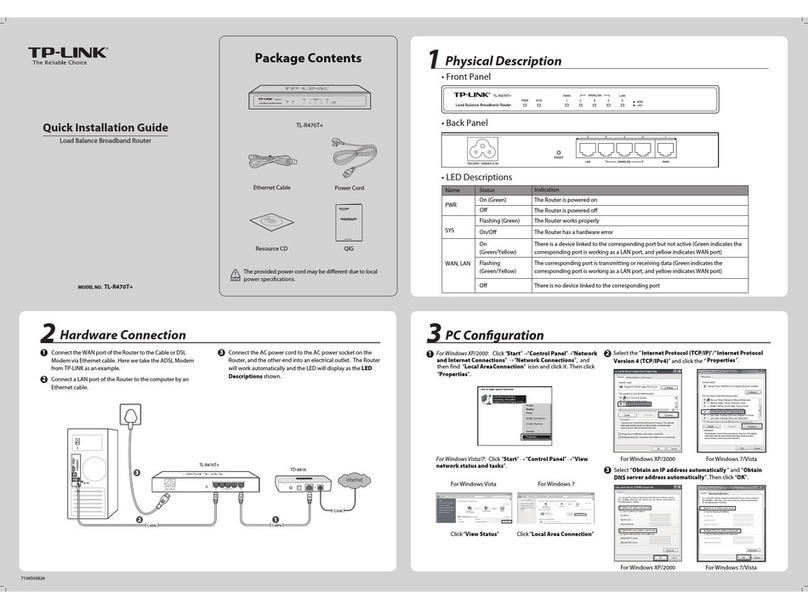
Wi-LAN Hopper Plus 120-24 Operator's manual

Hopper Plus 120-24
Wireless Ethernet Bridge
Installation and
Configuration Guide
Version 1.0 ev B
08/00

Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00
i
Contents
Notices ..................................................................................... v
Copyright Notice ........................................................................................ v
Regulatory Notice ...................................................................................... v
Other Notices ............................................................................................ vi
Contacting Wi-L N ................................................................................... vi
Contacting Customer Support vi
Description .............................................................................. 1
Hopper Plus 120-24 Wireless Ethernet Bridge ..........................................1
Making a Wireless Bridge 1
Creating a Wireless Network 2
bout Hopper Plus Units 2
Hardware Description ................................................................................3
Shipping Package Contents 3
Hopper Plus 120-24 Unit 3
Hopper Plus 120-24 Specifications ............................................................6
Installation ............................................................................... 9
Basic Installation Steps ..............................................................................9
Configuring a Unit as a Base ...................................................................10
Testing Basic Operation ..........................................................................11
Performing a Bench Test 11
Performing a Simple Network Test 13
Configuration ........................................................................ 15
ccessing the Main Menu ........................................................................16
ccessing Main Menu with M N GEMENT Port 16
ccessing Units via telnet 17
Setting VT100 rrows 18
Configuring with the Main Menu ..............................................................19
Unit Identification .....................................................................................20

ii
Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00
Viewing Unit Identification 20
Setting Unit Identification 21
Hardware/Software Revision ................................................................... 23
Viewing System Revision Information 23
System Software ROM Images ............................................................... 24
Viewing System Software ROM Images 24
Current System Status ............................................................................ 25
Viewing Current System Status 25
IP Network Configuration ........................................................................ 26
Setting the Internet IP ddress and Subnet Mask 26
Setting the Default Gateway IP ddress 27
Setting the SNMP NMS Trap IP ddress 28
IP Filter Configuration .............................................................................. 29
RF Station Configuration ......................................................................... 32
Setting Test Mode Time 32
Setting the Operating Mode 33
Setting the RF Transmit Status 35
Setting the Link Monitor Period 36
Setting Maximum Remote Distance (Base Station Only) 37
Setting Link Monitor Remote Station Rank
(Base Station Only) 38
Setting Throttling (Remote Station Only) 40
Radio Module Configuration .................................................................... 41
Setting the Station Type 42
Setting the Station Rank 43
Setting the Center Frequency 44
Setting Security Passwords 45
Setting the Scrambling Code 46
Setting the cquisition Code 47
Setting Config Test Minutes 48
Setting Repeater Mode (Base Station Only) 49
Setting System Symmetry Type (Base Station Only) 50
Setting Dynamic Polling Level (Base Station Only) 51
Setting Remote Unit RF Group 52
Rebooting and Saving RF Configurations 53
RF/Ethernet Statistics .............................................................................. 55
Viewing RF/Ethernet Statistics 55
System Security ...................................................................................... 58
Setting Community Names 58
Setting Login Passwords 59
Setting Remote ccess 60
Setting the utomatic Timeout 61
System Commands ................................................................................. 62
Setting Default System Image 62
Setting the Reboot System Image 63
Rebooting the Current Image 63
Restoring Configurations 64

Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00
iii
Resetting the RF/Ethernet Statistics 64
Link Monitor Display .................................................................................66
Viewing Link Monitor Statistics 66
Logout ......................................................................................................67
Logging Out 67
Setting Operating Mode with the MODE Button ......................................68
Using the MODE Button 68
Command Line Interface .........................................................................70
Using Basic Commands 70
Appendix A: Planning Your Wireless Link ......................... 71
Planning the Physical Layout ...................................................................71
Measuring the Physical Distance Between Units 71
Determining ntenna Requirements 71
Determining Cable Requirements 72
Calculating Fade Margins 72
Determining Environmental Requirements 72
Optimizing the RF Link .............................................................................72
Overview 72
Working with System Gain 74
Calculating EIRP (Effective Isotropically Radiated Power) 75
Optimizing ntenna Gain 76
Calculating Propagation Loss 76
Working with the Fresnel Zone 76
Calculating Cable Loss 77
Calculating Path Loss 78
Working with the Fade Margin 78
Link Budget Example ...............................................................................79
ntenna Basics ........................................................................................80
ntenna Parameters 80
Implementation Considerations 81
Selecting ntennas 82
Wi-L N’s ntenna Selection 82
ntenna Installation Factors 82
Minimal Clearance bove Obstructions 84
Installing ntennas 84
Fine-tuning ntennas 85
Co-locating Units 85
Appendix B: Using HyperTerminal .....................................87
Starting HyperTerminal ............................................................................87
Determining the Communications Port ....................................................91
Appendix C: Configuring a Simple Data Network .............93

iv
Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00
Checking the Network daptor Installation ............................................. 93
Configuring the Network .......................................................................... 94
Enabling the Sharing Feature on the Hard Disk Drive ............................ 97
Appendix D: SNMP MIB ....................................................... 99
bout SNMP MIB .................................................................................... 99
Wi-L N Object Identifier Nodes ............................................................ 100
Using Object Identifier Nodes ............................................................... 101
Appendix E: Technical eference Information ................ 111
Front Panel LEDs .................................................................................. 111
Power Connector Pinout ....................................................................... 112
Glossary .............................................................................. 113
Index .................................................................................... 121

Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00
v
Notices
Copyright Notice
Copyright' August 2000 Wi-LAN, Inc.
All rights reserved.
This guide and the application and hardware described herein are furnished under license
and are subject to a confidentiality agreement. The software and hardware can be used
only in accordance with the terms and conditions of this agreement.
No part of this guide may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means
electronic, mechanical, or otherwise, including photocopying and recording without the
express written permission of Wi-LAN, Inc.
While every effort has been made to ensure that the information contained in this guide is
correct, Wi-LAN, Inc. does not warrant the information is free of errors or omissions.
Information contained in this guide is subject to change without notice.
egulatory Notice
The Hopper Plus 120-24 product presented in this guide complies with the following
regulations and/or regulatory bodies:
¥ RSS-210 and/or RSS-139 of Industry Canada
¥ FCC Part 15
¥ CEPT/ERC Recommendations, ETS 300-328,
ETS 300-826, and EN 60950
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
¥ this device may not cause interference, and
¥ this device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause
undesired operation of the device.
This equipment generates, uses, and radiates radio frequency and, if not installed and used
in accordance with this guide, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which
can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to
correct the interference by one or more of the following methods:
¥ reorient or relocate the receiving antenna,
¥ increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
¥ connect equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.

