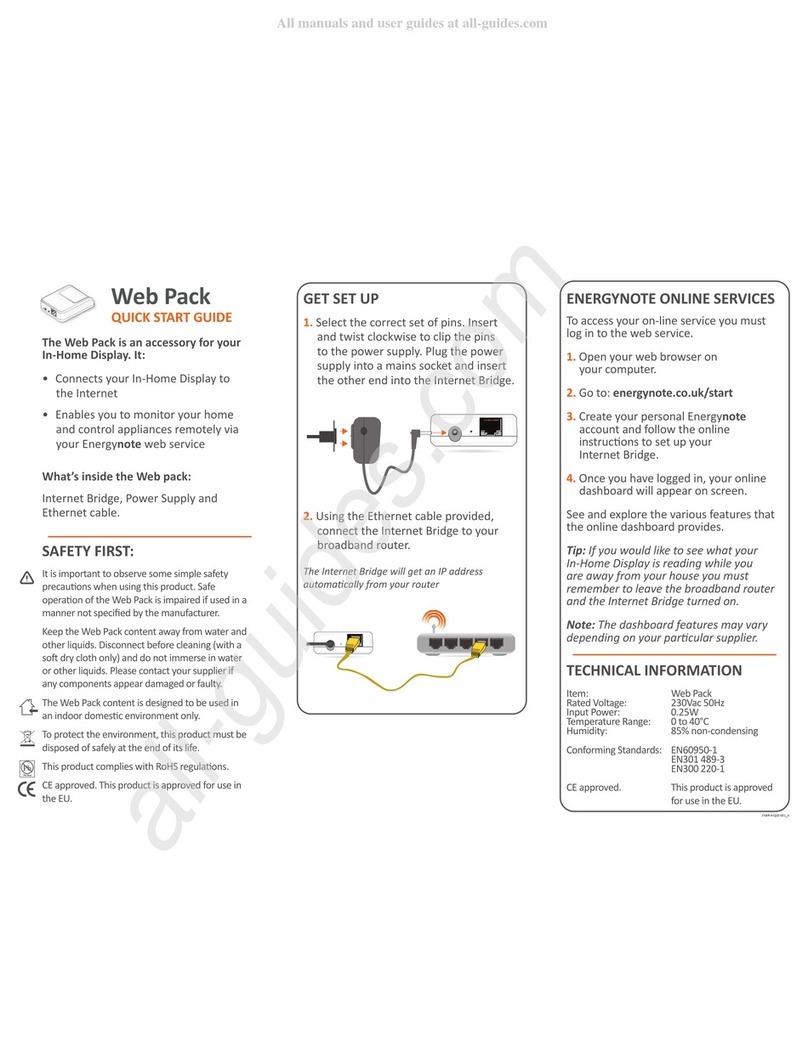
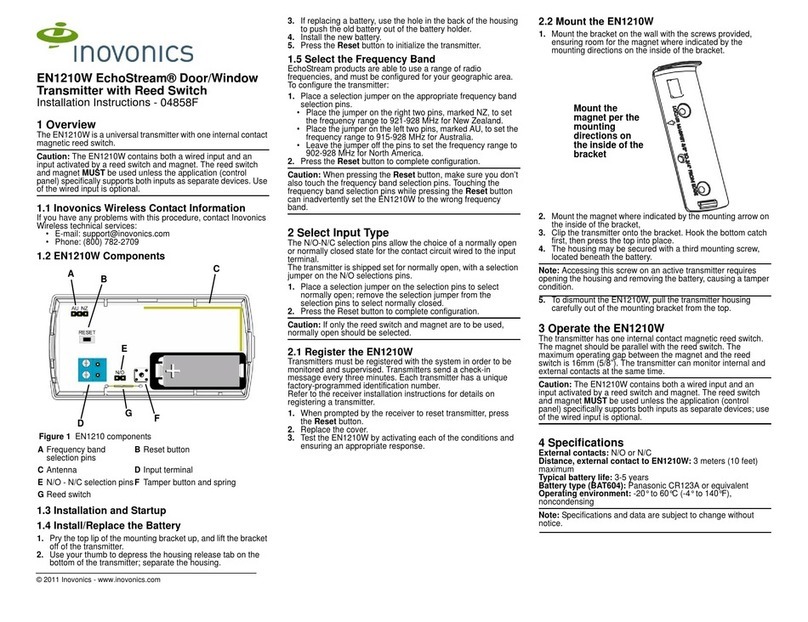
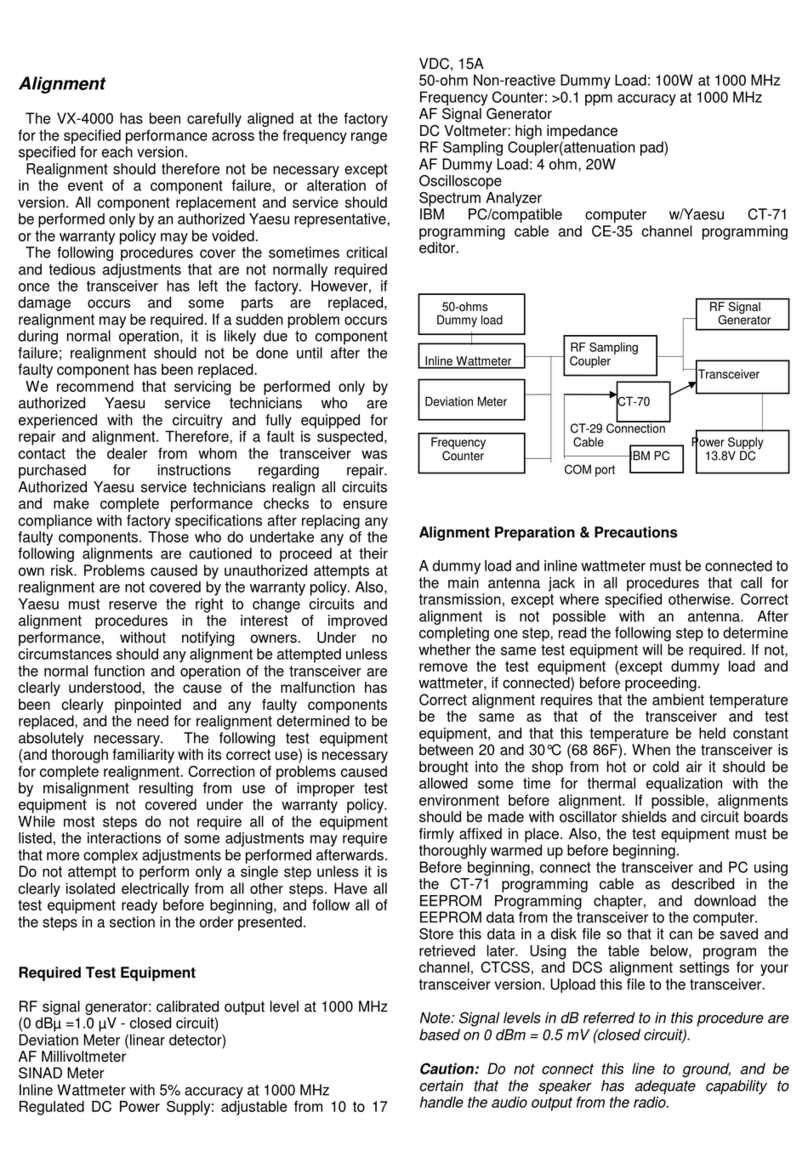
