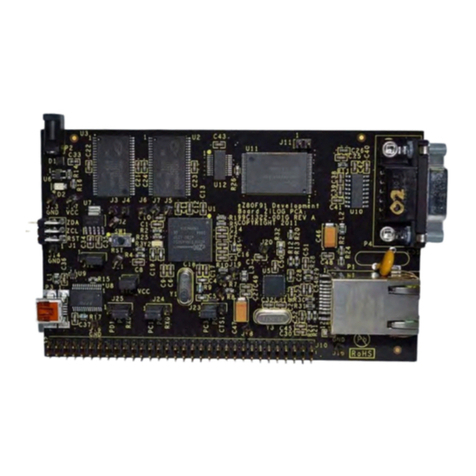
Trenz Electronic TE0300 User manual

Chipsmall Limited consists of a professional team with an average of over 10 year of expertise in the distribution
of electronic components. Based in Hongkong, we have already established firm and mutual-benefit business
relationships with customers from,Europe,America and south Asia,supplying obsolete and hard-to-find components
to meet their specific needs.
With the principle of “Quality Parts,Customers Priority,Honest Operation,and Considerate Service”,our business
mainly focus on the distribution of electronic components. Line cards we deal with include
Microchip,ALPS,ROHM,Xilinx,Pulse,ON,Everlight and Freescale. Main products comprise
IC,Modules,Potentiometer,IC Socket,Relay,Connector.Our parts cover such applications as commercial,industrial,
and automotives areas.
We are looking forward to setting up business relationship with you and hope to provide you with the best service
and solution. Let us make a better world for our industry!
Contact us
Tel: +86-755-8981 8866 Fax: +86-755-8427 6832
Email & Skype: [email protected]om Web: www.chipsmall.com
Address: A1208, Overseas Decoration Building, #122 Zhenhua RD., Futian, Shenzhen, China

Spartan-3E FPGA
Industrial Micromodule
Rev 1.19 as of 011-10-04 User Manual
Features
■High-density plug-in Xilinx Spartan-
3E module
■USB 2.0 interface with high speed
(480 Mbit/s) data rate
■Large SPI flash for configuration and
user storage accessible via USB or SPI
connector
■Large DDR-SDRAM
■FPGA configuration is implemented via
TAG, SPI Flash or USB
■3 on-board high-power, high-effi-
ciency, switch-mode DC-DC convert-
ers (1 A for each voltage rail: 1. V,
.5 V, 3.3 V)
■Power supply via USB or B B (carrier
board)
■Flexible expansion via high-density
shockproof B2B (board-to-board)
connectors
■Most I/O's on the B B connectors are
routed as LVDS pairs
■Evenly spread supply pins for good
signal integrity
■Industrial temperature grade avail-
able on request
■Low-cost, versatile and ruggedized
design
Specifications
■FPGA: Xilinx Spartan-3E XC3S500E –
XC3S1600E
■USB controller: Cypress EZ-USB FX
USB .0 microcontroller CY7C68013A-
56LFX
■Non volatile memory: 16 MBit - 64
Mbit SPI Flash for FPGA-configuration
and user data
■Volatile memory: 51 Mbit x 16 DDR
SDRAM with up to 666 Mbyte/s
■Up to 110 FPGA user I/Os
■Supply voltage range: 4.0 V – 5.5 V
■1 push-button
■1 LED
■Small size (only 40.5 mm x 47.5 mm)
Trenz Electronic GmbH 1
Trenz Electronic GmbH
www.trenz-electronic.de
Figure 2: TE0300: top view. Figure 1: TE0300: bottom view.

Table of Contents
Features........................................................................................................................1
Specifications................................................................................................................1
Applications...................................................................................................................3
Description....................................................................................................................3
Physical Features...........................................................................................................3
Power Supply.................................................................................................................5
FPGA User I/Os..............................................................................................................6
User Button and LED.......................................................................................................7
Configuration Switches...................................................................................................7
JTAG and SPI.................................................................................................................8
Clock Networks..............................................................................................................9
On-board Memories......................................................................................................10
Module Configuration....................................................................................................11
Changes from TE0300-00 to TE0300-01.......................................................................... 4
Ordering Information.................................................................................................... 4
Revision History........................................................................................................... 4
Legal Notices............................................................................................................... 5
Environmental protection............................................................................................... 6
Appendix..................................................................................................................... 7