Notices
vi
Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00
¥ consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
¥ selecting and testing different channels, if employing 2.4 GHz equipment.
As the Hopper Plus 120-24 is used on a license-exempt, non-frequency coordinated,
unprotected spectrum allocation, and thus can be subject to random unidentified
interference, applications must not be those of a primary control where a lack of
intercommunication could cause danger to property, process, or person. An alternative
fail-safe should be designed into any system to ensure safe operation or shut down, should
communication be lost for any reason.
Other Notices
¥ Changes or modifications to the equipment not expressly approved by Wi-LAN, Inc.,
could void the user s authority to operate the equipment.
¥ Appropriately shielded remote I/O serial cable with the metal connector shell and
cable shield properly connected to chassis ground shall be used to reduce the radio
frequency interference.
¥ FCC radio frequency exposure limits may be exceeded at distances closer than 23
centimeters from the antenna of this device.
¥ All antenna installation work shall be carried out by a knowledgeable and professional
installer.
¥ Use only a power adapter approved by Wi-LAN.
Contacting Wi-LAN
You can contact Wi-LAN applications engineers to help troubleshoot your Wi-LAN
products and to plan your wireless network applications.
Contacting Customer Support
You can contact Wi-LAN customer support at the locations listed below:
You can also contact the Wi-LAN dealer or representative in your region. Phone or email
Wi-LAN for information about the dealer in your area.
Mailing Address
Wi-LAN, Inc.
Suite 300, 801 Manning Road N.E.
Calgary, Alberta CANADA
T2E 8J5
Tel: +1-403-273-9133
Canada and US Call toll free: 1-800-258-6876
vailable from: 8:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m. (GMT-7:00)
Outside North merica Call: +1-403-273-9133
vailable from: 8:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m. (GMT-7:00)
ll locations Send an e-mail message to:
techsuppor[email protected]

Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00
1
Description
Hopper Plus 120-24 Wireless Ethernet Bridge
The Hopper Plus 120-24 is a wireless Ethernet bridge that provides high-speed, wireless
connectivity at a fraction of the cost of wired solutions. It uses multi-code direct sequence
spread spectrum technology over the license-exempt, 2.4 - 2.4835 GHz ISM radio band.
The maximum data rate is 12.0 Mbps.
The Hopper Plus 120-24:
¥ provides wireless connectivity at speeds up to eight times faster than regular T1 lines,
making the Hopper Plus ideal for providing high-speed Internet access or for wirelessly
extending existing communications infrastructures.
¥ supports point-to-point and point-to-multipoint networks. Contentionless polling ensures
efficient access to remote data networks.
¥ is self-contained and easy to use. Simply connect a Hopper Plus 120-24 to each LAN
segment, and the unit automatically learns where nodes are located on the network and
performs dynamic packet filtering to ensure the local LAN traffic does not overload the
wireless connection.
Making a Wireless Bridge
The simplest example of using the Hopper Plus 120-24 is a point-to-point wireless bridge,
which requires a minimum of two units: a base unit and a remote unit. The units make a
high-speed wireless communication link between two wired network segments.
Point-to-Point Wireless Bridge.
Base
Wired Network
RemoteRouter
Main Wired Network
Router
or
Repeater
Hub
Switch
Firewall
Switch
Hub
Firewall
Wireless Link

Description
2
Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00
Creating a Wireless Network
You can create a wireless network by adding remotes and taking advantage of the point-to-
multipoint capabilities of the Hopper Plus 120-24. Up to 255 remote units can be
contained in a wireless network.
Point-to-Multipoint Wireless Network
About Hopper Plus Units
Base Station:
A Hopper Plus 120-24 can operate as a remote unit or a base station,
however, at least one unit in the network
must
be configured as a base. A base station is
the central control unit of the wireless network. The base station polls all remote units and
controls how traffic is routed to and from remotes. The base usually connects to a major
access point of the wired network. The antenna of the base station must be capable of
transmitting and receiving radio signals to and from all the remote units in a system. If
remotes are spread over a large area, an omni-directional antenna is usually required.
Remote Units:
Remote units link wired segments of the network wirelessly to the main
network (via the base station). Remotes can limit the amount of data passed by the remote
(a function called throttling), and they can filter specific data packets. Because remote
units need to communicate only with the base station, their antennas can be more
directional and have higher gains than base antennas.
Repeaters:
A base unit can also be configured as a repeater. A repeater is needed when
remote units cannot communicate directly with each other, but direct transfers of data
between them are necessary (as in a true WAN). When configured as a repeater, the base
station passes data packets between remote stations based on the remote group status and
the MAC (Media Access Control) address filter. Remote stations ignore the packets they
hear from other remotes, and listen only to the repeated packets from the base. See
Setting
Repeater Mode (Base Station Only)
, page 49 for more information.
Base
RemoteRouter
RemoteRouter
Wired Network
Wired Network
Wired Network
RemoteRouter
Main Wired Network
Router
or
Repeater
Hub
Switch
Hub
Switch
Firewall
Firewall
Switch
Hub
Firewall
Switch
Hub
Firewall

