6
2 Attach top motor to arm
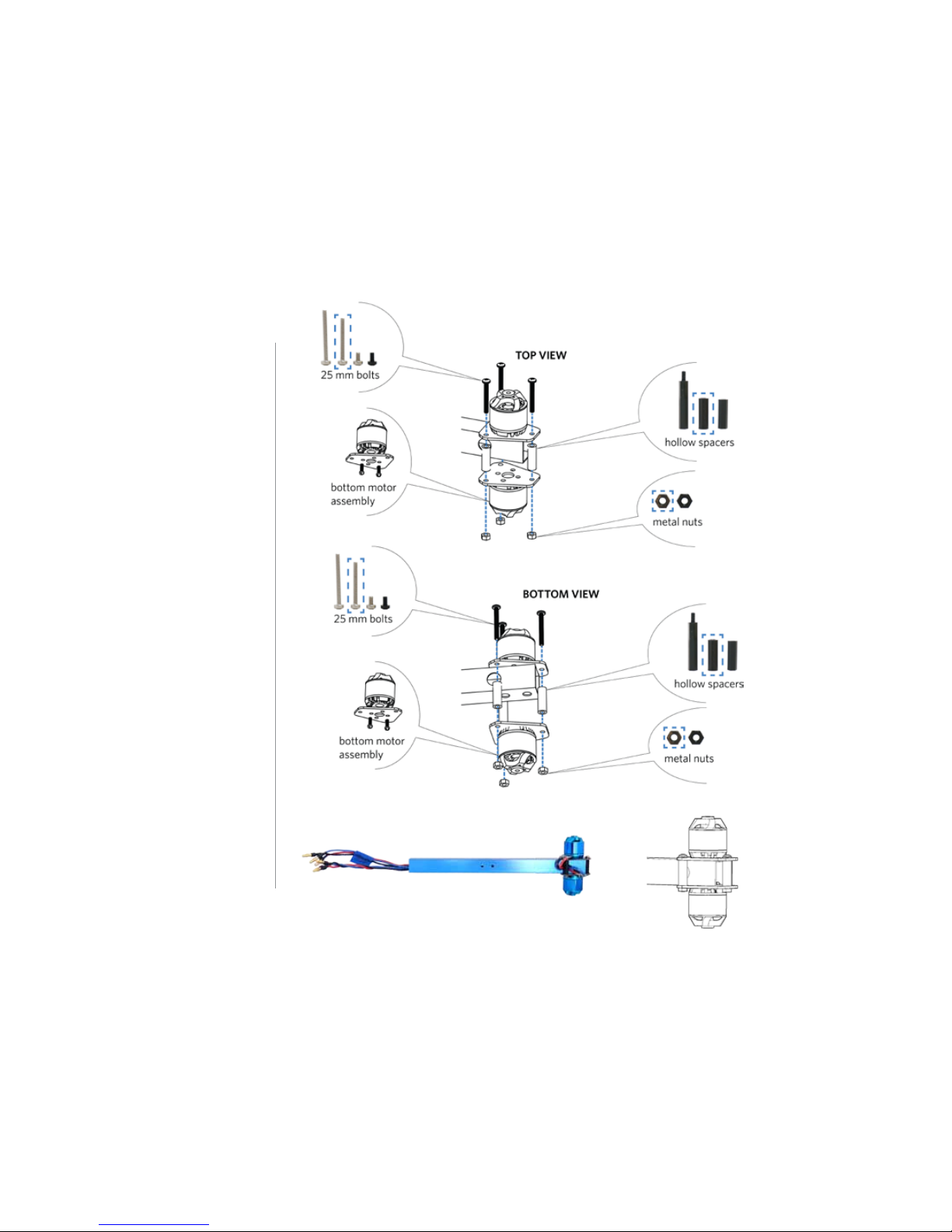
Place a motor plate on top of the arm
with the short end of the plate facing
towards the end of the arm. Place the
motor on top of the plate, and align
the two small holes in the motor,
plate, and arm. Orient the motor with
the cables as close as possible to the
hole in the side of the arm.
Apply threadlocker to two 5 mm
bolts (less than one drop covering
four or five threads at the end of the
bolt), and secure the motor and
plate to the arm from below by
accessing through the two large holes
in the bottom of the arm. Make sure
to insert the bolts into the holes in
the bottom of the motor and not into
the slots where they could interfere
with the motor.