Spartan-3E FPGA Industrial Micromodule User Manual
Applications
■IP (intellectual property) development
■Digital signal processing
■Image processing
■Cryptography
■Industrial control
■Low-power design
■General-purpose prototyping platform
Description
The FPGA industrial micromodule integ-
rates a leading edge Xilinx Spartan-3E
FPGA, an USB .0 microcontroller, config-
uration Flash, DDR SDRAM and power sup-
plies on a tiny footprint. A large number of
configurable I/Os are provided via B B
mini-connectors.
The module is intended to be used as an
OEM board, or to be combined with our
carrier boards. It is a powerful system
widely used for educational and research
activities.
Boards with other configurations, larger
FPGA's or equipped with industrial temper-
ature grade parts are available on request.
Software for SPI flash programming over
USB as well as reference designs for high
speed data transfer over USB are included.
Physical Features
Board Dimensions
The module measures 40.50 mm by 47.50
mm.
Board-to-Board Connectors
The module has two B B (board-to-board)
receptacle connectors (J4 and J5) for a
total of 160 contacts (Figure 5).
The ordering numbers of the connector re-
ceptacles are given in Table 1.
Trenz Electronic GmbH 3
Figure 5: micromodule receptacle.
Figure 4: connector receptacles 4
and 5 (bottom view).
Figure 3: module dimensions in mm
(top view).

Spartan-3E FPGA Industrial Micromodule User Manual
supplier header
Digikey
H11113CT-ND
H11113TR-ND
H11113DKR-ND
Hirose DF17(3.0)-80DS-0.5V(57)
Trenz Electronic 684
Table 1: equivalent part numbers of
the receptacle connectors 4 and 5.
The on-board receptacles mate with their
corresponding headers on the carrier board
(Figure 6).
The ordering number of the headers is giv-
en in Table .
supplier header
Digikey
H11148DKR-ND
H11148TR-ND
H11148CT-ND
Hirose DF17(4.0)-80DP-0.5V(57)
Trenz Electronic 938
Table 2: equivalent part numbers of
the mating connectors.
Figure 7 shows the definition of stacking
height featured by the combination of the
TE0300 receptacle with its corresponding
header.
The stacking height of the TE0300 B B
connectors is 7 (seven) mm. The stacking
height does not include the solder paste
thickness.
USB Connector
The micromodule uses a mini-USB (B type)
receptacle connector.
Power Supply
The module can be powered by the B B
connector or the USB connector. If both
power supplies are available, the B B con-
nector power supply takes precedence,
disabling the USB power supply automatic-
ally.
B2B Connector Power Supply
The B B connector power supply requires
a single nominal 5 V DC power supply. The
power is usually supplied to the module
through the 5 V contacts (5Vb b) of the
B B connectors J5 (see Appendix). The re-
commended minimum supply voltage is
Trenz Electronic GmbH 4
Figure 8: mini-USB (B type) receptacle
connector.
Figure 6: mating header.
Figure 7: stacking height (h).