Hardware Description
Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00
3
Hardware Description
Shipping Package Contents
When you receive a Hopper Plus, the shipping package contains the following items:
¥ Hopper Plus 120-24 unit
¥ indoor antenna
¥ power supply cord
¥ AC/DC power adapter
¥ straight-through ethernet cable (RJ45)
¥ crossover ethernet cable (RJ45)
¥ DB9 (M) to DB25 (F) adaptor
¥ RS-232 DB9 serial cable
¥ Installation and Configuration Guide
¥ Warranty Card
If any of the above items are not included in the Hopper Plus 120-24 shipping package,
contact Wi-LAN customer support immediately.
Hopper Plus 120-24 Unit
The Hopper Plus 120-24 has connectors and LEDs on the front and back panels.
Front Panel
LED IndicatorsRS-232 Management Port

Description
4
Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00
The the front panel connector and LEDs are described below. The color of a LED
indicates its status See
Front Panel LEDs
, page 111 for detailed information.
Connectors for power, antenna and wired network are located on the back panel, as well as
a mode button and a link LED.
ear Panel
M N GEMENT
Port
n RS-232, DB9 connector used to communicate with a
PC. Use this port to configure, test and set up the Hopper
Plus.
IR LED Color of LED indicates the status of the wireless link
during transmit, receive, or listen. Normal color: Orange.
MODE LED Color of LED indicates the test status of the unit when
unit is in test mode. Normal color: Off.
WIRE LED Color of LED indicates the status of the wire link during
transmit, receive, transmit and receive, or listen. Normal
color: Green, Red, Orange or Off.
POWER LED Shows the status of the unit’s power. Normal color:
Green.
MODE button
LINK LED
Network
Port
Power Connector
ntenna
(TNC)
Connector

Hardware Description
Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00
5
Items located on the back panel are described below:
NTENN Connector The antenna connector is located at the top left of the rear
panel. It is TNC (Threaded N-type Connector) male or
female. This port should always be connected to an
antenna directly or through a 50 ohm coaxial cable.
POWER Connector 3-pin power connector. See
Power Connector Pinout
, page
112 for detailed pinout illustration.
MODE Button The mode button can be used to set the operating mode of
a unit without a terminal. See
Setting Operating Mode with
the MODE Button
, page 68 for information about the mode
button.
10/100 B SET standard RJ45 female connector. To connect to a PC
Ethernet card, you must use the crossover twisted-pair
cable (provided). To connect to a hub, use a straight-
through twisted-pair cable.
LINK LED The color of the LED indicates the data rate and status of
the twisted-pair connection.
Green = 10 BaseT link, functioning properly.
Orange = 100 BaseT link, functioning properly.
Off = No link.

Description
6
Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00
Hopper Plus 120-24 Specifications
General Specifications
Modulation Method: Multi-Code Direct Sequence Spread
Spectrum
Wireless Data Rate: 12 Mbps
RF Frequency Range: 2.4 - 2.4835 MHz (unlicensed ISM band)
Number of Center Frequencies: 7 independent, 3 concurrent
Power Requirements: 48W @ 12VDC (via 110/240 V C 50/60 Hz
adaptor)
Physical Dimensions: 24 x 8 x 21 centimeters
(9.5 x 3.2 x 8.3 inches)
adio Specifications
ntenna Connector: Reverse TNC
TNC
Output Power: +18.5 dBm
Receiver Sensitivity: – 83 dBm
Processing Gain: >10 dB
Network Support
Packet Format: IEEE 802.3 and Ethernet II
(High-level protocol transparent)
L N Connection: 10/100 BaseT (autonegotiates)
Bridge Functionality: Local Packet Filtering (self-learning), Static IP
address filtering, throttling capability
Wireless Networking Protocols
Network Topologies: Point-to-Point, Point-to-Multipoint,
Multipoint-to-Multipoint
Repeater Mode: User Configurable
RF Collision Management: Dynamic Polling, with Dynamic Time
llocation
Security
Data Scrambling: User Configurable
Data Security Password: Security password of up to 20 bytes in length
(10
48
combinations)
Configuration, Management, and Diagnostics
Configuration Methods: SNMP, Telnet, and RS-232 Management Port

Hopper Plus 120-24 Specifications
Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00
7
SNMP: Version I compliant (RFC 1157), MIB standard
and enterprise (RFC 1213)
Management Port Functionality: Supports system configuration, security,
access control, wireless L N diagnostics and
management, menu-driven SCII interface via
RS-232 DB-9.
Environment
Units must be located in a weatherproof
environment with an ambient temperature
from 0 to 40º Celsius and humidity 0 – 95%
non-condensing.

