4
2. INSTALLATION
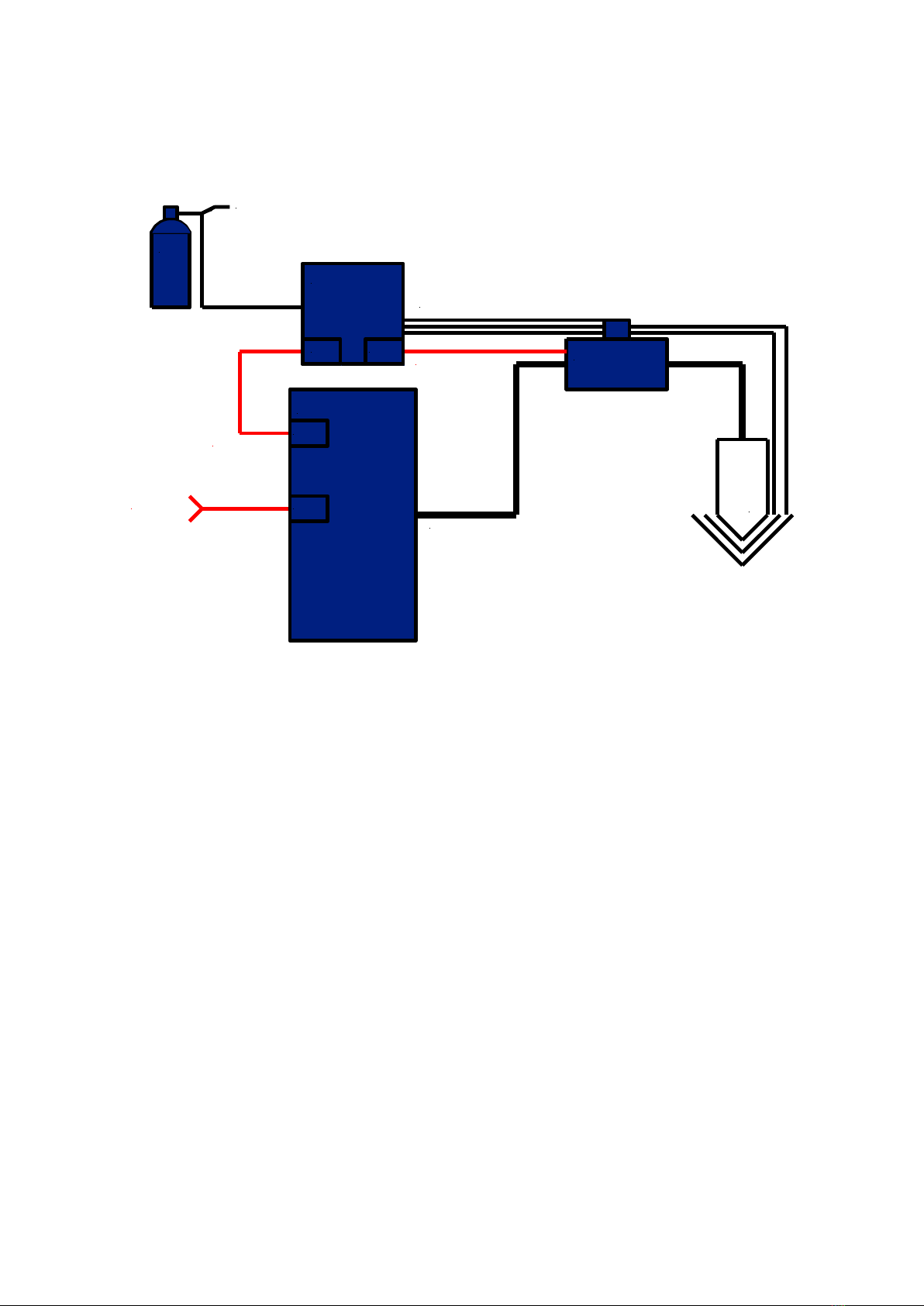
Below is a scheme over the principle of the system and its components. These instructions are
aimed at system builders with experience in mechanised plasma cutting. If such competence
is not available it is advised that SPT be contacted for guidance.
To obtain satisfactory cutting quality and economy it is vital that the CNC-machine be
equipped with a suitable height control device for plasma cutting. The plasma technology
requires a very well defined process control. The height control must be able to handle
different heights for ignition, piercing and cutting. Most robots can easily be programmed to
handle the process.
If a suitable height control system is not available one can be delivered by SPT. Contact us for
advice.
Electrical supply:
SPARCIN 4000: 3~50 Hz, 400V, 80A slow blow
Note that the SPARCIN 4000 is an inverter power source and it requires a stable power
supply. Make sure that the power supply is stable and within 400 V +6/-10 %. A circuit
breaker should be present at the wall socket.
Gas supply:
Connect the gases to the rear of the gas console. Use only 2-step pressure regulators of high
quality and adjust to 9-10 bar on each bottle. Also the compressed air shall be adjusted to 9-10
bar. The compressed air should be dry, oil free and free from particles.
Bear in mind that pressurized oxygen and oil is an explosive combination that can lead to loss
of life as well as destruction of property.
Remote control from robot or CNC
The plasma system is controlled via a multi-pole connector marked “CNC” on the rear panel
of the power source. This should be connected according to diagram further back in this
manual. The system is highly sensitive and it is therefore vital to connect it properly. Pins in
the connector that are not used by the remote control must be left unconnected. If they are
connected to a wire that is left unconnected in the other end this works as an antennae and this
will lead to unwanted behavior.
In some cases it may be necessary to screen the cables.
Safety
Only specially trained personnel should install the SPARCIN 4000 system. National law and
regulations must be followed. Note that parts of the system are electrically live when
connected even though the main power switch is off.