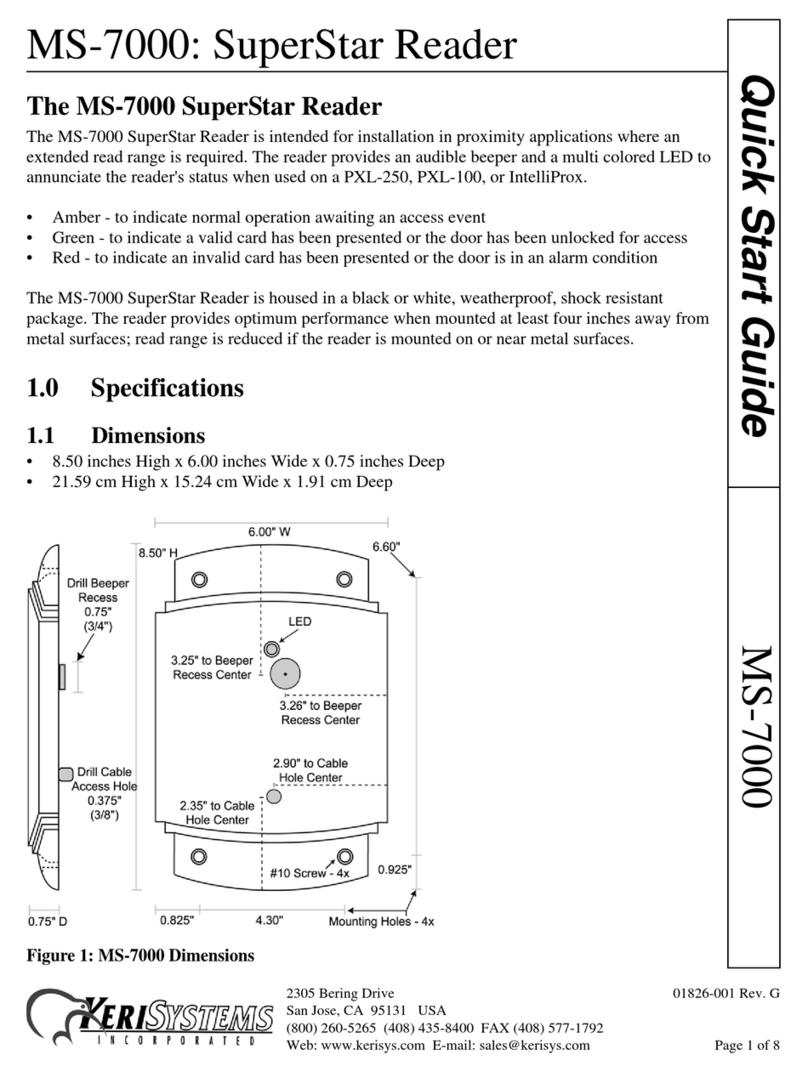
Figure 1. Smart-Net Gateway Connections
To connect the Smart-Net Gateway, perform the following steps:
1. Place the Smart-Net Gateway at the desired location
2. Use Category-5e Cable to attach the Smart-Net Gateway to the network via the
Ethernet port.
3. Connect the power cord and plug the transformer into a wall-socket.
Connecting Smart-Net Devices
The Smart-Net Gateway has a built-in RJ-11 connector that controls a Smart-Net Device
Network. Every Smart-Net device has two RJ-11 connectors to allow for daisy chaining
of devices. Simply connect one of the devices on the Smart-Net Network to the RJ-11