Spartan-3E FPGA Industrial Micromodule User Manual
4 V. The maximum supply voltage is 5.5 V.
The recommended maximum continuous
supply current is 1.5 A.
USB Power Supply
The module is powered by the USB con-
nector if the following conditions are met:
■the module is equipped with an USB
connector,
■the module is connected to a USB bus,
■no power supply is provided by the B B
connectors.
In this case, other components (e.g. ex-
tension or carrier boards) may also be
powered by the corresponding 5 Volt line
(5V) of the B B connector J5.
On-board Power Rails
Three on-board voltage regulators provide
the following power supply rails needed by
the components on the micromodule:
■1. V, 1 A max
■.5 V, 1 A max
■3.3 V, 1 A max
The power rails are available for the FPGA
and can be shared with a baseboard by the
corresponding lines of the B B connect-
ors J4 and J5. Please note that the power
consumption of the FPGA is highly de-
pendent on the design actually loaded.
So please use a tool like Xilinx Xpower to
determine the expected power consump-
tion.
Even if the provided voltages of the mod-
ule are not used on the baseboard, it is re-
commended to bypass them to ground
with 10 nF - 100 nF capacitors.
I/O Banks Power Supply
The Spartan-3E architecture organizes
I/Os into four I/O banks (see Table 3).
Bank Supply
Voltage (V)
Min
(V)
Max
(V)
B0 VccIO 1. 3.3
B1 ,5 - -
B 3,3 - -
B3 3,3 - -
Table 3: I/O banks power supply.
Voltage for banks B1, B and B3 is fixed
respectively to ,5 V, 3,3 V and 3,3 V.
Voltage VccIO for bank B0 shall span from
1. V to 3.3 V. VccIO can be supplied
either externally or internally to the micro-
module.
Warning! Spartan-3 I/Os are not 5 V tol-
erant. Applying more than the recommen-
ded operating voltages at any pin, results
in a damaged FPGA (see Xilinx Answer
AR#19146).
Externally Supplied VccIO
VccIO can be externally supplied over the
B B connector J4. If bank B0 is not used,
then VccIO can be left open.
Internally Supplied VccIO
If VccIO is not externally supplied, it can
be internally supplied by one of the intern-
al power rails of .5 V and 3.3 V. This is
possible by short-circuiting one of the two
pad pairs placed on the right of connector
J4 at the top right corner of the bottom
side of the micromodule.
Figure 9 shows how to short-circuit VccIO
to internal 3.3 V power rail.
Figure 10 shows how to short-circuit VccIO
to internal .5 V power rail.
Trenz Electronic GmbH 5

Spartan-3E FPGA Industrial Micromodule User Manual
Two suitable ways of shirt-circuiting the
paid pair are by means of a zero-ohm
0603 (1608 metric) chip resistor or a
solder blob.
FPGA User I/Os
A total of 110 FPGA user I/Os are available
on corresponding contacts of B B connect-
ors J4 and J5 (see Appendix).
■37 differential digital I/O pairs:
each pair is configurable as single-en-
ded digital I/Os, corresponding to a
maximum of 74 single-ended digital
I/Os;
■4 differential clock input pairs:
each pair is configurable as differential
digital I/O pair or single-ended clock
inputs or single-ended digital I/Os (or
combination thereof), corresponding to
from a maximum of 8 independent clock
inputs to a maximum of 8 independent
digital I/Os;
■1 differential clock input pair:
the pair is configurable as differential
digital input pair or as single-ended
clock inputs or single-ended digital in-
puts (or combination thereof), corres-
ponding to from a maximum of inde-
pendent clock inputs to a maximum of
independent digital inputs;
■1 single-ended digital I/Os;
■5 single-ended inputs.
Table 4 summarizes the maximum avail-
able FPGA user I/Os divided by supply
voltage.
type VccIO 3.3 V
diff. I/O pairs ≤ 18 ≤ 3
diff inputs ≤ 1 none
diff. clocks ≤ 4 ≤ 1
s. e. I/Os ≤ 46 ≤ 58
s. e. inputs ≤ ≤ 4
s. e. clocks ≤ 8 ≤ 3
Table 4: maximum FPGA user I/Os by
supply voltage.
Differential Pairs
The micromodule has a total of 4 differ-
ential signal pairs routed pairwise with a
differential impedance of 100 ohm to adja-
cent connector pins. These lines can be
used for high speed signaling up to
666 Mbit/s per differential pair (see Xilinx
Application Note XAPP485).
User Button and LED
LED
The LED is lit when the U_LED line (pin
R10) is set high as detailed in the follow-
ing table.
Signal FPGA pin FPGA ball
U_LED IO_L15P_
(bank ) R10
Table 5: user led signal details.
Push Button
The push button is connected to the PB in-
put (pin V16). as detailed in the following
table.
Trenz Electronic GmbH 6
Figure 10: R103 pad pair (blue high-
light) for 2.5 V internal supply.
Figure 9: R102 pad pair (blue high-
light) for 3.3 V internal supply.

