AETA Scoopy+ S User manual

Mono/stereo portable audio codec for real time
transmission over ISDN / POTS / MOBILE / IP
User Manual


SCOOPY+ S - User Manual
Table of contents
1. Presentation –Getting started...............................................................................1
1.1. Install and connect SCOOPY+ S.............................................................................................................3
1.2. Audio settings.....................................................................................................................................3
1.3. Select and set up network to be used: wired networks.....................................................................3
1.3.1. Set up an ISDN link ..................................................................................................................... 3
1.3.2. Set up a (wired) IP link................................................................................................................ 4
1.3.3. Set up a POTS link....................................................................................................................... 4
1.4. Select and set up network to be used: mobile networks...................................................................5
1.4.1. Set up a link in voice mode......................................................................................................... 5
1.4.2. Set up a (mobile) IP link.............................................................................................................. 6
2. Functions.................................................................................................................7
2.1. Transmission interfaces......................................................................................................................8
2.1.1. Ethernet/IP interface.................................................................................................................. 8
2.1.2. ISDN interface........................................................................................................................... 11
2.1.3. POTS interface .......................................................................................................................... 12
2.1.4. Mobile network access............................................................................................................. 13
2.1.5. Managing calls.......................................................................................................................... 14
2.2. Audio encoding and decoding..........................................................................................................15
2.2.1. G711 coding.............................................................................................................................. 16
2.2.2. Mobile telephony coding: GSM , AMR ..................................................................................... 16
2.2.3. Mobile HD Voice coding: AMR-WB .......................................................................................... 16
2.2.4. CELP coding .............................................................................................................................. 16
2.2.5. G722 coding.............................................................................................................................. 17
2.2.6. TDAC coding ............................................................................................................................. 17
2.2.7. 4SB ADPCM coding................................................................................................................... 17
2.2.8. MPEG Audio Layer 2 coding ..................................................................................................... 18
2.2.9. MPEG AAC algorithms .............................................................................................................. 18
2.2.10. OPUS coding ........................................................................................................................... 19
2.2.11. Linear coding .......................................................................................................................... 19
2.3. Audio interfaces and functions ........................................................................................................20
2.3.1. Mic/Line inputs......................................................................................................................... 20
2.3.2. Line outputs.............................................................................................................................. 21
2.3.3. Headphone outputs: monitoring.............................................................................................. 21
2.3.4. USB interface (device) .............................................................................................................. 21
2.3.5. Recording/Playing audio files................................................................................................... 22
2.3.6. Mixing and routing ................................................................................................................... 22
2.3.7. Audio level monitoring ............................................................................................................. 26
2.4. Auxiliary transmission functions ......................................................................................................27
2.5. Supervision and control interface ....................................................................................................28
2.5.1. "Local" control.......................................................................................................................... 28
2.5.2. Embedded html server: "web pages"....................................................................................... 28
2.5.3. Remote control interfaces........................................................................................................ 28
2.5.4. Remote access.......................................................................................................................... 29
2.5.5. GPIO.......................................................................................................................................... 31

SCOOPY+S - User Manual
2.5.6. Configuration and dialling memories ....................................................................................... 32
2.5.7. Test functions ........................................................................................................................... 32
3. Operation ...............................................................................................................33
3.1. General principles –Control means ................................................................................................ 33
3.2. Physical description of the equipment............................................................................................ 34
3.2.1. Front panel ............................................................................................................................... 34
3.2.2. Rear panel: transmission interfaces ......................................................................................... 38
3.2.3. Left side: inputs 1 and 3............................................................................................................ 40
3.2.4. Right side: input 2 and line outputs ......................................................................................... 40
3.2.5. Battery compartment............................................................................................................... 40
3.3. Putting in service ............................................................................................................................. 41
3.4. Initial setup of the Ethernet interface............................................................................................. 42
3.4.1. DHCP server available............................................................................................................... 42
3.4.2. "Static" IP configuration ........................................................................................................... 42
3.4.3. Checking the IP configuration................................................................................................... 43
3.4.4. Optional configuration of the "link" Ethernet layer ................................................................. 43
3.4.5. Configuration of the secondary Ethernet interface ................................................................. 43
3.5. Managing links................................................................................................................................. 44
3.5.1. Setting up and releasing links................................................................................................... 44
3.5.2. Auto-redial feature................................................................................................................... 44
3.5.3. GPIO control ............................................................................................................................. 44
3.6. First level maintenance ................................................................................................................... 45
3.6.1. Using the test loops .................................................................................................................. 45
3.6.2. Clearing / Saving / Restoring settings....................................................................................... 45
3.6.3. Backup reset ............................................................................................................................. 46
3.6.4. Firmware updating ................................................................................................................... 46
4. Detailed operating mode –User interface...........................................................47
4.1. Equipment start-up ......................................................................................................................... 47
4.2. Principles for the navigation............................................................................................................ 47
4.3. Dialing and text input keypad.......................................................................................................... 49
4.4. Description of the menus ................................................................................................................ 50
4.4.1. Network sub-menu.................................................................................................................. 51
4.4.2. Algorithm sub-menu................................................................................................................ 61
4.4.3. Audio sub-menu....................................................................................................................... 62
4.4.4. Coordination sub-menu .......................................................................................................... 63
4.4.5. Directory menu ........................................................................................................... 64
4.4.6. About sub-menu....................................................................................................................... 66
4.4.7. Misc sub-menu ......................................................................................................................... 67
4.4.8. Maintenance sub-menu........................................................................................................... 69
4.5. Setting up a link ............................................................................................................................... 70
4.5.1. Basic options............................................................................................................................. 70
4.5.2. Preparing the network interface(s) .......................................................................................... 71
4.5.3. Setting the coding configuration .............................................................................................. 75
4.5.4. Launching calls (outgoing) ........................................................................................................ 76
4.5.5. Receiving calls........................................................................................................................... 78
4.6. Management of the configuration profiles..................................................................................... 80
4.7. Recording function .......................................................................................................................... 81