Description
8
Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00

Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00
9
Installation
Basic Installation Steps
The following basic steps are required to successfully install your Hopper Plus 120-24
wireless bridge. For detailed information about performing the steps, see the references
provided.
1. Plan your network. Before you install any equipment, you need to determine the phys-
ical layout of your wireless link, plan antenna and fade margin requirements, and opti-
mize the wireless link. For help, refer to Appendix A: Planning Your Wireless Lin or
contact Wi-L N customer support. You will require a minimum of two Hopper Plus
units (one configured as a base, and one configured as a remote) to create a wireless
link between two wired network segments.
2. Check the contents of each shipping carton to ensure all the required parts are
present. See Hardware Description, page 3 for a list of parts.
3. Configure one Hopper Plus unit as a base station. See Configuring a Unit as a Base,
page 10. (Units come from the factory configured as remotes).
4. Test the basic operation of the bridge. See Testing Basic Operation, page 11 for more
information.
5. Place the units in their field locations and connect them to antennas, the wired net-
work, and power.
Warning: External antennas must be professionally installed and follow accepted safety,
grounding, electrical, and civil engineering standards.
lways connect an antenna to the NTENN port before you power up a unit or you
can damage a unit.
6. Configure each unit as follows:
l View and set the Unit Identification. See Viewing Unit Identification, page 20
and Setting Unit Identification, page 21.
l Set the Station Rank. See Setting the Station Ran , page 43.
l Set the Center Frequency. See Setting the Center Frequency, page 44.
l Set the Security Passwords. See Setting Security Passwords, page 45.
l Set the cquisition Code. See Setting the Acquisition Code, page 47.
l Set the Remote Unit RF Group. See Setting Remote Unit RF Group, page 52.
l Change the default passwords. See Setting Login Passwords, page 59.
7. Test the installed wireless network using ping, ftp, or file transfers.
If you have problems, contact Wi-L N customer support.

Installation
10 Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00
Configuring a Unit as a Base
Hopper Plus 120-24 units are delivered from the factory configured as remote units. To
make a wireless bridge, you need to configure one unit as a base unit (base station). All
other units in the wireless network can remain configured as remote units (so you do not
need to change the "station type" of remotes). No user software is required to install a unit.
To configure one unit as a base unit
1. Connect a PC to the MANGAGEMENT port to the Hopper Plus unit that will be the
base unit.
Connecting PC to MANAGEMENT Port
2. Start the terminal emulation program (for example, HyperTerm¤—seeAppendix B:
Using HyperTerminal, page 87).
3. Press Enter. Enter the default password (choose supervisor). The Main Menu is
displayed.
AI
MODE
WIE
POWE
PLUS
Hopper Plus Unit
PC
Serial Cable
to PC COM port
Management Port

Testing Basic Operation
Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00 11
4. Select Radio Module Configuration. The Radio Module Configuration
window is displayed.
5. Select Station Type.
6. Select Base Unit and press Enter.
7. Select Reboot New RF configuration and press Enter. The unit reboots.
8. Log in to the unit.
9. Select Save Current Config to Flash and press Enter. The settings are stored in flash
memory.
10. Select Logout from the Main Menu to exit.
Testing Basic Operation
Wi-LAN recommends that you bench test units before placing them the field. You should
first perform a standalone test, then test the bridge as part of a simple network.
Once one unit has been set to a base unit, it can then be used to test all other remote units
without making configuration changes to the remotes.(Units are shipped from factory
configured as remotes).
Performing a Bench Test
To perform a bench test of the bridge
1. Ensure that you have configured a unit as a base unit.
2. Ensure that the station type of all other units is Remote Unit. See Setting the Station
Type, page 42.
Radio Module Configuration
New Current Flash
Station Type -> Remote Unit Remote Unit Remote Unit
Station Rank (1-1000) 1 1 1
Center Frequency 2.4400 GHz 2.4400 GHz 2.4400 GHz
Security Password 1 (Hex) 1 1 1
Security Password 2 (Hex) 10 10 10
Security Password 3 (Hex) 100 100 100
Security Password 4 (Hex) 1000 1000 1000
Security Password 5 (Hex) 10000 10000 10000
Scrambling Code (Hex) 0 0 0
Acquisition Code (0-15) 1 1 1
Config Test Minutes (1-120) 30 30 30
Base Station Only Parameters
Repeater Mode off off off
System Symmetry Type Asymmetric Asymmetric Asymmetric
Dynamic Polling Level (1-100)
Remote Station Only Parameters
Remote Unit RF Group (0-63) 0 0 0
Reboot New RF configuration Press Enter to Execute
Save Current Config to Flash Press Enter to Execute

