characteristic, or constant-current output characteristic. With the drooping
_____________________________________________________________________
characteristic , a small change in arc voltage will produce a much smaller change in arc current, depending
upon the open circuit voltage (OCV) of the welding machine. This means the wire ‘burn-off’ rate is much
slower for MMA welding, or put another way, for any given change in arc length the welding current
change is small. This allows manual welding to take place, as even in the hands of a skilled welder, arc
length will vary as welding is progressed, but under these circumstances the current changes will only be
small.
For MIG/MAG, GMAW and ‘No Gas’flux cored wire arc welding, the welding power source
characteristic curve is a typical ‘flat’ characteristic, or constant-voltage output characteristic. With the
‘flat’ characteristic , a large change in current will produce a small change in voltage. This means
the wire ‘burn-off’ rate is much quicker, or put another way, for any given change in arc length the
welding voltage change is small. Therefore, in all semi-automatic welding the arc-length and the wire
‘burn-off’ rate are controlled by the welding machine. The welding current increases as the
arc-length decreases so as to rapidly compensate for the increase in wire ‘burn-off’ rate. This
response rate needs to be extremely rapid. Of course the welder needs to try and maintain a consistent
wire ‘stick-out’ length. The wire ‘stick-out’ length may best be described as the distance from the contact
tip of welding gun to the workpiece.
If the same person were asked to make a weld using MMA, in the same training period, it would be most
unlikely they would succeed. This is because the only variable parameter is output current of the MMA
welding power source. Get that wrong and the results will be poor. Whereas MIG/MAG
welding or ‘No Gas’flux cored wire arc welding, being semi-automatic, controls voltage and wire feed
speed automatically, thereby, it is easy to mastery in a shorter period of time. This means training courses
don’t need to be lengthy affairs.
In the MIG/MAG, GMAW and ‘No Gas’flux cored wire arc welding processes, methods of molten
globules transfer are mainly “dip” or “globular” transfer.The “dip” transfer, also known as
short-circuiting transfer, is carried out using currents below 200 amps and voltages below 24 volts. Under
these conditions the arc is so short that the molten globules at the electrode tip ‘short-circuit’ to the
workpiece at rapid, regular intervals. The welding current during short-circuiting melts off the electrode
tip and allows re-establishment of the arc. This is ideal for welding on thin materials and out of position
working and/or root runs for butt welds.The “globular” transfer, that is a kind of transfer without
short-circuiting, is carried out using currents over 200 amps and voltages over 24 volts. Under these
conditions the arc is so long that the molten globules at the electrode tip ‘not short-circuit’ to the workpiece.
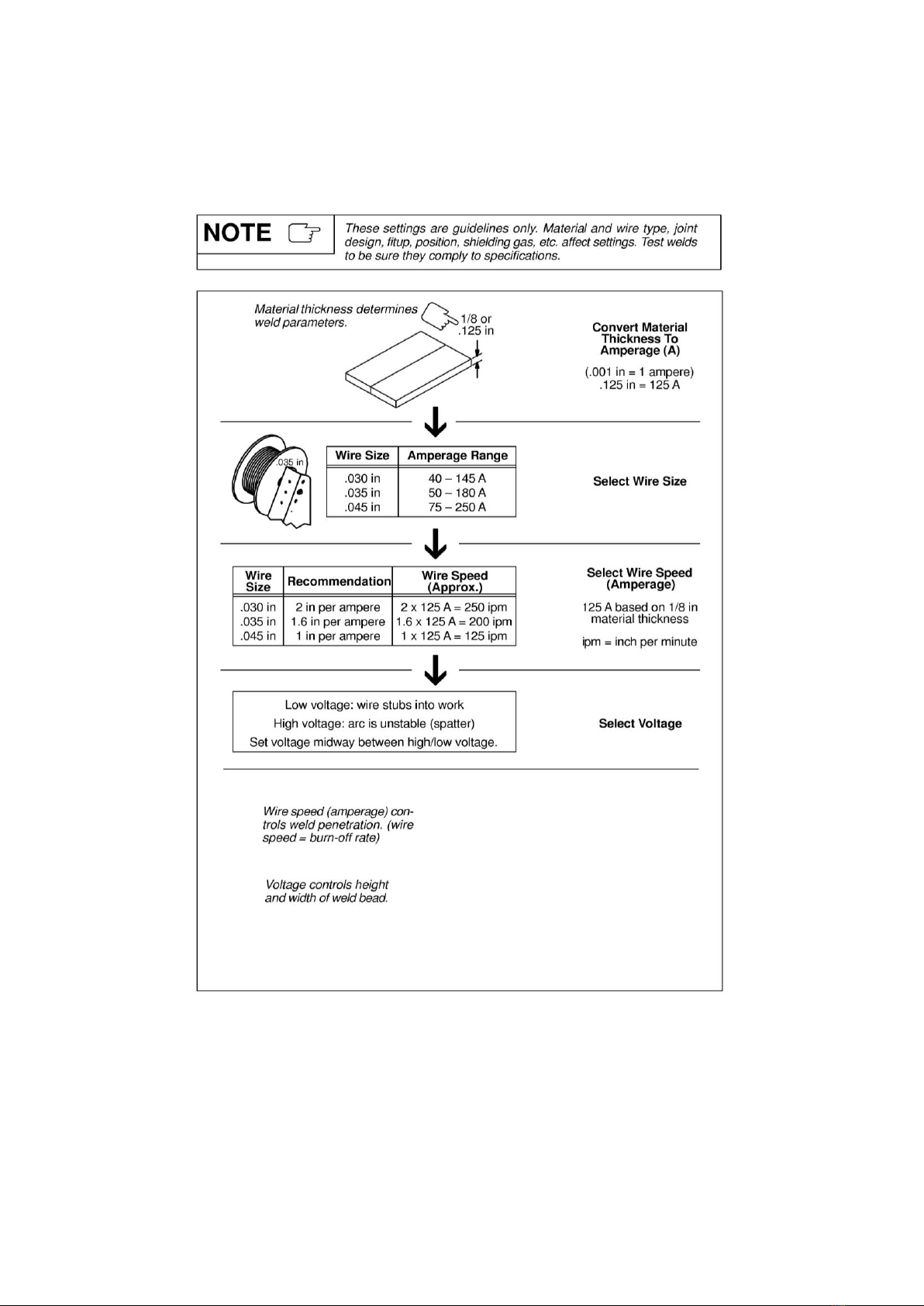
This is ideal for welding on thick materials.So,in setting up the machine, you must a suited welding voltage,
which needs to be in keeping with the wire feed speed or the welding current . If the wire feed speed and
welding voltage to be set are not suited, incorrect arc condition may be produced.
In the MIG/MAG arc welding processes,Gas flow rates will depend on the worksite conditions and the
workpiece to be welded. If you use a mixture of argon and C02,
_____________________________________________________________________