SCOOPY+ S - User Manual
4.7.1. Recording.................................................................................................................................. 81
4.7.2. Playing back.............................................................................................................................. 82
4.7.3. Simple editing........................................................................................................................... 83
4.7.4. Management of recordings...................................................................................................... 84
4.8. Restricted operation mode ..............................................................................................................85
4.8.1. Principles .................................................................................................................................. 85
4.8.2. Locking the front panel ............................................................................................................ 85
4.8.3. Unlocking the front panel......................................................................................................... 85
4.8.4. Lost the password?................................................................................................................... 86
4.9. Clearing all settings ..........................................................................................................................86
4.10. Backing up and restoring the configuration...................................................................................86
4.11. Specific display screens ..................................................................................................................87
4.11.1. Display statistics about the IP transmission ........................................................................... 87
4.11.2. Case of the Opus algorithm: bit rate change "on the fly" ...................................................... 88
4.11.3. Display the state of the transmitted INFO 1 and INFO 2........................................................ 88
4.11.4. Displaying received SMS......................................................................................................... 88
5. Operating mode –Embedded HTML pages........................................................89
5.1. Accessing the SCOOPY+ S html pages ................................................................................................89
5.2. Principles of operation with html pages ..........................................................................................90
5.3. "STATUS" tab......................................................................................................................................91
5.4. "CONNECTIONS" tab ............................................................................................................................92
5.5. "PROFILES" tab....................................................................................................................................93
5.5.1. "CALL PROFILES" page .................................................................................................................. 93
5.5.2. "PRESETS" page .......................................................................................................................... 93
5.5.3. Snapshots ................................................................................................................................. 93
5.6. "NETWORK" tab ..................................................................................................................................94
5.6.1. "CHANGE NETWORK" page: default interface selection............................................................... 94
5.6.2. "ETHERNET PARAMETERS" page..................................................................................................... 94
5.6.3. "AOIP PARAMETERS" page ........................................................................................................... 95
5.6.4. "ISDN PARAMETERS" page........................................................................................................... 95
5.6.5. "POTS PARAMETERS" page .......................................................................................................... 96
5.6.6. "MOBILE PARAMETERS" page........................................................................................................ 96
5.7. "AUDIO" tab .......................................................................................................................................97
5.8. "CODING" tab .....................................................................................................................................98
5.9. "MISC" tab.........................................................................................................................................99
5.10. "MAINTENANCE" tab........................................................................................................................100
5.10.1. "LOGIN DATA" page ................................................................................................................. 100
5.10.2. "TESTS" page.......................................................................................................................... 100
5.10.3. "SYSTEM UPDATE" page ........................................................................................................... 100
5.10.4. "RESET" page ......................................................................................................................... 101
5.10.5. "EVENT LOG" page................................................................................................................... 102
5.10.6. "SETUP TRANSFER" page .......................................................................................................... 103
5.10.7. "REMOTE ACCESS" page ........................................................................................................... 104
5.11. "ALARM" tab ..................................................................................................................................105
6. How to use the remote access service .............................................................106
6.1. Using the remote assistance ..........................................................................................................106
6.1.1. Step 1: connect the SCOOPY+ S to the server.......................................................................... 106