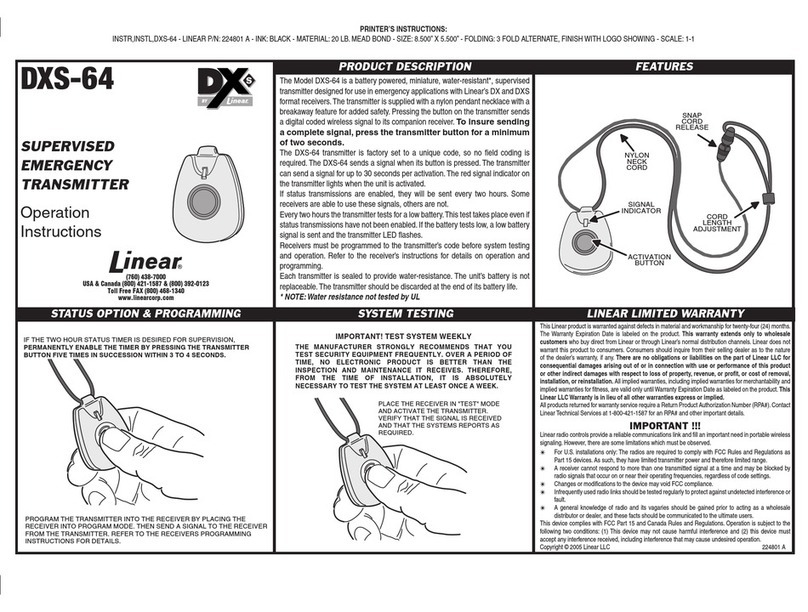
The transmitter
is
now tuned for maximum out-
put.
