1Parker Hannifin Corporation
Tube Fittings Division
Columbus, OH
FluidConnectors
Bulletin 4390-974250 Cut 250 Saw Use and Maintenance Manual
CHAPTER 7______________________________________
Regulating the Machine ................................................... 7
7.1 – Saw head ................................................................ 7
7.2 – Vice ......................................................................... 7
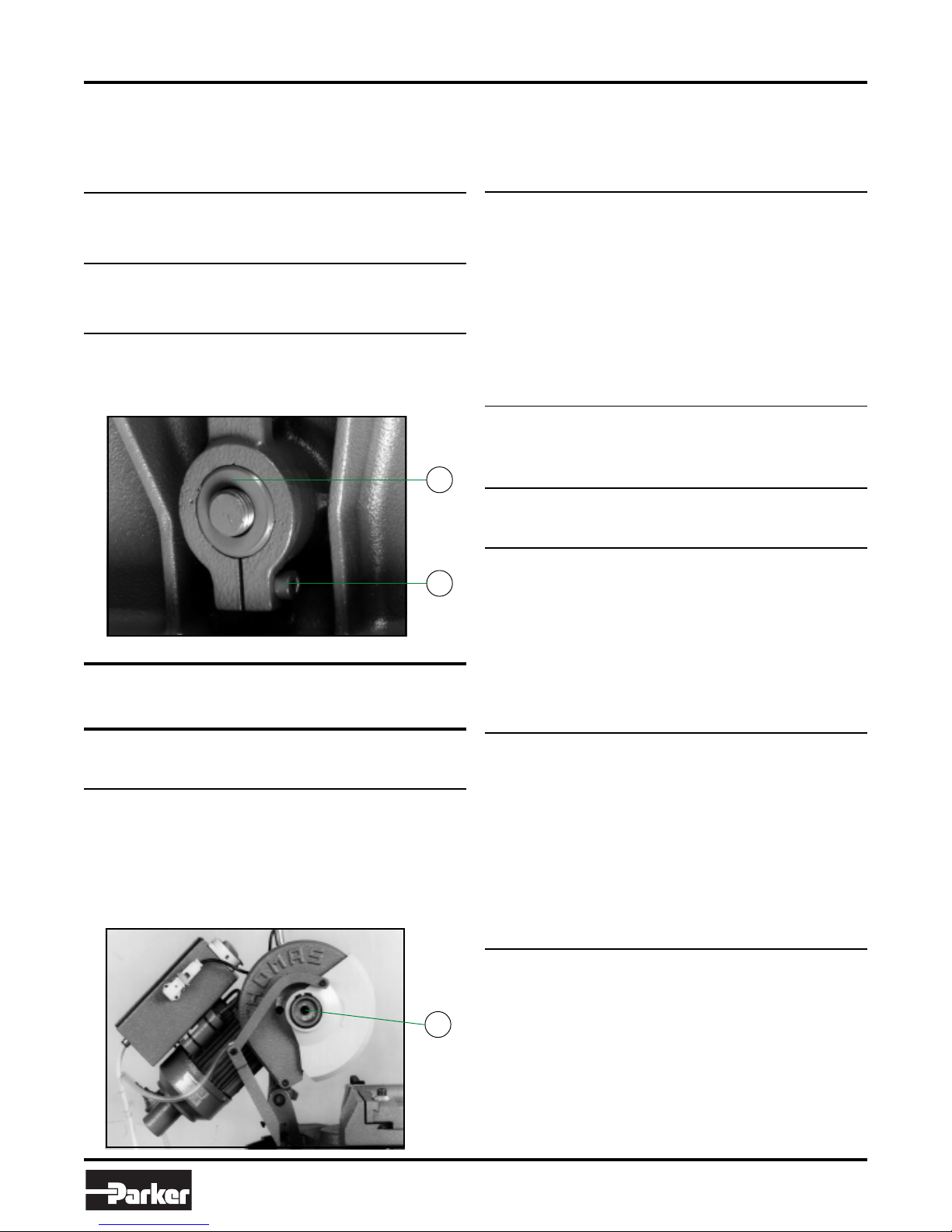
7.3 – Regulating arm blockage ........................................ 7
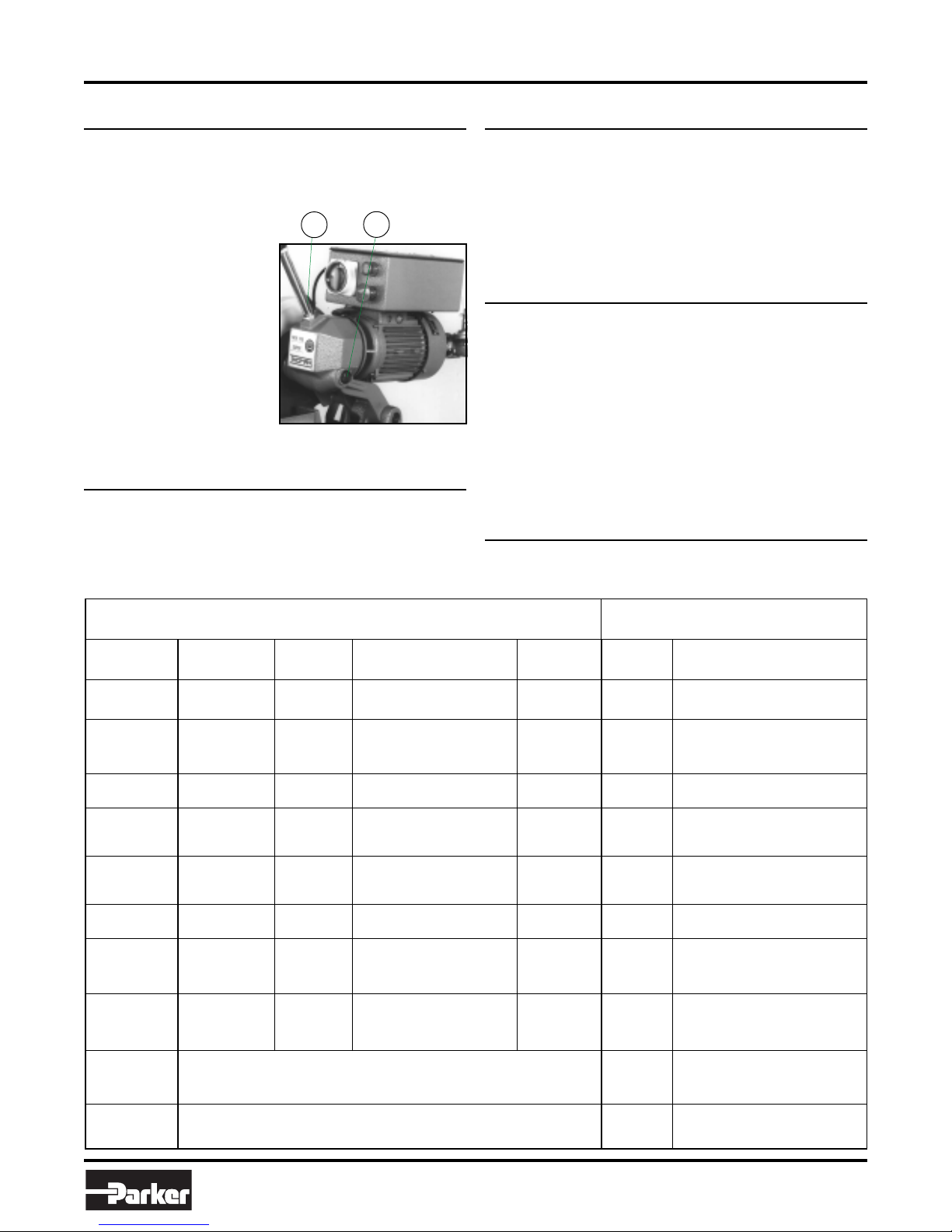
7.4 – Changing the blade................................................. 7
7.5 – Changing the lubricating coolant pump .................. 7
CHAPTER 8______________________________________
Routine and Special Maintenance .................................. 7
8.1 – Daily maintenance .................................................. 7
8.2 – Weekly maintenance .............................................. 7
8.3 – Monthly maintenance ............................................. 7
8.4 – Six-monthly maintenance ....................................... 8
8.5 – Oils for lubricating coolant ...................................... 8
8.6 – Special maintenance .............................................. 8
CHAPTER 9______________________________________
Material Classification and Choice of Tool .................... 8
9.1 – Definition of materials ............................................. 8
9.2 – Choosing the blade................................................. 9
9.3 – Teeth pitch .............................................................. 9
9.4 – Cutting and advance speed.................................... 9
9.5 – Breaking in the blade .............................................. 9
9.6 – Type of blade........................................................... 9
Tooth shape ............................................................ 9
Tooth cutting angle ................................................. 9
Sharpening circular saws ..................................... 10
9.6.1 – Table of recommended cutting parameters.......... 10