SCOOPY+S - User Manual
6.1.2. Step 2: open the remote session............................................................................................ 106
6.2. Using the remote html access ....................................................................................................... 107
6.2.1. Step 1: connect the SCOOPY+ S to the server .......................................................................... 107
6.2.2. Step 2: open the remote session............................................................................................ 107
6.3. Security aspects............................................................................................................................. 109
6.3.1. Protection measures............................................................................................................... 109
6.3.2. Tips for firewalls ..................................................................................................................... 109
7. Technical characteristics ...................................................................................110
7.1. Characteristics of the audio interfaces.......................................................................................... 110
7.1.1. Mic/line inputs........................................................................................................................ 110
7.1.2. Line outputs............................................................................................................................ 110
7.1.3. Headphone outputs................................................................................................................ 110
7.1.4. Audio performance................................................................................................................. 111
7.2. Characteristics of network interfaces............................................................................................ 112
7.2.1. Ethernet Interface .................................................................................................................. 112
7.2.2. ISDN interfaces ....................................................................................................................... 112
7.2.3. POTS/PSTN interface .............................................................................................................. 112
7.2.4. Antenna socket (mobile networks) ........................................................................................ 112
7.2.5. Network protocols and ports ................................................................................................. 113
7.3. Miscellaneous interfaces............................................................................................................... 114
7.3.1. GPIO ("EXTENSION" socket) ................................................................................................... 114
7.4. Power supply ................................................................................................................................. 115
7.4.1. DC power supply..................................................................................................................... 115
7.4.2. Batteries ................................................................................................................................. 115
7.5. Dimensions and weight ................................................................................................................. 115
7.6. Environmental characteristics....................................................................................................... 116
7.7. Options .......................................................................................................................................... 116
7.7.1. Network options..................................................................................................................... 116
7.7.2. Other options.......................................................................................................................... 116
7.8. Accessories and related products.................................................................................................. 117
8. Annexes ...............................................................................................................118
8.1. Additional information on the algorithms and protocols used..................................................... 118
8.1.1. Auxiliary data in the MPEG frames......................................................................................... 118
8.1.2. Reed-Solomon encoding (ISDN only)...................................................................................... 118
8.1.3. H221 framing .......................................................................................................................... 118
8.2. Overview of the SIP protocol......................................................................................................... 119
8.2.1. What is SIP? ............................................................................................................................ 119
8.2.2. Setting a link with SIP ............................................................................................................. 119
8.2.3. Setting a link without a SIP server .......................................................................................... 120
8.3. Some methods to deal with NAT routers and firewalls ................................................................ 121
8.3.1. Links via a private network..................................................................................................... 121
8.3.2. Links through a public network (Internet).............................................................................. 121
8.3.3. Summary and reminder of essential rules.............................................................................. 125
8.4. Notice regarding open source code .............................................................................................. 126
9. Index.....................................................................................................................127

SCOOPY+ S - User Manual
1
1. Presentation –Getting started
The SCOOPY+ S codec allows the bidirectional transmission of one or two audio signals with bit rate
reduction, over various transmission media: ISDN lines, PSTN telephone lines, IP protocol networks,
mobile networks…
The standard version of the codec includes an Ethernet interface for IP transmission. The unit can be
complemented with many options providing additional network interfaces, coding algorithms, etc.
One outstanding feature of AETA codecs in ISDN mode is the 5A System: on receiving an incoming ISDN
call, the unit can automatically detect the coding algorithm and parameters of the calling codec, and
then adjust itself in a compatible configuration so that the connection succeeds regardless of the initial
configuration and that of the remote unit.
In IP mode, the codec features the same ease of operation thanks to the use of the SIP and SDP
protocols.
This chapter gives basic instructions for a quick start. It obviously does not provide all the information
for full control. For comprehensive information one can refer to the rest of this manual:
Chapter 2 describes all the functions and features of the SCOOPY+ S (but not necessarily with all
the operating modes).
Chapter 3 gives a physical description of the unit, shows its setting up and operation
principles.
Chapter 4 details menus and operating modes.
Chapter 5 deals with using the html server embedded in SCOOPY+ S.
Chapter 6 shows how to use the remote access service via Internet.
Chapter 7 provides all the technical characteristics of the SCOOPY+ S.
The annexes bring miscellaneous additional information, including an index you can use to look
for a given information topic.
The following table shows the main features of the product. Functions marked with in this table are
available as options.
Note: this document is relevant for units with firmware version 1.10.
Previous versions have differences in the features and the user interfaces.
5AS = Aeta Audio Advanced Automatic Adjustment System

2
SCOOPY+ S - User Manual
Characteristics
Optional
Operation modes
Single wide band codec
Single codec and coordination using a mobile voice link (with HD-4G option)
IP transmission interface
Ethernet Interface, 10BaseT / 100BaseT; TCP/IP, UDP/IP, RTP protocols
Audio transmission in unicast mode: SIP signalling protocol, SDP, RTP streaming
Audio transmission in multicast mode: RTP streaming
Net bit rate 16 to 256 kbit/s (depending on coding algorithm, linear coding excluded)
ISDN transmission interface
One S0 interface, single codec 64 or 128kbit/s
5AS auto configuration on incoming calls
Transmission interface on PSTN telephone line
One "2 wire" telephone interface
"POTS codec" mode with integrated V34 modem and CELP coding, 12 to 24 kbit/s
Telephone hybrid mode
Mobile network access
Integrated 2G/3G/3G+/LTE network access module, double internal antenna and antenna socket
Voice mode: standard telephone or "HD Voice" (7 kHz with AMR-WB)
Packet data mode: IP protocol, SIP signalling, SDP, RTP streaming, net bit rate 16 to 256 kbit/s
(depending on coding algorithm)
External 3G/LTE module connection via USB socket (data mode only)
SMS reception
Audio coding algorithms
(audio modes)
G711 (standard telephone)
GSM, AMR (mobile telephone)
AMR-WB / G722.2 (mobile "HD Voice"
G722 SRT, H221, H242
CELP 7 kHz
MPEG Audio Layer II
MPEG AAC-LC , HE-AAC, HE-AAC v2
4 sub-band ADPCM (low latency)
OPUS (AoIP only)
Linear L16, L24
TDAC (ISDN mode only)
Mono
Mono
Mono
Mono
Mono
Mono, Stereo, Dual mono, Joint stereo
Mono, Stereo
Mono, Stereo
Mono, Stereo
Mono, Stereo
Mono
Audio interfaces
3 analog MIC/line inputs and two analog outputs with adjustable gain
Level display for encoder inputs and decoder outputs
2 stereo headphone sockets for monitoring, balanced send/receive
Auxiliary functions (available depending on transmission interface)
Relay management : 2 inputs and 2 outputs
Audio coordination channel with Mobile option ( up to 7kHz )
SMS reception via optional mobile access
Control and supervision
Keyboard and LCD display on front panel
Programmable set-up/dial memories
Ethernet/IP remote control, embedded html server
Control and status GPIO
Remote access via Internet
Secondary Ethernet interface for remote control
Recording
Table 1 –Main features of the SCOOPY+ S