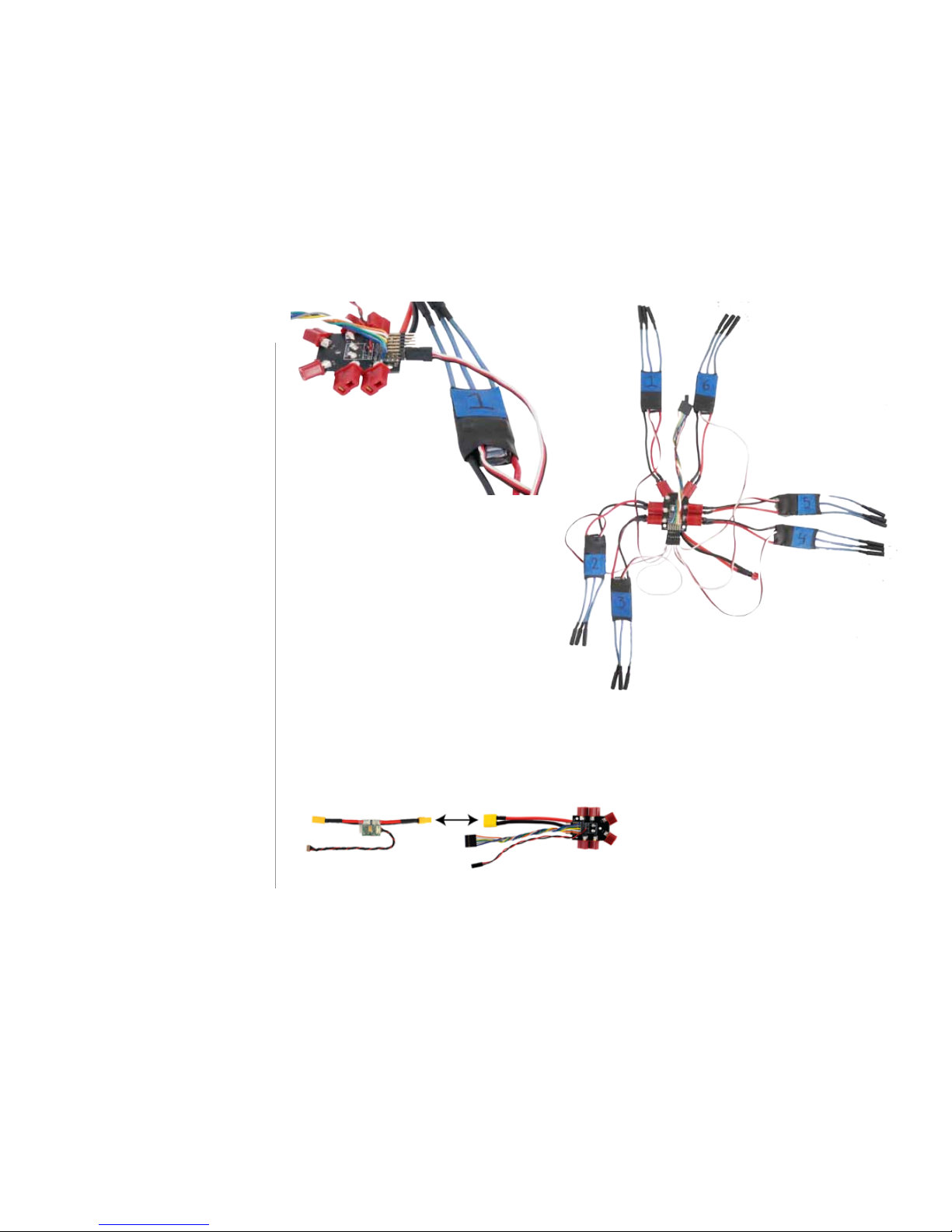
3 Thread motor cables through arm
Now you’ll thread the cables from
both motors through the arm. First,
thread the cables from the top motor
through the hole in the side of the
arm, and use a piece of tape to label
the cables so that you can distinguish
between the top and bottom
motor cables. Once you’ve labelled
the top motor cables, thread the
bottom motor cables through the
hole in the arm.