7
port on the Smart-Net Gateway. The devices will automatically be detected and no
additional configuration is necessary.
There are a few points to keep in mind when installing a Smart-Net Network:
•Polarity – The Smart-Net network uses standard RJ-11 connectors to make it
easy and convenient to wire and extend. If standard telephone cable is used, it is
important to ensure that it is not of a “flipped” type. The cable must be “straight-
through”, that is pin 1 on one end of the cable must conduct directly to pin 1 on
the other end of the cable. The same goes for all the pins on the cable.
•Topology – The recommended topology of wiring devices in the Smart-Net
Network is in a “daisy chain” fashion. That is, each additional device should
extend from the last device on the network. Wiring the network this way will
ensure reliable communication and the longest distances. Branching off to other
groups of Smart-Net devices from one point will cause signal errors and greatly
deteriorate the reliability and maximum distance of the network.
•Cable Grade – Using Category 5 or Category 6 wire will support the longest
distances with minimal communication errors. However, if the network is very
short, lower grade cable may be used.
Configuring an IP Address
When the Smart-Net Gateway has been powered up for the first time, it will attempt to
retrieve an IP Address with DHCP. If a DHCP server is unreachable, it will set a default
IP Address of 169.254.x.x (where x.x is the last two bytes of the Smart-Net Gateway’s
MAC Address) with subnet mask 255.255.0.0. The device will also listen to a Multicast
group at 224.0.10.10 on port 6082.
Using the IPGatewaySetup Java Utility
The supplied Java program, “IPGatewaySetup”, will configure Smart-Net Gateways via
the Multicast group described above. When changes are made to a Smart-Net Gateway
with this utility, DHCP will be automatically disabled to ensure your configuration
changes take effect. To configure the IP Address with the IPGatewaySetup Java Utility,
perform the following steps:
1. Connect the Smart-Net Gateway to the same networking hardware as a PC with
the Java Virtual Machine runtime environment installed.
2. Power on the Smart-Net Gateway and wait about one minute for it to initialize.
3. Run the program “IPGatewaySetup” on the PC.
•For example, on Windows, open a command prompt, change to the directory
where “IPGatewaySetup” is installed, and type:
java –cp . IPGatewaySetup

8
4. The program will connect to the Multicast group, search for all Smart-Net
Gateways, and display them to the screen with the device’s MAC address, IP
Address, and Subnet Mask (Figure 2).
Figure 2. IPGatewaySetup Java Program
5. Select the device you are configuring and press enter.
6. Type in the new IP Address for the device and press enter.
7. Type in the new Subnet Mask for the device and press enter.
8. Type in the new Default Gateway for the device and press enter. If there is no
gateway address, leave the field blank and press enter.
9. The program will send the request and refresh the list of Smart-Net Gateways
found.
10. Proceed with the configuration from the “Web Interface” section of this manual.
Using a Web Browser
To configure the IP Address with a Web Browser by changing the PC’s network settings:
1. If you have a DHCP server on your network, check the server logs or use the Java
utility (described above) to determine the Smart-Net Gateway’s IP Address. If
you do not have a DHCP server, determine the default IP Address of the Smart-
Net Gateway by analyzing the last two bytes of the MAC (Physical) address and
appending them to 169.254. For example, if the MAC Address of the Smart-Net
Gateway is 00:60:35:01:A0:2F then convert the hexadecimal values A0 and 2F to
decimal (160 and 47) to obtain 169.254.160.47 for the IP Address.
2. Configure the PC to an address on the same network as the Smart-Net Gateway.
For example: 169.254.0.1
3. Using a web browser, go to: http://169.254.xxx.xxx (where xxx.xxx are the values
calculated in step 1). If the Smart-Net Gateway obtained its IP Address through
DHCP, use the assigned address, instead.
4. A login page will appear. Enter admin for the username and smartworks for the
password and click “Login” (Figure 3).

9
Figure 3. Web Interface Login Prompt
5. Click “System Settings” in the Menu on the left-side of the screen.
6. Enter new values for the IP Address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, and DNS
Servers (Figure 4). Enable or Disable DHCP as needed for your network.

10
Figure 4. Web Interface System Configuration Page
7. Click “Update”.
8. When you see the text, “Saving Settings… Please Wait”, your browser may time
out if you changed the IP Address to an unreachable network. This is normal and
you can proceed to the next step.
9. Change the PC back to an IP Address on the same network as you just configured
and proceed with configuration from the “Web Interface” section of this manual.

11
Web Interface
The Smart-Net Gateway provides a user-friendly web-based interface to change and view
its configuration. The web interface is password-protected to only allow authorized users
to make changes.
Logging in
To log into the Web Interface, open a Web browser, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer,
and visit: http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/, where xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the IP Address of the
Smart-Net Gateway. If you have not yet configured an IP Address for the Smart-Net
Gateway, refer to the Installation section of this manual.
When the web browser prompts for a username and password, enter admin for the
username and smartworks for the password (all lower-case) if you have not yet changed
the password.
Once logged in, the “Status” screen will appear, giving a brief summary of the Smart-Net
Gateway’s configuration (Figure 5).