SCOOPY+ S - User Manual
3
1.1. Install and connect SCOOPY+ S
Plug on a power source or insert 6 C-size batteries.
Switch on SCOOPY+ S by holding down for 3 seconds. (And hold down for 3 seconds to
switch off)
Connect the necessary audio interfaces (details: page 20)
Connect SCOOPY+ S on the transmission network (details: page 38 and following)
Using the SCOOPY+ S menus: key or key to activate the main menu, use the joystick to
select a sub-menu or a parameter, enter or validate with the key. jumps back up to the
previous menu level, until getting back to the base screen (with level display).
(details: page 47)
1.2. Audio settings
The microphone(s) to be used must be active ("ON" LED); for instance press for
microphone 1 if not yet done.
Set the microphone gain to the middle position, white dot up. Make a test with the
microphone. If the level is too strong or too weak on the meters, adjust the gain via the menu
Setup / Audio / Inputs / Input x Settings / Gain, so that you reach an adequate level (see
details further on page 62).
1.3. Select and set up network to be used: wired networks
Select network: Setup menu then Network, then select Change Network, . In the
proposed choice, select the desired network (ISDN, Ethernet, POTS). Validate with .
Select the audio coding: menu Setup / Algorithm, then Other, then . Browse the available
choice with the arrows, and make a selection with . Restart the same procedure to change
for another coding setup.
The available choice depends on the transmission network! For more details on coding, see
page15.
1.3.1. Set up an ISDN link
If needed, select the protocol with Setup / Network / ISDN Parameter / Protocol. More
details: see page 57.
Enter the remote number to dial, using the keypad, and press the key.
If more than one B channel is involved due to the coding algorithm used, you must enter a
second number, then . If the last dialled number is adequate, just confirm by pressing
without typing a number again.
Hang up with the key to release the connection (you must confirm by pressing again).

4
SCOOPY+ S - User Manual
1.3.2. Set up a (wired) IP link
For a link over a public IP network via an access router with NAT1, it is recommended to use
a STUN server.
The address of a STUN server can be set in the SCOOPY+ S html pages (see page 95) or via the menu:
Setup / Network / AoIP Parameter / STUN Server, enter the address of a STUN server (we
propose our server stun.aeta-audio.com, look also the support pages on our web site www.aeta-
audio.com). Enable or disable STUN with Setup / Network / AoIP Parameter / STUN Mode (On
or Off).
More details: see page 122.
Check the Ethernet interface is active thanks to the LED on the Ethernet socket on the back,
and check an IP address is allocated: menu Tools / About / Local IP.
The default setting uses a DHCP server to get an IP address, which is suitable for most
occasions. In other situations, look for more details on page 42.
Using the keypad, enter the remote number to call (numeric IP address, or SIP URI if a SIP
server is used), then press the key.
Hang up with the key (you must confirm by pressing again).
When using a SIP server, some data must be entered beforehand using the AoIP Parameter
menu; for more details, refer to page 54. Similarly, some preliminary settings may have to be
done for the "Direct RTP" mode (without the SIP protocol).
1.3.3. Set up a POTS link
For connecting the line, you must plug the POTS line in ANALOG socket.
If needed, adjust the POTS line parameters using Setup / Network / POTS Parameter.
Details on these settings: see page 58.
Enter the remote number to dial, using the keypad, and press the key.
Hang up with the key to release the connection (you must confirm by pressing again).
1Network Address Translation, which is performed in most cases by the access router.

SCOOPY+ S - User Manual
5
1.4. Select and set up network to be used: mobile networks
To set links over a mobile network, you must have a SIM card with a subscription suitable for the use.
Specifically, for an IP mode transmission the subscription must include access to data transmission, and
RTP audio streams must be allowed.
While the unit is switched off, insert the SIM card into the drawer on the rear side of the
SCOOPY+ S.
Switch on the SCOOPY+ S (depress a few seconds).
Select the network: Setup menu then Network, then select Change Network, . In the
proposed choice, select the desired network (Mobile (Int.)). Validate with .
Enter the menu Setup / Network / Mobile Parameters / PIN. Enter the PIN code for the
SIM card using the keypad then .
1.4.1. Set up a link in voice mode
This mode allows communicating with any telephone terminal through the regular telephone service. It
also allows to benefit from the 7 kHz wide band service known as "HD Voice" whenever the remote
terminal is compatible and the network supports the service.
In the menu Setup / Network / Mobile Parameters, select Mode / Cellphone
Afterwards, go to the menu Setup / Network / Mobile Parameters. In the sub-menu
Preferred Techno, if needed you can select a priority among the 2G, 3G and 4G networks.
The normal choice is Auto.
The Network Select menu enables you to select among the available operators, if your mobile
subscription entitles you to do so.
Come back to the main menu. Enter the remote number to dial, using the keypad, and press
the key.
Hang up with the key to release the connection (you must confirm by pressing again).