9.6.2 – Table of cutting speed according to
blade diameter ...................................................... 11
CHAPTER 10_____________________________________
Machine Components .................................................... 12
10.1 – List of spare parts................................................. 12
CHAPTER 11_____________________________________
Wiring Diagrams ............................................................. 15
CHAPTER 12_____________________________________
Troubleshooting .............................................................. 17
12.1 – Blade and cut diagnosis ....................................... 17
12.2 – Electrical components diagnosis .......................... 19
CHAPTER 13_____________________________________
Noise Tests ...................................................................... 19
Plates and Labels ........................................................... 20
Offer of Sale .................................................................... 21
Contents ............................................................................ 1
Ordering Spare Parts ....................................................... 1
Guarantee .......................................................................... 1
Machine Certification and Identification Marking......... 2
CHAPTER 1______________________________________
Reference to Accident-Prevention Regulations............ 3
1.1 – Advice for the operator ........................................... 3
1.2 – Location of shields against accidental contact with
the tool .................................................................... 3
1.3 – Electrical equipment according to European
Standard "CENELEC EN 60 204-1" (1992)............ 3
1.4 – Emergencies according to European Standard
CENELEC EN 60 204-1" (1992)............................. 3
CHAPTER 2______________________________________
Recommendations and Advice for Use.......................... 3
2.1 – Recommendations and advice
for using the machine ............................................. 3
CHAPTER 3______________________________________