Spartan-3E FPGA Industrial Micromodule User Manual
Signal FPGA pin FPGA ball
PB IP
(bank ) V16
Table 6: user button signal details.
The input is normally low. The input is
pulled up when pressed.
Configuration Switches
The micromodule hosts 4 DIP switches on
the top side: S1; S , S3 and S4.
For customers requesting a sufficient
amount of units, the micromodules can be
manufactured replacing the switches by
fixed connections.
DIP Switch S1
S1 enables / disables the communication
between the Cypress EZ-USB FX micro-
controller and the I C CMOS Serial EEP-
ROM.
Turn S1 off when programming the USB
EEPROM (storing the USB vendor ID and
device ID). This will force the USB micro-
controller to provide its default vendor ID
and device ID.
S1 position
EEPROM (on)* EEPROM enabled
Off (off) EEPROM disabled
Table 7: S1 (* default: EEPROM).
For further information, please read para-
graph “Software Configuration”.
DIP Switch S2
S enables / disables the reset line. The
reset line (available also on contacts of
the B B connector) resets the USB micro-
controller and the FPGA.
S has to be turned off (Reset) if the user
wants to program the SPI Flash memory in
direct mode. For programming the SPI
Flash memory in indirect mode over JTAG,
S has to be turned on (Run).
S2 position
Run (on)* system running
Reset (off) system reset
Table 8: S2 (*default: Run).
For further information, please read para-
graph “Software Configuration”.
DIP Switch S3
S3 conditionally / unconditionally enables
the 1. V and .5 V power rails.
When S3 is turned on, the 1. V and .5 V
power rails are controlled by the USB mi-
crocontroller. At start-up, the USB micro-
controller switches off the 1. V and .5 V
power rails and starts up the module in
low-power mode. After enumeration, the
USB microcontroller firmware switches the
1. V and .5 V power rails on, if enough
current is available from the USB bus.
When S3 is turned off, the 1. V and .5 V
power rails are always enabled.
S3 position
FX PON (on)* rails controlled by FX
PON (off) rails always enabled
Table 9: S3 (* default: FX2 PON).
Warning! When S3 is turned on (FX2
PON), make sure that no signals are ap-
plied to the input pins when power-rails
are disabled by the USB microcontroller.
The 3.3 V power-rail though is out of the
control of the USB-microcontroller and is
supplied down-converting the 5 V power
supply provided by either the USB-bus or
the B B receptacle connector. In this case,
signals that are applied to the 3.3 V I/O
Trenz Electronic GmbH 7

Spartan-3E FPGA Industrial Micromodule User Manual
banks do not need to be disconnected
when power-rails are disabled by the USB
microcontroller.
DIP Switch S4
S4 enables / disables the FPGA configura-
tion through the SPI interface. The FPGA
configuration through the JTAG interface
cannot be disabled.
When S4 is turned on, the FPGA tries to
configure from the SPI Flash memory. The
FPGA can be configured by the JTAG inter-
face at any time.
When S4 is turned off, the FPGA waits to
be configured by the JTAG interface.
For further information about direct (pure
SPI) / indirect (SPI over JTAG) in-system
programming of SPI flash memories,
please see Xilinx Application Notes XAP-
P951 “Configuring Xilinx FPGAs with SPI
Serial Flash” and XAPP974 “Indirect Pro-
gramming of SPI Serial Flash PROMs with
Spartan-3A FPGAs”.
S4 position
SPI (on)* FPGA configuration: JTAG + SPI
JTAG (off) FPGA configuration: JTAG
Table 10: S4 (* default: SPI).
Warning! When downloading via parallel
JTAG programmer to FPGA, it can happen
that programming fails with Error: "'1' :
Programming terminated. DONE did not
go high." Try setting DIP switch S4 to
JTAG-only. A bug in certain Xilinx iMPACT
versions can cause this.
DIP Switches Overview
Figure 11 summarizes functions and loca-
tion of the four DIP switches.
TAG and SPI
The offset holes for J and J3 allow a re-
movable press fit of standard 0.100 inch
header pins to connect the fly wires
without any soldering necessary.
TAG Header
JTAG signals are available on the dedic-
ated header J through a JTAG program-
mer with flying leads as described in Table
11.
Trenz Electronic GmbH 8
Figure 11: DIP switches overview.