6
SCOOPY+ S - User Manual
1.4.2. Set up a (mobile) IP link
For a link over a public IP network via an access router with NAT1, it is recommended to use
a STUN server.
The address of a STUN server can be set in the SCOOPY+ S html pages (see page 95) or via the menu:
Setup / Network / AoIP Parameters / STUN Server, enter the address of a STUN server (we
propose our server stun.aeta-audio.com, look also the support pages on our web site www.aeta-
audio.com). Enable or disable STUN with Setup / Network / AoIP Parameter / STUN Mode (On
or Off).
More details: see page 122.
In the menu Setup / Network / Mobile Parameters, select Mode / IP Mode
Come back to the menu Setup / Network / Mobile Parameters. In the sub-menu Preferred
Techno, if needed you can force a priority for 3G or 4G networks. The standard setting is
Auto.
Still in the Setup / Network / Mobile Parameters menu, enter the sub-menu Access Point
/ APN: enter the operator’s APN code, using the keypad, then press .
Come back to the previous level (Setup / Network / Mobile Parameters) by pressing .
Go to the Data Active line and press to activate the mobile data (the box is then
checked)2.
Come back to the home screen using the key.
Select the audio coding: menu Setup / Algorithm, then Other, then . Browse the available
choice with the arrows, and make a selection with . Restart the same procedure to change
for another coding setup.
Using the keypad, enter the remote number to call (numeric IP address, or SIP URI if a SIP
server is used), then press the key.
Hang up with the key (you must confirm by pressing again).
When using a SIP server, some data must be entered beforehand using the AoIP Parameters
menu; for more details, refer to page 54. Similarly, some preliminary settings may have to be
done for the "Direct RTP" mode (without the SIP protocol).
Note: the sequence is much simpler for further calls as long as you keep the same SIM card, because
the network related settings are kept memorized even if the unit is switched off; so you don’t need to
make these settings again (IP Data mode, APN, data activation...). It is even possible to memorize
the PIN code: check the box in Setup / Network / Mobile Parameters /PIN Save.
1Network Address Translation, which is performed in most cases by the access router.
2Like on a smartphone, this data activation stays memorized, and you need not do this again each time the unit starts. Conversely, make sure
to disable it if later you don’t want any data traffic.

SCOOPY+ S - User Manual
7
2. Functions
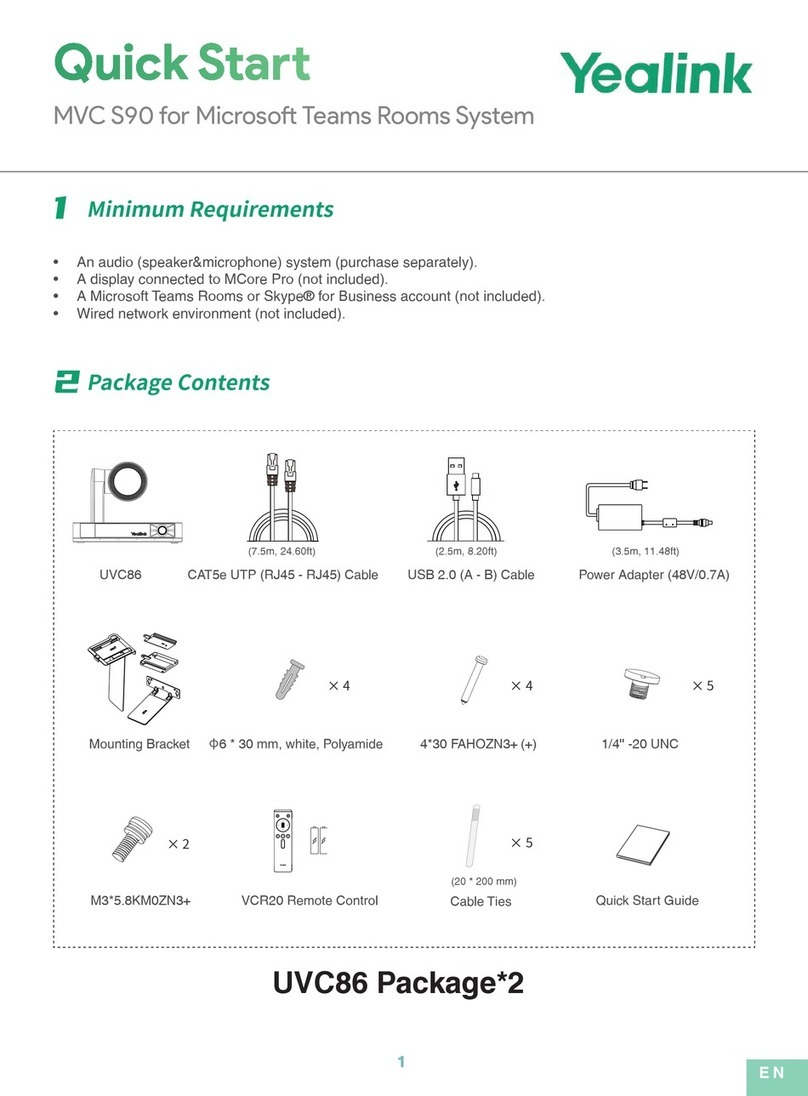
The following synoptic diagram shows the basic functions of the equipment.
Figure 1 –Functional diagram of the equipment
The audio signals to be transmitted are mixed and digitized, then the encoding function reduces the bit
rate, using a selectable algorithm; the resulting bit flow is sent to one of the available transmission
interfaces: Ethernet interface, ISDN interface, PSTN interface, mobile network...
The transmission interface functional block also extracts compressed data coming from the network and
sends them to a decoding block that reproduces uncompressed audio data. Last, the audio signals are
fed to the outputs.
Monitoring the audio interfaces is possible thanks to headphones and level meters for the
inputs/outputs.
In addition to the main task of transmitting an audio programme, the SCOOPY+ S can also transmit
auxiliary information, usually by embedding them inside the transmitted audio streams.
Supervision and controlling the unit is performed using various remote control interfaces, and of course
by means of the displays and controls on the front panel.
Audio
Inputs
Audio
Outputs
Encoding
Decoding
Transmission
Interfaces
Control Interfaces
Network
Supervision
Auxiliary Functions
Relays / GPIO
Monitoring Audio
monitoring
Routing
and
Mixing
Input
processing
Output
processing