Installation
12 Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00
3. Locate base unit and one remote unit at least twenty meters apart with a clear line of
sight between them.
4. Attach the provided indoor antenna to the antenna port of each unit, and orient the
antenna vertically.
5. Power up both units.
Basic Test Setup
6. Observe the AIR LED of each unit and look for normal status. A normal status is
indicated when the AIR LEDs on the base and the remote unit are both orange. The
status of the AIR LED is indicated as follows.
Note: If antennas are too close together, the strong transmit signal will cause distortion at
the receiveing unit. You can fine-tune antennas by physically moving the antenna. When
the remote antenna is correctly aligned, the AIR LED is orange, indicating that data from
the base station is being received and acknowledged.
7. Run the Link Monitor test on the remote unit. See Setting Link Monitor Remote Station
Rank (Base Station Only), page 38.Check for RSSI below 40% and BER = 0. If you
have problems ensure that the unit is configured to its basic default settings or contact
Wi-LAN customer support.
8. Disable Link Monitor.
9. When both AIR LEDs are orange, power down both units and perform the simple
network test. See Performing a Simple Network Test, page 13.
Orange (both stations) The stations are continuously sending and receiving
sync packets.
Red (base station) The stations are configured incorrectly, and the base
station is transmitting without receiving
acknowledgment.
Green (remote station) The stations are configured incorrectly, and the remote
station is receiving packets to which it cannot respond.
Off Nothing is being received (by the remote) or transmitted
(from the base).
AI
MODE
WI E
POWE
PLUS
20m
minimum
IR LED = orange
Base Unit Remote Unit
AI
MODE
WI E
POWE
PLUS
IR LED = orange
Indoor
ntenna
Indoor
ntenna

Testing Basic Operation
Version 1.0 Rev B - 08/00 13
Performing a Simple Network Test
To perform a simple network test
1. Connect one Hopper Plus 120-24 to the LAN.
2. Connect a PC from your network directly to the other Hopper Plus 120-24 (connect
with a 10/100 BaseT crossover cable if no hub is used).
Note: Cabling between 10/100 BaseT nodes is generally done through a net-
work hub. To make a direct 10/100 BaseT connection between a Hopper Plus
120-24 and a PC, you need a standard crossover cable (swap pins 1&3; 2&6).
Simple Network Test Setup
3. Power up each Hopper Plus 120-24 unit. Initially the LEDs should appear as follows:
4. Create some network traffic to test the bridge (for example, transfer a file across the
bridge). The WIRE LED indicates the activity. See Appendix C: Configuring a Simple
Data Network, page 93 for more information.
5. Repeat the steps for each remote you install.
6. To test network configuration further, see Appendix C: Configuring a Simple Data
Network, page 93 for moreinformation about configuring simple peer-to-peer
networks.
POWER LED Green
MODE LED Off
IR LED Orange
IR LED = orange
Base Unit Remote Unit
MODE LED = Off
POWER LED = Green
IR LED = orange
MODE LED = Off
POWER LED = Green
PC
L N
10/100 BaseT HUB
10 BaseT Cable
Direct 10 BaseT Cable (Crossover)
AI
MODE
WI E
POWE
PLUS
AI
MODE
WI E
POWE
PLUS
20m
minimum
Indoor
ntenna
Cables connect to
10 BaseT network port
(Straight
Through)
Cable
10 BaseT
Table of contents
Other Wi-LAN Network Router manuals