12
Figure 5. Web Interface Status Screen
Changing Network Settings
To change the Network Settings, click “System Settings” on the menu on the left-hand
column. Make changes to the values as needed and click the “Update” button to apply
the changes. Refer to Figure 4. The network settings are described below:
•Use DHCP – If this box is checked, the Smart-Net Gateway will attempt to
retrieve an IP Address by broadcasting to a DHCP server. If the DHCP server
is unreachable, the alternate/manual network configuration will be applied
until an IP is successfully leased. If this box is not checked, the
alternate/manual network configuration is always used.
•MAC Address – This value cannot be changed and represents the current
Physical (MAC) Address of the network interface. This value is unique to
every Smart-Net Gateway.

13
•IP Address – This value represents the TCP IPv4 Address of the Smart-Net
Gateway when not using DHCP.
•Subnet Mask – This value represents the subnet mask associated with the IP
Address of the Smart-Net Gateway when not using DHCP.
•Gateway – This is the IP Address of the default gateway or router to let the
Smart-Net Gateway access an external network or the Internet when not using
DHCP.
•DNS Server 1 – This is the IP Address of the primary Domain Name Server
to resolve domain names when not using DHCP.
•DNS Server 2 – This is the IP Address of the backup Domain Name Server to
resolve domain names if the primary Domain Name Server is inaccessible
when not using DHCP.
•DNS Timeout – This is the number of milliseconds to wait before giving up
on trying to resolve a domain name. Setting this value to zero indicates that a
fallback and retry procedure should take effect. In this case, the Smart-Net
Gateway will retry starting at 2 seconds and doubling until reaching 16
seconds. The Smart-Net Gateway will try four times in this period to resolve
the name. * 2s * 4s * 8s * 16s. The default value for this option is 5000 ms.
•SMTP Mail Server – This is the IP Address or hostname of a mail server that
allows the Smart-Net Gateway to send alerts and notifications via e-mail.
Adjusting the Date and Time
To change the date and time settings of the Smart-Net Gateway, click “System Settings”
on the menu on the left-hand column. Below the Network Settings is a section for the
“Date and Time Options” and the current date and time of the Smart-Net Gateway will be
displayed (Figure 6). When you are finished setting the date and time options, click the
Update Time Options button at the bottom to save and apply the new settings.

14
Figure 6. Web Interface Date and Time and Reboot Option
Note: When the date and time is changed or updated (either manually or automatically)
on the Smart-Net Gateway by a significant amount, all connected Smart-Watt devices
will have their previous reading data cleared. This ensures that an average Watt
consumption calculation will be accurate since this calculation is based on timestamps
that are stored on the devices.
Setting the Time Zone
The “Timezone” drop down list allows you to configure the timezone setting of the
Smart-Net Gateway. By default, it is set to GMT. This time zone is used to adjust the
clock for daylight saving time (DST) when necessary and save the appropriate time zone
offset in the log files.
Manually Setting the Date and Time
To set the date and time of the Smart-Net Gateway manually, select “Manually”, enter a
date and time into the provided fields in 24-hour format, then click the Update Time
Options button. When the page reloads, the top will inform you if the update was

15
successful, and the new time will be displayed in the “Date and Time Options” section. It
is only recommended to use this option if the Smart-Net Gateway will not have access to
a time server.
Automatically Setting the Date and Time
To set the date and time of the Smart-Net Gateway automatically, select “Automatically”.
In the NTP Server text box, enter the IP Address or hostname of a network time protocol
server to use. In the Update Interval box, enter the frequency (in days) that the time
server should be polled and the time synchronized. When finished, click the Update
Time Options button to save the changes and set the time. When the page reloads, the
top will inform you if the automatic time update was successful, and the new time will be
displayed in the “Date and Time Options” section.
When this option is selected, the Smart-Net Gateway will attempt to resynchronize its
clock with the specified time server during each boot and each time the Update Time
Options button is selected, then periodically thereafter according to the update interval
setting.
By default, the Smart-Net Gateway will attempt to obtain its time automatically every 7
days from “smart-works.com”.
Rebooting the Smart-Net Gateway
To reboot the Smart-Net Gateway, click “System Settings” on the menu on the left-hand
column. At the bottom of the page, there is a link to Reboot (Figure 6). The Smart-Net
Gateway will take about one minute to reboot, during which time it is unavailable to the
network. Rebooting the Smart-Net Gateway is functionally equivalent to removing and
reapplying power, and does not erase any settings or log files. If DHCP is enabled,
remember that the IP Address might change depending on the DHCP server’s
configuration.
Changing the System Password
Click the “System Password” link on the menu on the left-hand column (Figure 7). Type
in the old password (smartworks if it has not yet been set) in the “Current Password”
field and the new password in the “New Password” and “Verify New Password” fields.
Then click “Submit” to apply the changes.