8
SCOOPY+ S - User Manual
2.1. Transmission interfaces
The SCOOPY+ S features in all versions an Ethernet interface for IP protocol networks.
An optional ISDN interface can be added, as well as optional PSTN/POTS and mobile network access
interfaces.
2.1.1. Ethernet/IP interface
The IP interface is a 10BaseT/100BaseT Ethernet interface allowing transmission of the audio
programmes in a wide range of possible bit rates. The audio stream is always transported under the
RTP/UDP protocol.
AoIP unicast mode
The most classical transmission mode is unicast: audio connection with one remote device, generally
bidirectional. This mode can be used on all types of networks links, LAN or WAN, including links via
Internet. The SCOOPY+ S implements the SIP protocol, which allows it to interoperate with IP phones and
other SIP compatible audio codecs, in a way similar to ISDN or POTS connections. Links can be set up in
two ways:
"Peer to peer" connection between two compatible units
Use of a SIP proxy server to set up the link, or a SIP PBX
Details about the SIP protocols can be found in the annex (see 8.2, Overview of the SIP protocol).
It is also possible to operate in a "Direct RTP" mode, without using the SIP protocol. This operation mode
can be used for interoperation with devices that do not support SIP, or for overcoming possible network
blocking that would specifically affect the SIP protocol.

SCOOPY+ S - User Manual
9
Available audio coding algorithms
The audio coding algorithm can be selected depending on the required quality and the available
network bandwidth. The following algorithms are currently available:
Codec
Bit rate
(coding)
Bit rate
(total)1
Audio
bandwidth
Typical use, main features
G711
64 kbit/s
86 kbit/s
3 kHz
Voice, telephony
Compatible with IP phones
CELP
24 kbit/s
28.5 kbit/s
7 kHz
Suitable for high quality speech;
Low network bandwidth consumption
G722
64 kbit/s
86 kbit/s
7 kHz
High quality speech.
Compatible with some IP phones.
MPEG Layer II
64 to 256
kbit/s
73 to 275
kbit/s
Up to
20 kHz
Highest quality, suitable for speech and music
MPEG AAC-LC
16 to 256
kbit/s
30 to 277
kbit/s
Up to
20 kHz
Low bit rate, suitable for speech and music
MPEG HE-AAC and
HE-AAC v2
16 to 128
kbit/s
23 to 139
kbit/s
Up to
20 kHz
Very low bit rate, suitable for speech and music
4SB ADPCM
128 or 256
kbit/s
173 or 301
kbit/s
15 kHz
Low latency, suitable for speech and music
OPUS
12 to 256
kbit/s
28 to 272
kbit/s
Up to
20 kHz
Low bit rate and low latency, suitable for
speech and music
Linear L16/L20/L24
512 to 2304
kbit/s
592 to 2384
kbit/s
Up to
20 kHz
Best quality, very low latency
Table 2 –Overview of algorithms available in IP mode
IP multicast mode
The multicast mode allows an encoder device to transmit an audio programme to several decoders by
sending a single encoded stream to a multicast group address. The link is unidirectional by nature. This
mode can be used on a local area network, and on larger private networks that can manage the
multicast mode. On the other hand, Internet cannot support this routing mode.
In this mode, the SCOOPY+ S uses the RTP protocol to manage the audio stream, like in the unicast mode,
but the SIP protocol is not applicable here; instead a proprietary signalling system is used. As the link is
unidirectional, the unit has to be set either as a "sender" in order to encode and transmit the audio
stream to the selected group address, or as a "receiver" to receive and decode such stream coming from
a "sender" device.
The audio coding algorithm can be selected with just the same capability as for the unicast mode
described above.
SIP and SDP protocols
The SIP protocol is a signalling protocol, used for IP connections, which allows the SCOOPY+ S to
interoperate with IP phones and other SIP compatible audio codecs, in a way similar to ISDN or POTS
connections. Details about the SIP protocols can be found in the annex (refer to 8.2, Overview of the SIP
protocol).
1Informative value; higher than the "net" encoded audio bit rate because of the protocol overhead

