Introduction of BP6 Features 1-1
User’s Manual
Chapter 1 Introduction of BP6 Features
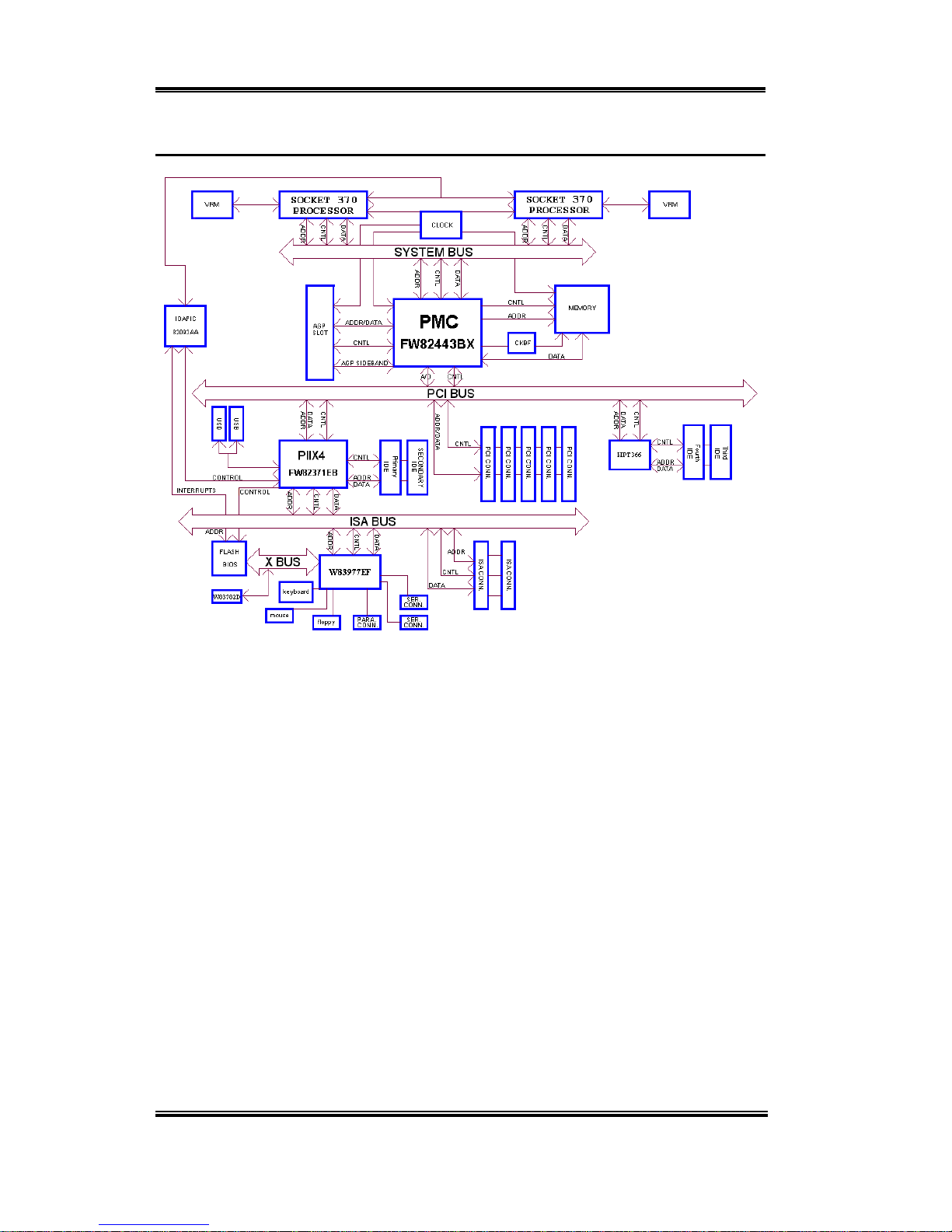
1-1.Features of this Motherboard
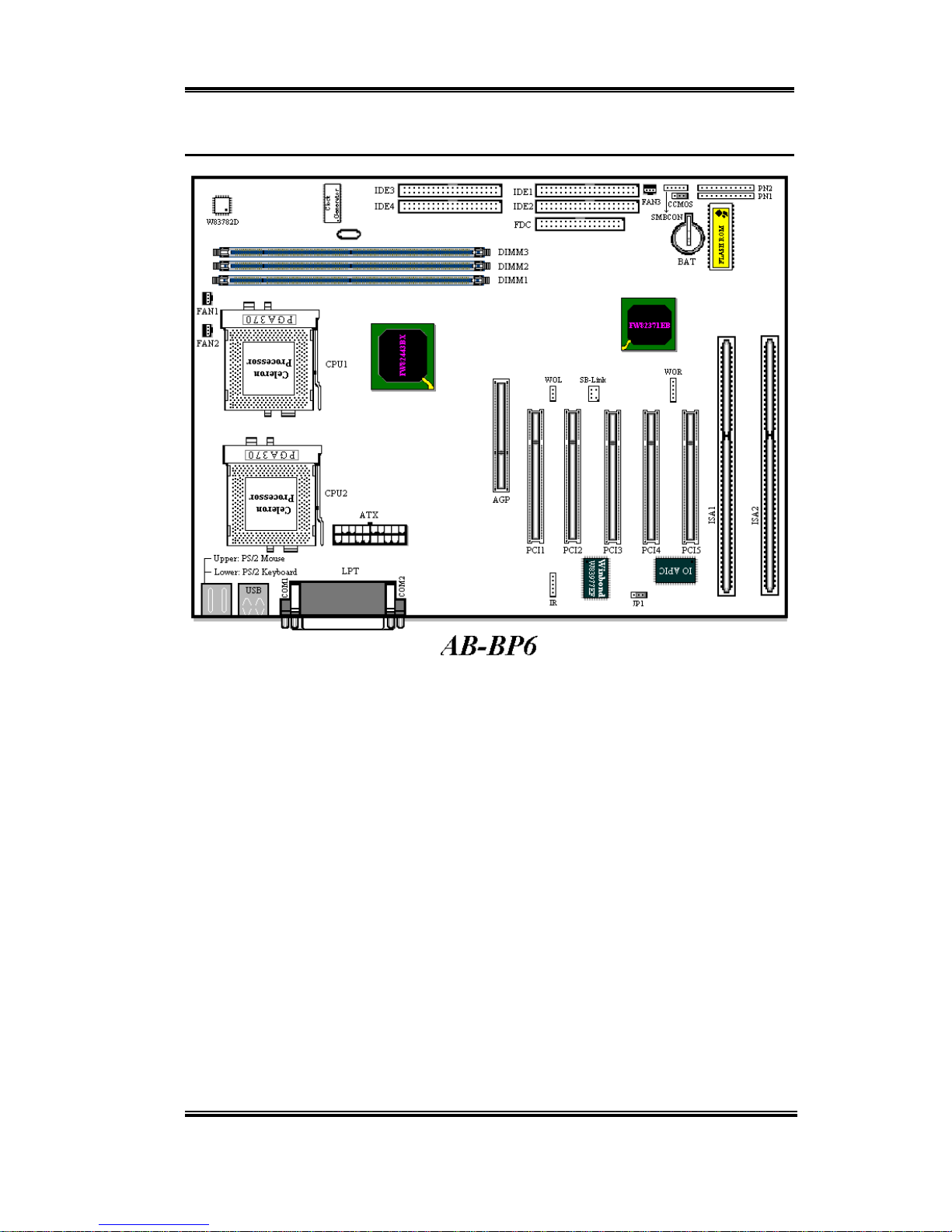
This motherboard is a specialdesign forSocket 370 CPUs. It is equipped withtwo PGA 370
sockets with which you can install two Socket 370 processors.
The BP6 has the HPT366 Ultra ATA/66 Chipset built-in. This means, the BP6 will support
Ultra ATA/66 IDE devices. Ultra ATA/66 is the new standard for IDE devices. It enhances
existing Ultra ATA/33 technology by increasing both performance and data integrity. This
new high-speed interface doubles the Ultra ATA/33 burst data transfer rate to 66.6
Mbytes/sec. The result is the maximum disc performance using the current PCI local bus
environment. Another benefit is, you can connect another four IDE devices in your system
either Ultra ATA/33 IDE devices or Ultra ATA/66 IDE devices. You will have more
flexibility to expand your computer system.
The BP6 has built-in hardware monitoring functions (you can refer to Appendix C for
detailed information), they can monitor and protect your computer insuring a safe
computing environment. The BP6 also supports both the PS/2 keyboard and PS/2 mouse
wake up features (you can refer to section 3-8 for detailed information), letting you easily
wake up your system by these devices. The motherboard can provide high performance for
workstations and meets the requirements for desktop systems for multimedia in the future.
Sets You Free From the Y2K Threat
The potential threat of Year 2000 (Y2K) problems are making everyone very nervous. The
Y2K issue applies to almost any device, firmware, or software that operates on or with year
based dates. This problem is caused by a design flaw in the Real Time Clock (RTC) unit.
The RTC only changes the last two digits of the year code, but not the century information.
As a result, when it comes to 12:00 AM January 1, 2000 the RTC will switch from
December 31 11:59 PM 1999 to 12:00 AM January 1 1900.
Y2K compliance deals with the date change over from 31 December 1999 to 1 January 2000,
and with recording and reporting of all dates from the RTC including leap year dates. This
motherboard is free from the Y2K problem because its BIOS are Y2K compliant.