Return
the CARRIER control arm fully
CCW
(counter-clockwise) to zero position.
NOTE: Depressing the MOX switch in the above
procedures may be eliminated by simply
operating the microphone PTT switch
when the microphone
is
attached to the
transmitter.
SSB
OPERATION
After completion
of
the final tuning described
above, set the MODE switch to a
desir~d
sideband
LSB
or
USB
position. Set the METER switch to
the ALC position. Be certain
that
the
CARRIER
control
is
fully
CCW
to
the zero position. Depress
the MOX switch
to
activate the transmitter and
advance the
MIC
GAIN control until the
meter
kicks down to mid scale in the green colored
portion marked ALC; when speaking normally
into
the microphone.
The
transmitter returns to
receive condition by depressing the PTT switch
down.
For
PTT (push-to-talk) operation, depress
the PTT switch down, and depress the PTT switch
on the microphone whi)e speaking
into
the micro-
phone.
Depress the VOX switch down.
For
VOX (voice
operated relay) operation, adjust the VOX GAIN
control until your voice actuates the transmitter.
Set the ANTI TRIP control
to
a minimum
point
to prevent the speaker
output
from tripping the
transmitter. Do
not
use the VOX GAIN and
ANTI TRIP GAIN controls more than necessary.
Adjust the DELAY control for suitable release
time.
NOTE: When the METER
is
set to the IC
position, voice modulation peaks will
indicate 150 -200 mA. Actual peak
current, however,
is
approximately two
times
that
of
the indicated value.
An
optional
RF
processor (PB-1550) can be
installed
to
increase talk power.
The
following
is
an operating procedure for the FL-101 with the
optional
RF
processor built in.
(
1)
Set the RF processor switch
to
OFF
position
and a
meter
switch ALC position. Tune up
the transmitter on the frequency in use.
Speaking
into
the microphone normally and
the ALC meter indication stays in green
portion
of
the scale on voice peaks.
(2) Set
the
RF
processor switch ON and set the
LEVEL control
to
the level where the ALC
indication does
not
exceed green portion
of
the scale on
the
voice peaks.
(3) The
MIC
GAIN control may be increased
about
two steps more than the position set
at Step
1.
However, excessive setting
of
the
MIC
GAIN may decrease the S/N ratio
of
the
transmitted signal.
CW
OPERATION
Upon completion
of
the final tuning, insert a key
plug in the jack marked KEY on the rear panel
of
the transmitter. Set the MODE switch to the
CW
position. Power
output
from
the
transmitter
is
determined by the CARRIER control arm position.
The operator may select any power
output
desired
by simply setting the CARRIER control within
the limit
of
its range.
CAUTION
CARE MUST
BE
TAKEN
TO
AVOID
AN EX-
CESSIVE
DRIVE
TO
PREVENT SPURIOUS
RADIATION
AND
DESTRUCTION OF
FINAL
TUBES.
MAXIMUM
KEY DOWN
CURRENT
SHOULD
BE
KEPT
WITHIN
350MA FOR
THE
BANDS UNDER 15 METERS
AND
280MA FOR
10 METERS BAND. KEEP
THE
KEY
DOWN
CURRENT
WITHIN
THE
ABOVE LIMITS.
The transmitter may be operated manually
or
break-in by setting the MOX-PTT-VOX switch
to
either MOX (manual)
or
VOX (break-in) for the
desired mode
of
operation.
To
release from manual
transmission, depress the PTT switch down.
AM
&
FSK
OPERATION
AM
operation
of
the transmitter
is
accomplished
by setting the MODE switch to
AM
position and
inserting the proper
amount
of
carrier with the
CARRIER control.
After completion
of
the basic transmitter tune-up,
set the CARRIER control to the point where the
IC
indication shows .15
(l
50mA). While speaking
into the microphone normally, increase-the
MIC