10
SCOOPY+ S - User Manual
One significant advantage is the inclusion of SDP, a protocol which allows the connecting devices to
automatically negotiate and agree on the coding profile to use. Thanks to this system, it is not necessary
to set the units in the same way before setting up a connection. Moreover, the calling party needs not
know how the remote unit is configured before initiating a link.
Note: the SIP protocol does not mandatorily imply the use of a server. Codecs can set up point-to-
point links using this protocol, and benefit from some its advantages.
Conversely, for the "Direct RTP" mode, which includes no signalling, it is necessary to configure
beforehand in the same way the two units to be connected.
"Factory" SIP account
AETA has set up a public SIP server, dedicated to broadcast audio over IP applications. Our customers
can subscribe accounts and register their codecs on this server.
In addition, each SCOOPY+ S is provided a "factory set" SIP account on this server. This account is
permanently and definitively bound to the unit, and at any time it is possible to load its parameters and
register the SCOOPY+ S on the server. However, you can also configure another account from any other
SIP server.
Packet replication
SCOOPY+ S also proposes an RTP transmission mode with enhanced reliability, using packet replication.
When enabling this mode, every packet is transmitted twice; with such system a lost packet has no
effect since the receiver still gets the other copy of the packet. In this way, stable links can be obtained
even with a high packet loss rate. Of course, as a disadvantage the bit rate is double; you must make
sure this stays compatible with the transmission medium.
Remote control via IP
The Ethernet interface can also be used for configuring or remote controlling the unit.
SCOOPY+ S provides html pages which provide complete control over the unit using a web browser, via
port 80 (default port for HTTP protocol), or port 443 (default port for HTTPS protocol). See in chapter 5
the detailed operating mode.

SCOOPY+ S - User Manual
11
2.1.2. ISDN interface
For access to the ISDN, the transmission interface is an S0 BRI (Basic Rate Interface), for transmission
over one to two 64 kbit/s B channels. Thus, the total available bit rate is 64 or 128 kbit/s.
The codec synchronises itself onto the ISDN network clock when a link is active.
Network protocols
Available protocols:
"Euro ISDN" (or ETSI), default protocol valid for a large number of countries, especially all over
Europe.
"NTT": valid for the Japanese network of NTT
"NI-1": valid for numerous operators in North America. This choice is also suitable for the
connection to network equipment with "NI-2" protocol".
In North America (USA and Canada), the available interface is often a U0 interface (instead of S0). In
such case an "NT1" network adapter must be inserted between the line and the SCOOPY+ S. Such
adapter can be found on the local market.
5A System®
Setting an ISDN connection is often difficult, at least because of the numerous coding parameters to be
set. Moreover, with most proprietary algorithms, it is mandatory for the two devices to have exactly the
same settings, otherwise the connection will fail, and sometimes it is not easy to find out the reason.
5A stands for Aeta Audio Advanced Automatic Adjustment. This system makes it easier to set an ISDN
connection, because the codec, on receiving a call, automatically adjusts itself, following the calling
party algorithm and parameters.
When the 5A System is enabled on the unit and a call is received, the unit first detects the coding
algorithm used by the calling codec, and also senses its parameters: audio mode (mono, stereo…),
sampling rate, bit rate, inverse multiplexing protocol, etc. Then the unit can decode the compressed
audio from the remote unit. In addition, the unit will use these same settings for encoding and sending
audio to the remote unit, so that the remote unit can also decode the outgoing audio programme. The
whole process just takes a few seconds. Of course, all compatible coding configurations can be detected
automatically by the 5A System.
Note that the 5A system is only active for ISDN connections.
J52
The ITU-T J52 recommendation was defined in order to allow the interoperability of multimedia
terminals over the ISDN1, using common coding standards. It includes the following features:
Support of ITU-T recommended coding algorithms: G711, G722, MPEG Layer II
Framing as per ITU-T H221 recommendation, ensuring byte synchronisation and interchannel
synchronisation when more than one 64 kbit/s B channel is required for the desired bit rate;
Interoperation procedures according to ITU-T H242 recommendation;
In the case of MPEG encoding, optional protection against transmission errors (Reed-Solomon
error correction codes).
Details about MPEG and J52 can be found in the annexes (refer to 8.1, Additional information on the
algorithms and protocols used).
1J52 is only relevant for ISDN connections