16
Figure 7. Changing the System Password with the Web Interface
Remember, a forgotten password can not be recovered! If you have forgotten the
password, you must reset the Smart-Net Gateway to factory defaults.
Viewing the Connected Devices History
To view a table of the history of connected devices, click the “Connected Devices” link
on the menu on the left-hand column. The Connected Devices History shows a table of
Smart-Net devices the FTP Logger function has logged since the last time the Smart-Net
Gateway was powered on or the list was cleared (Figure 8). The Connected Device
History table provides a convenient way to view the Smart-Net ID, Smart-Net Device
Type, UserID, and the Date/Time the device was last seen on the network. The oldest
devices show up at the top of the list to help troubleshoot unresponsive devices.

17
Figure 8. Connected Device History
To clear the Connected Device History, press the Clear button below the table. If the
FTP Logging function has not seen any devices, a “No Devices Found” message will be
displayed instead of a table. The FTP Logging function must be enabled for this table to
be updated.
Changing FTP Logging Settings
To change the options for FTP Logging, click the “Ftp Logging” link on the menu on the
left-hand column (Figure 9). Make the changes necessary and click “Update” or “Test”
to apply the changes. For details on FTP Logging and its options, refer to the FTP
Logging section of this manual.
Changing Dial Up Networking Settings
Note: Dial Up Networking support requires a Smart-Net Gateway with a modem and this
option may not be present in devices without this feature.
To change options for Dial Up Networking support, click the “Dial Up Networking” link
on the menu on the left-hand column (Figure 10). Make the necessary changes and click
“Update” to apply the changes. For details on Dial Up Networking support, refer to
“Attaching a Modem/PPP” of the FTP Logging section of this manual.

18
XML-RPC
Overview
The Smart-Net Gateway features an XML-RPC server that accepts commands from
remote systems. Issuing XML-RPC commands to the Smart-Net Gateway provides a
simple and platform independent way to remotely manage the Smart-Net Gateway and
devices on the Smart-Net Network.
XML-RPC (http://www.xml-rpc.com/) was designed by UserLand Software
(http://www.userland.com/) in an effort to ease cross-platform remote procedure calls.
XML-RPC client implementations are available at the XML-RPC website.
XML-RPC uses the Extended Markup Language (XML) to execute Remote Procedure
Calls (RPC) using the HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP). Because XML-RPC relies
on XML for describing its procedure calls, its data can be read on any platform that is
capable of parsing XML documents. Additionally, since it uses HTTP as its transport
protocol, it can easily pass through most firewalls and is already implemented on many
platforms. Combined, this makes it easy to implement XML-RPC support to nearly any
platform that supports internet access and XML.
The descriptions for the XML-RPC Requests in this section are documented with the
following notation:
<> denotes an array
Array elements are separated by a comma. Three dots (…) indicates that more
elements that follow the same pattern can be present. A vertical pipe symbol (‘|’)
indicates that either the element to the left of or to the right of (not both) the ‘|’
symbol may be specified.
{} denotes a struct
Structure members are separated by a comma. Each name/value pair is separated
with an ‘=’ (equal) sign.
[] denotes an optional argument
Square brackets indicate that the enclosed data is optional. It may be an optional
parameter to a method or it may be a response that is not received in some
situations.
() indicates the data type
Possible data types are: integer, double, boolean, string, and date.
Accessing XML-RPC Methods
The Smart-Net Gateway’s XML-RPC server listens to the /XmlRpc/ subdirectory of the
web server on port 80. To access the XML-RPC Methods described below, send a call to
the URL: http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:80/XmlRpc/ where “xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx” is the IP
Address of the Smart-Net Gateway. Within several seconds, the Smart-Net Gateway will
send a response, depending on the method called.