Technical Characteristics ................................................ 4
3.1 – Table of cutting capacity and technical details ....... 4
CHAPTER 4______________________________________
Machine Dimensions – Transport –
Installation – Dismantling................................................ 4
4.1 – Machine dimensions ............................................... 4
4.2 – Transport and handling of the machine .................. 4
4.3 – Minimum requirements for the premises
housing the machine .............................................. 5
4.4 – Anchoring the machine ........................................... 5
4.5 – Instructions for electrical connection ...................... 5
4.6 – Instructions for assembly of
the loose parts and accessories............................. 5
4.7 – Deactivating the machine ....................................... 5
CHAPTER 5______________________________________
Machine Functional Parts ................................................ 5
5.1 – Operating head ....................................................... 5
5.2 – Vice ......................................................................... 6
5.3 – Bed.......................................................................... 6
CHAPTER 6______________________________________
Description of the Operating Cycle ................................ 6
6.1 – Starting up and cutting cycle .................................. 6
Ordering Spare Parts
• When ordering spare parts you must state:
Machine model
Serial number
Part reference number
Withoutthesereferences
we will not supply
thespareparts.
See point 10.1 – List of spare parts.
Guarantee
• The Company guarantees that the machine to which this
manual refers has been designed and built to comply with
safety regulations and that it has been tested for functional-
ity in the factory.
• The machine is guaranteed for 12 months: the guarantee
does not cover the electric motors, electric components,
pneumatic components or any damage due to dropping or
machine misuse, the failure to observe maintenance stan-
dards or bad handling by the operator.
Contents