Spartan-3E FPGA Industrial Micromodule User Manual
TMS
TDI
TDO
TCK
GND
Vref (3.3 V)
Table 11: TAG header ( 2).
SPI Header
SPI signals are routed to / from bank of
the FPGA as detailed in Table 1 and made
available on the dedicated header J3 ac-
cessible through an SPI programmer with
flying leads as described in Table 13.
Signal FPGA pin FPGA ball
SPI /S IO_L01P_ U3
SPI D IO_L03N_ T4
SPI Q IO_L16N_ N10
SPI /C IO_L 6N_ U16
Table 12: SPI signal details (bank 2).
SPI /S
SPI D
SPI Q
SPI /C
GND
Vref (3.3 V)
Table 13: SPI header ( 3).
Clock Networks
24 MHz Clock Oscillator
The module has a 4 MHz SMD clock oscil-
lator providing a clock source for both the
USB microcontroller and the FPGA as de-
tailed in Table 14.
Trenz Electronic GmbH 9

Spartan-3E FPGA Industrial Micromodule User Manual
Signal FPGA pin FPGA ball
4MHZ1 IO_L1 P_
(bank ) N9
Table 14: 24 MHz clock signal details.
Main Clock Oscillator
The module has a main SMD clock oscillat-
or providing a clock source for the FPGA as
detailed in Table 15.
Signal FPGA pin FPGA ball
100MHZ
1 5MHZ
GCLK0
(bank ) U10
Table 15: main clock signal details.
Standard frequencies are 100 MHz and 1 5
MHz (please visit Trenz Electronic website
for current ordering information). The
lower the main clock frequency, the lower
the module power consumption. Moreover,
as the main clock is preferably used as
DDR SDRAM clock, a lower clock frequency
makes easier for the development tools to
meet the timing requirements (particularly
for DDR SDRAM). For customized boards,
this clock can be changed according to
user requirements.
Interface Clock (IFCLK)
The IFCLK line synchronizes the commu-
nication between the USB microcontroller
and bank3 of the FPGA as detailed in Table
16.
Signal FPGA pin FPGA ball
IFCLK LHCLK5
(bank 3) K4
Table 16: interface clock signal details
(bank 3).
Digital Clock Manager (DCM)
The DCMs of the FPGA can be used to syn-
thesize arbitrary clock frequencies from
any on-board clock network, differential
clock input pair or single-ended clock in-
put. For further reference, please read Xil-
inx data sheet DS485 "Digital Clock Man-
ager (DCM) Module" (dcm_module.pdf)
and Xilinx application note XAPP46 "Using
Digital Clock Managers (DCMs) in Spartan-
3 FPGAs" (xapp46 .pdf).
On-board Memories
The TE0300 has three on-board memories:
■DDR SDRAM
■SPI Flash
■serial EEPROM
DDR SDRAM
TE0300 modules have a 51 Mb DDR
SDRAM component for operation (code and
data) accessible through the FPGA.
Commercial-grade modules mount the fol-
lowing component:
Micron Technology MT46V3 M16BN-6
Industrial-grade modules mount the fol-
lowing component:
Micron Technology MT46V3 M16BN-6 IT
You can get the exact part number of the
component mounted on your module from
the Micron FBGA decoder:
http://www.micron.com/support/part_info
/fbga/decoder
When developing DDR SDRAM designs
with Xilinx tools (e.g. MIG, MPMC, ...), you
should select the following product type:
MT46V3 M16-6.
Should it be not available, you can use one
of the following product types:
■MT46V3 M16-5
■MT46V3 M16XX-5B
■MT46V3 M16BN-5B
■MT46V3 M16FN-5B
■MT46V3 M16P-5B
■MT46V3 M16TG-5B
Trenz Electronic GmbH 10