19
Common Field Descriptions
Several of the XML-RPC methods described below share the same fields between each
other. For brevity, the descriptions of these fields are provided here instead of duplicated
in the descriptions of each XML-RPC method.
Timestamp
The “Timestamp” (integer) field represents the time of the Smart-Net Gateway at the
time of the method request. This field is an integer value of the number of seconds since
January 1, 1970 at 00:00:00. Since the Smart-Net Gateway has no concept of time-zones,
this value will normally be expressed in Universal Time Coordinated (UTC) or
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
Status
The “Status” (integer) field is returned for all methods that require Smart-Net
communications. This field is a series of bits used as flags to help troubleshoot Smart-
Net or protocol problems. If this field is zero (0), this indicates that no Smart-Net
problems occurred during the method call. For any other value, convert the integer to a
32-bit binary number and observe the bits that are set (logical 1). Bits 0-7 are related to
Smart-Net communications. Bits 8-15 are related to the XML-RPC methods in general.
Bits 24-31 depend on the specific method called. If a specific method makes use of bits
24-31, a description will be provided under that method’s description.
Bit Number Error Description
0 Internal Error Occurred
1 Smart-Net Port Adapter was not detected
2 Smart-Net is shorted or improperly wired
3 Communications, device, or Signal Error on Smart-Net
4 Requested Device/Parent was not found
5 Requested Device/Parent is of the wrong type or was not a Parent
6 (Reserved)
7 (Reserved)
8 Invalid parameter(s) supplied
9 Too many parameters supplied
10 Too few parameters supplied
11 Required parameter not supplied
12 (Reserved)
13 (Reserved)
14 (Reserved)
15 (Reserved)
The Bit Number referred to in the table is counted from the least significant bit (0) to the
most significant bit (7). For example, if the integer returned is “4”, its binary
representation would be: 0000 0000 0000 0100. Since bit number 2 is set, it is
determined that the Smart-Net is shorted or improperly wired.

20
ROMID
The “ROMID” field (string) is the Smart-Net identification string that is unique to every
Smart-Net device. Knowing the ROMID is the only way to read or reconfigure a Smart-
Net device. If the ROMID is not known, the SmartNet.Find method can be used to
discover devices on the network.
ParentID
The “ParentID” field (string) is the ROMID of a parent device that contains another
device. The only way to access a device that is behind a parent device is to know both
the Smart-Net identification string of the device (ROMID) and the Smart-Net
identification string of its parent device (ParentID).
For example, assume there is a Blade Meter with a ROMID of “2B00000005E0861D-2”
connected to a socket of a SmartPDU with a ROMID of “BF0000000101741F”. To
access the Blade Meter, the ROMID field would have to be “2B00000005E0861D-2” and
the ParentID field would be “BF0000000101741F”.
The SmartNet.Find method can be used to discover devices and their parent’s on the
network.
UserID
The “UserID” field (string) is a user-programmable value that can be stored in most
Smart-Net devices. The maximum length of this field depends on the physical
capabilities of the Smart-Net device being accessed. The UserID stored in a device can
be used, for example, to help identify the physical location of a device or the name of a
server that the device is attached to. The UserID is not a replacement for knowing the
ROMID or a ParentID in the XML-RPC Methods.
Smart-Net Gateway XML-RPC Methods
SmartNet.Status
Parameters: <>
Response: { Timestamp=(integer), [FtpLogFileSize=(integer)], [FreeMemory=(integer)],
[Uptime=(integer)], [IpAddress=(string)], [MacAddress=(string)],
[FirmwareVersion=(string)], [FirmwareBuild=(string)] }
Field Descriptions:
•FtpLogFileSize – An integer representing the current size of the log files used by
the FTP Logging feature, in bytes.
•FreeMemory – An integer representing the amount of free memory in the Smart-
Net Gateway, in bytes.
•Uptime – An integer representing the number of seconds since the Smart-Net
gateway has been rebooted.
Table of contents
Popular Gateway manuals by other brands
Multitech
Multitech MultiConnect Conduit Getting started guide

Multitech
Multitech MULTIVOIP MVP-130 user guide

Multitech
Multitech MULTIVOIP MVP-210 supplementary guide

2-Wire
2-Wire HomePortal 2701HGV installation guide

seeed studio
seeed studio BeagleBone Green reference guide

3One data
3One data GW11X8-8D (3IN1)-RJ45 Series user manual