3
I、Outline
Zhejiang Ailipu Technology Co., Ltd. mainly researches, develops, produces and sells plunger metering pumps,
mechanical diaphragm metering pumps, hydraulic diaphragm metering pumps and other special pumps. The
technical parameters, testing rules, and others of our metering pumps are in strict accordance with GB7782-2008
Metering Pump andAPI std 675-2014 Positive Displacement Pumps-Controlled Volume.
Two flow regulation modes are available for metering pumps: 1. To change the stroke of the plunger (optimal
stroke: 30-100%) of the pumps during shutdown or operation, in which the measurement accuracy is controlled
within ±1%. Therefore, the measuring pump can be used as a measuring instrument (for manual regulation, the
relative stroke of the pumps is indicated by a stroke scale and micrometer; for automatic control, remote control
and computer based flow control, see also the regulation instructions); 2. To regulate the pump speed by
changing the power frequency through frequency conversion for remote control and computer-based
management on flow regulation.
Our metering pumps are used to pump liquids with a temperature of -30~250℃, a viscosity of 0.3~2,000mm2/s
and solid particle size not more than 0.1 ㎜. Regular hydraulic metering pump are used in the temperature of
-15~120℃and a viscosity of 0.3~50mm2/s. (if exceed this range, please advice AILIPU company). Hydraulic
metering pump has the characteristics of non-leakage, which can transport flammable 、combustible 、
crystallizable、
volatile、
radioactive、
toxic、
suspension and expensive liquid. Especially for diaphragm metering
pump which contains alarm device, able to send an alarm within 2 seconds in case of diaphragm rupture, thus
guaranteeing the safety of operators and specific operation.
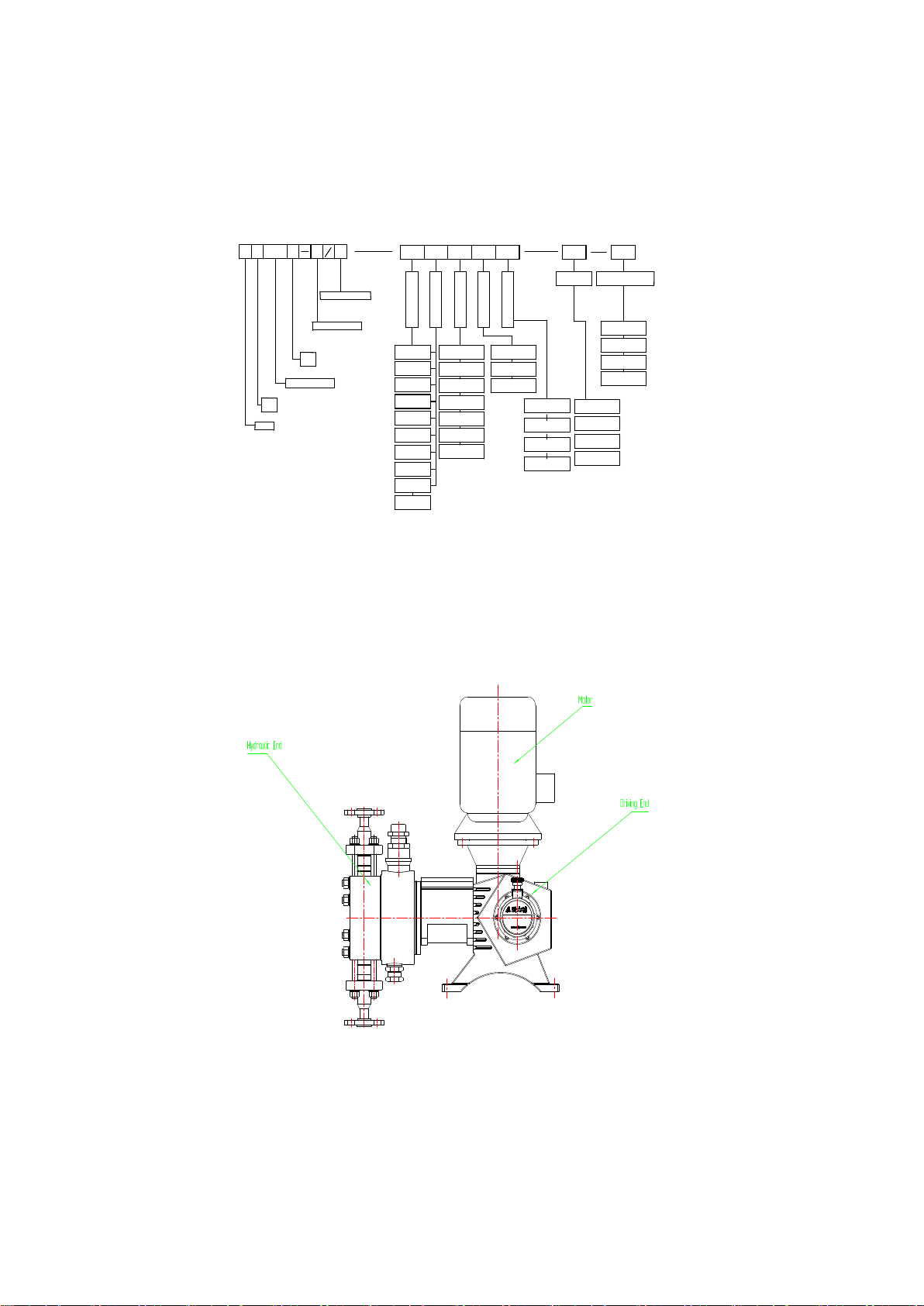
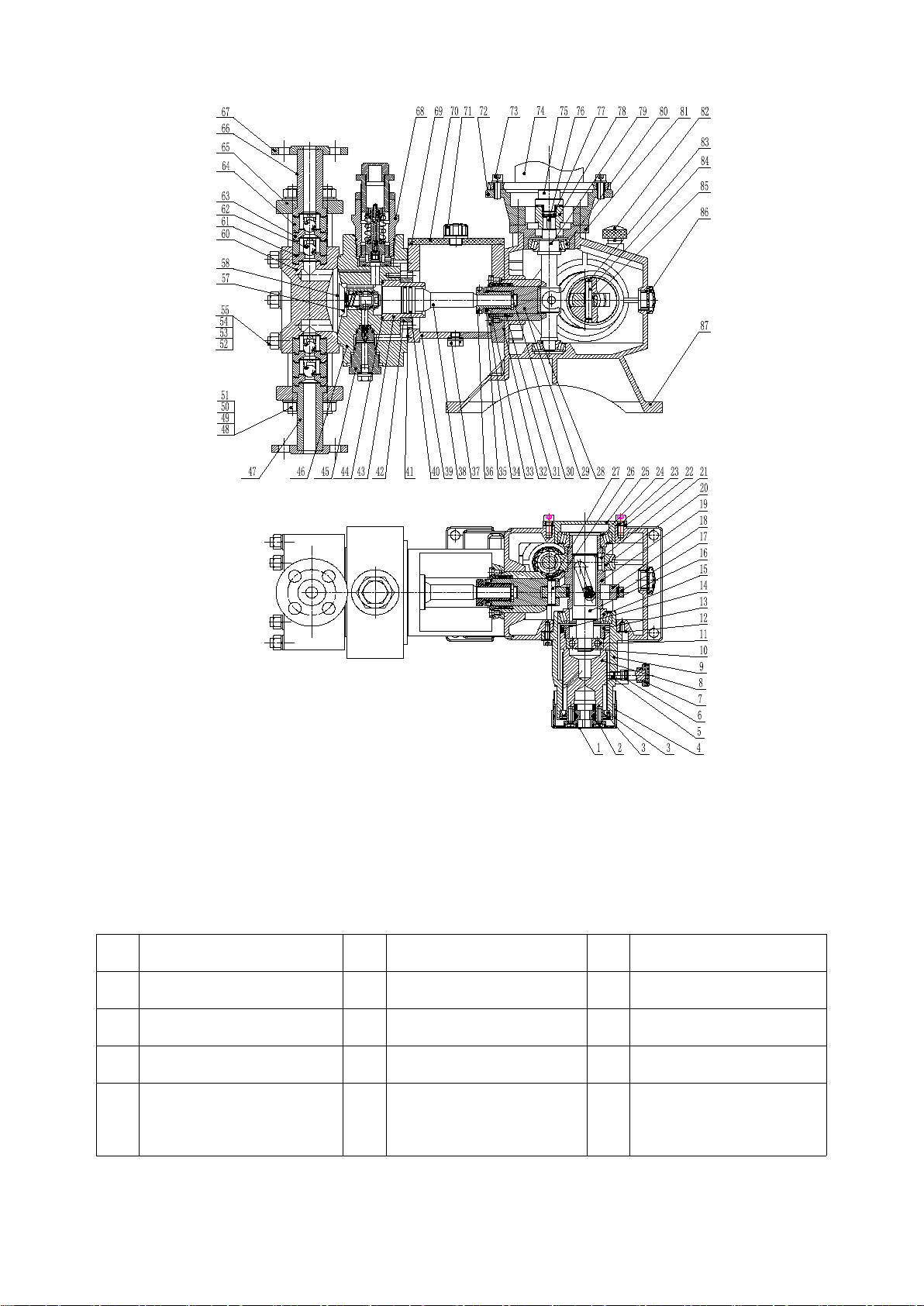
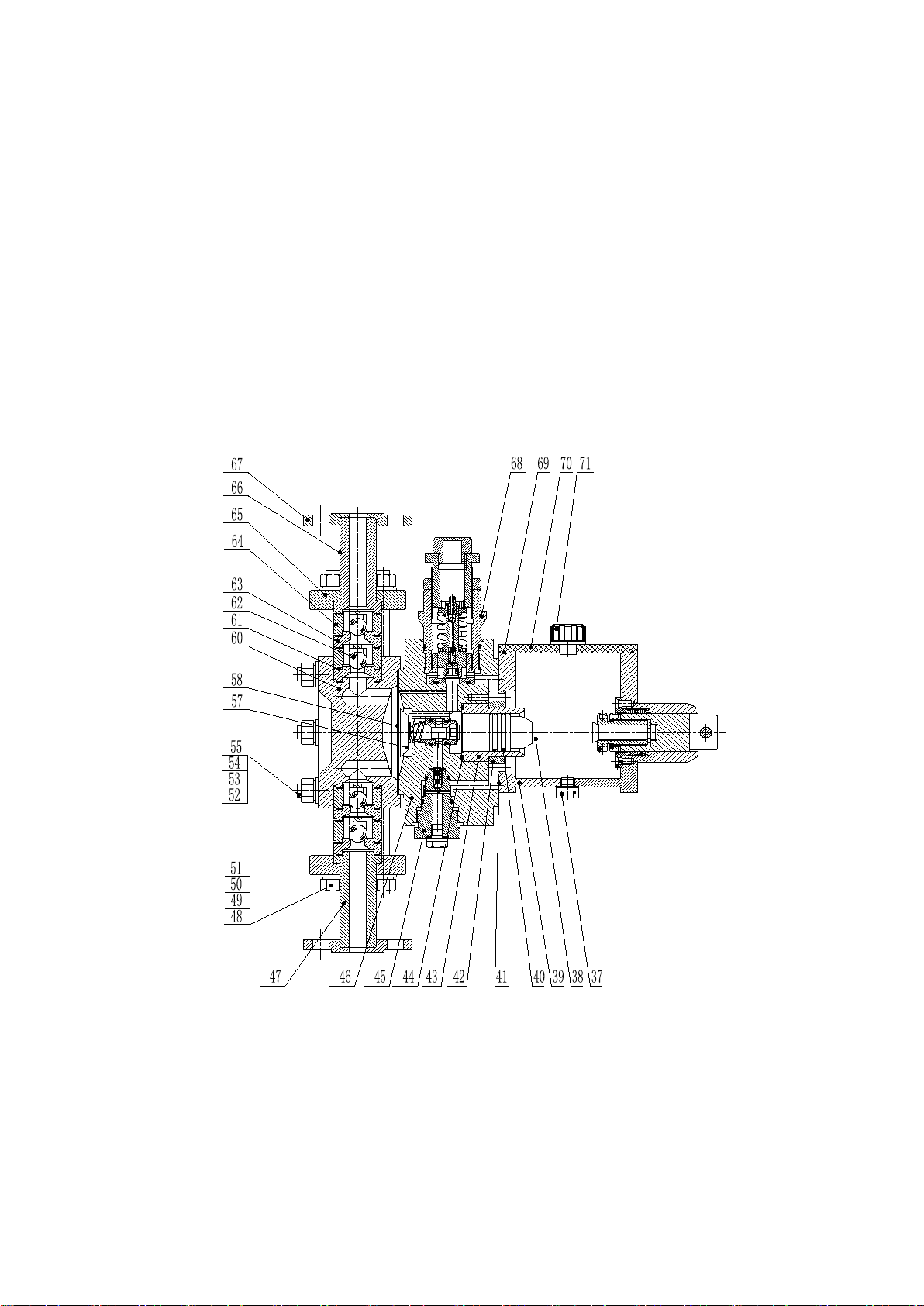
The Instructions are only applicable to JYM1.6 Hydraulic diaphragm metering pumps.