Spartan-3E FPGA Industrial Micromodule User Manual
TE0300 modules with the following part
numbers
■TE0300-00
■TE0300-00-4I5C
■TE0300-00B
■TE0300-01
■TE0300-01B
■TE0300-01BLP
are assembled with
Qimonda HYB 5DC51 160CF-6
51 Mb DDR SDRAM components. When
developing DDR SDRAM designs with Xilinx
tools, you should select the following
product type:
HYB 5D51 160BF-6.
SPI Flash
TE0300 modules have a
STMicroelectronics M 5P3
3 -Mbit, low voltage, serial Flash memory
with 75 MHz SPI bus interface for configur-
ation and operating storage accessible
through USB or SPI.
Serial EEPROM
TE0300 modules have a
Micron Technology 4LC1 8
1 8K I C CMOS Serial EEPROM. It used for
EZ-USB FX firmware, vendor ID and
device ID storage. EEPROM accessible
through the EZ-USB FX microcontroller.
Module Configuration
This section describes how to configure the
TE0300 module and access some of its re-
sources.
The JTAG interface allows a fast, frequent
but volatile configuration of the TE0300
module. However, only through the JTAG
interface it is possible to develop and de-
bug with Xilinx tools (e.g. Xilinx Chip-
Scope, Xilinx Microprocessor Debugger.
The SPI interface allows a fast, frequent
and non-volatile configuration of the
TE0300 module.
Configuration of the TE0300 module
through a USB host is recommended for
occasional, non-volatile on-site operations
such as firmware upgrade.
System Requirements
TE0300 modules can be configured
through a host computer with the following
system requirements:
■Operating system: Microsoft Windows
000, Microsoft Windows XP, Microsoft
Vista;
■Xilinx ISE 10.1 or later for indirect SPI
in-system programming (see Xilinx An-
swer AR # 5377);
■Xilinx EDK for some reference designs;
■Interface: USB host;
■JTAG/SPI USB cable with flying leads.
EZ-USB FX2 Microcontroller
Firmware
If the EEPROM has never been pro-
grammed before (virgin board), S1 can be
switched to EEPROM. The USB microcon-
troller will detect an empty EEPROM and
will provide its default vendor ID and
device ID to the USB host.
DIP
switch
on (left) off (right)
S1 EEPROM -
S Run -
S3 X X
S4 X X
Trenz Electronic GmbH 11

Spartan-3E FPGA Industrial Micromodule User Manual
If the EEPROM has been programmed be-
fore (EEPROM not empty), S1 must be
switched to Off. The USB microcontroller
will detect a missing EEPROM and will
provide its default vendor ID and device ID
to the USB host.
DIP
switch
on (left) off (right)
S1 - Off
S Run -
S3 X X
S4 X X
Generic USB Microcontroller Driver
installation
If the USB microcontroller (Cypress EZ-
ESB FX ) driver is not installed on the host
computer, then the easiest way to do it is
the following:
■disconnect the micromodule or leave
the micromodule unconnected;
■configure the micromodule such that
the USB microcontroller will provide its
default vendor ID and device ID to the
USB host (i.e. S1 = OFF -- see para-
graph “EZ-USB FX Microcontroller
Firmware”);
■connect the micromodule to the host
computer through the USB interface;
■wait until the operating system detects
new hardware and starts the hardware
assistant;
■if S1 is not already switched to EEP-
ROM, do it now;
■answer the hardware assistant ques-
tions as shown in the following ex-
ample.
Trenz Electronic GmbH 1

Spartan-3E FPGA Industrial Micromodule User Manual
Check that in the “Device Manager” under
“USB-Controller” the “Cypress Generic USB
Device” has been added.
Now the USB microcontroller can be ac-
cessed from the host computer through
dedicated software.
EZ-USB F 2 EEPROM Programming
First of all, check that S1 is actually
switched to EEPROM.
The USB EEPROM can be programmed by
opening the dedicated software “Cypress
USB Console” (double click the “CyCon-
sole.exe” file in the “1st_program\CyCon-
sole” folder).
Click “Options > EZ-USB Interface” to
Open EZ-USB Interface window.
“S EEPROM” button refers to the small EE-
PROM ( 56 bytes) whereas the “Lg EEP-
ROM” refers to the large EEPROM (64 KB).
Press the “Lg_EEPROM” button, select the
“USB.iic” file and press the “Open” button
to start writing to EEPROM.
Trenz Electronic GmbH 13

Spartan-3E FPGA Industrial Micromodule User Manual
Upgrade progress is displayed in status
window and is completed when “Download
Successful” text is displayed.
Disconnect the USB cable.
Dedicated USB Firmware Driver
Installation
Check the configuration switches against
the following table:
DIP
switch
on (left) off (right)
S1 EEPROM -
S Run -
S3 FX PON -
S4 X X
Reconnect the USB cable to run the newly
uploaded firmware in the USB microcon-
troller. Under the default switch configura-
tion, the USB microcontroller is now ready
to provide dedicated vendor ID and device
ID. Wait until the operating system detects
new hardware and starts the hardware as-
sistant and answer the hardware assistant
questions as shown in the following ex-
ample.
Trenz Electronic GmbH 14

Spartan-3E FPGA Industrial Micromodule User Manual
Check that in the “Device Manager” under
“USB-Controller” the “DEWESoft USB
Device 0” has been added.
FWU File Generation
The TE0300 micromodule can be con-
figured by means of a firmware-upgrade
(FWU) file (see next section “Micromodule
Configuration” for further reference). The
first step in generating the FWU file is to
generate the fpga.bin file corresponding to
a given FPGA design.
Open Xilinx IMPACT from Start /
Programs / Xilinx ISE / Accessories / Im-
pact
Select “create new project”.
Trenz Electronic GmbH 15

Spartan-3E FPGA Industrial Micromodule User Manual
Select “prepare PROM file”.
Select “BIN” as output.
Set “PROM File Name” to “fpga” and
change “Location” to a suitable name and
location.
Check “Auto Select PROM”.
Navigate to your project’s IMPLEMENTA-
TION folder and select “download.bit”.
Trenz Electronic GmbH 16

Spartan-3E FPGA Industrial Micromodule User Manual
The following warning is a normal situ-
ation.
This is probably the one and only file with
your design.
Congratulations!
Click GENERATE FILE or select from menu
Operations / Generate file.
You are done.
Trenz Electronic GmbH 17

Spartan-3E FPGA Industrial Micromodule User Manual
Don’t forget to save your project for fur-
ther use
Once you have got your fpga.in file, you
can proceed and generate your FWU file.
The FWU file is a ZIP file containing 3 files:
■Boot oad.ini – booting settings
■fpga.bin – FPGA programming file
■usb.bin – FX firmware
To create your FWU file, you need to
■replace the existing
USBFWUToo \FWUs\fpga.bin with the
latest fpga.bin (Boot oad.ini and usb.bin
are always unchanged)
■zip the 3 files
■change the “zip” fi e extension to “fwu”
■upload the file as explained in the next
section (Micromodule Configuration).
Warning! file and path names are given
and must NOT be changed!
Micromodule Configuration
The micromodule can now be programmed
with its dedicated firmware upload tool.
Turn S1, S , S3 and S4 on. Open the ded-
icated firmware upgrade tool “USB Firm-
ware Upgrade Tool” (double click the “US-
BFirmwareUpgradeTool.exe” file in the
“USBFWUTool” folder).
Press the “...” button corresponding to the
“File name” field and select for instance
the sample firmware upload file
“TE0300_v101 .fwu” in the
“USBFWUTool\FWUs” folder.
Trenz Electronic GmbH 18

Spartan-3E FPGA Industrial Micromodule User Manual
Press the “Upload” button to upload the
micromodule firmware and check the
“FPGA uploading...” progress bar.
After successful completion of the firmware
upload procedure, the following message
should pop up.
Reboot the micromodule with the new
firmware by disconnecting and reconnect-
ing the USB cable. You may want to test
the sample application “TE0300_API_Ex-
ample.exe” in the
“TE0300_API_Example\Debug” folder.
To generate your own firmware upload file,
please read the document
“Generating_FWU_file.doc” in the “USB-
FWUTool” folder.
SPI Direct In-System
Programming (ISP)
Make sure S is switched to “Reset” (off)
during programming.
Connect the host computer to the micro-
module through both the SPI flying leads
cable and the USB cable.
Start Xilinx ISE iMPACT. The following ex-
ample shows the case of iMPACT 9. . If the
“iMPACT Project” window pops up, press
the “Cancel” button.
Double click the “Direct SPI Configuration”
option in the “Modes” panel.
Right click the “Direct SPI Configuration”
panel to add a device and select “Add SPI
Device”.
Trenz Electronic GmbH 19
Table of contents
Other Trenz Electronic Microcontroller manuals
Popular Microcontroller manuals by other brands

STMicroelectronics
STMicroelectronics AN3248 Application note

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments SimpleLink MSP432E4 Technical reference manual
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments SimpleLink CC2650 Getting started
NXP Semiconductors
NXP Semiconductors i.MX 8M PLUS EVK quick start guide

Fujitsu
Fujitsu ALL FR 460 Series Application note

Silicon Laboratories
Silicon Laboratories Si1010 user guide