12
SCOOPY+ S - User Manual
It must be noted that, thanks to the interoperation protocol, J52 codecs, when setting up a link, can
negotiate automatically and agree on a configuration that is compatible with the capability of both units
(regarding bit rate, channel mode, etc.). In this way, when the units differ in their capability (or make),
the resulting configuration may be different from expected beforehand, but in most cases the link will
work and audio will be transmitted.
As another useful consequence, this also gives users more tolerance to mistakes when configuring the
units on the two sides of the transmission links, as the codecs will adapt automatically even with
differences in the initial settings of the two units.
2.1.3. POTS interface
The interface is a "two wire" analog telephone access, with characteristics adjustable depending on the
country. Dialling normally uses DTMF, but for older switching equipment it is possible to use pulse
dialling.
SCOOPY+ S includes a V34 modem which transmits via this line a bidirectional audio flow, encoded at a
nominal 24 kbit/s bit rate. Depending on the line quality and the quality of the link with the remote
codec, this bit rate is automatically negotiated and dynamically adjusted from 12 to 24 kbit/s.
A "protected" mode can be activated, which increases the resilience to transmission errors, at the cost
of a higher latency (encoder to decoder delay). You must make sure to set this parameter the same way
on both devices / both ends of the link.

SCOOPY+ S - User Manual
13
2.1.4. Mobile network access
Units equipped with the "HD-4G" option include an integrated module for access to mobile networks,
and a holder for a SIM card.
Depending on the version the accessible networks are 2G (GSM, EDGE), 3G (UMTS), 3G+ (HSDPA,
HSUPA, HPA…), and 4G/LTE.
The SCOOPY+ S includes an integrated double multiband antenna. This antenna "diversity" feature is
useful when the radio reception is poor: the signal strength and stability is improved thanks to the
second antenna. This can specially increase the radio coverage area in rural areas.
An external multiband antenna (to be selected for compliance with the mobile network characteristics)
can be connected to the SCOOPY+ S as well. It will in such case replace one of the internal antennas. Such
arrangement takes a greater advantage of diversity, as the two antennas involved are set at a larger
distance from one another.
Lastly, SCOOPY+ S can display the received SMS messages.
Mobile voice mode –HD Voice
The integrated module allows using the mobile phone service, for communicating with all ISDN or PSTN
telephone terminals or hybrids, or with other mobile terminals. The quality is in such case that of mobile
connections, with a 300-3400 Hz bandwidth and coding such as GSM, EFR, AMR...
Now many mobile networks also propose "HD Voice", an extension of this mobile telephone service.
With this new capability, compatible terminals implement the AMR-WB coding algorithm (standardised
as G722.2 by the ITU-T) and provide speech transmission with a 50-7000 Hz bandwidth and a quality
very similar to the well-known G722. Automatic fallback to the standard coding takes place if the
network does not support the service or one of the terminals does not feature this capability.
No special subscription, other than to the regular telephone service, is needed, but for most operators
only the 3G/3G+ base stations support the service.
This sometimes makes people believe that HD Voice is related to the mobile IP service, but this is
definitely not the case.
More and more mobile phones now support this service, especially (but not only, and not all)
smartphones. All AETA codecs in "Wireless" version support HD Voice, namely:
Scoop 4+ in "wireless" version
Scoopy+ HD (except old units, in doubt consult us)
ScoopFone HD, ScoopFone HD-R.
Scoop 5 and Scoopy+ with the HD-4G option
ScoopFone 4G and ScoopFone 4G-R
Scoop5 S with the HD-4G option
ScoopTeam with the HD-4G option

14
SCOOPY+ S - User Manual
Mobile IP mode
The other service available with mobile access is the data packet transmission mode, with IP protocol.
This mode brings similar capabilities as a wired IP connection via the Ethernet interface, as described
above in 2.1.1, with some distinctive characteristics:
This requires a subscription including access to the data service, with conditions compliant with
the application. Among other requirements, an APN (Access Point Name) must be provided
that allows this type of media stream. Some operators provide such allowance in a "VoIP"
option.
The available bit rate depends on various factors; first the network technology (3G/3G+/LTE…),
but also the traffic level in the radio cell, the operator’s network capacity, possibly the type of
subscription. This may bring on restrictions for the usable compression algorithms.
The multicast mode is not available on mobile networks
Setting a link implies first activating the data connection, before actually initiating an audio
stream transmission link
Using an external USB device
Instead of the integrated module, it is possible to plug a USB mobile module or "key", in order to access
mobile IP transmission, with more or less similar conditions as described above.
However be aware:
This capability is optional.
The USB module must be from the list of devices supported by AETA. As this list is evolving,
please check our web site for up to date information.
The "HD Voice" mode is not available in this way.
USB devices do not feature antenna diversity.
2.1.5. Managing calls
The audio transmission implies a link/session setup phase.
One of the transmission interfaces is selected as the default interface on the SCOOPY+ S.
A call towards a remote unit, initiated by the user of the SCOOPY+ S, is implicitly sent through this default
interface.
On the other hand, an incoming call on any interface (regardless of the default interface) can be
processed and the link established, under following conditions:
The "called" interface must be connected and active. As an example, for mobile IP the data
connection must be active.
The codec must not be already busy with another connection.
If the call comes on an interface other than the default interface, the codec first switches to the suitable
interface, and then processes the incoming call. When the link is released, it will come back to its
previous state (and default interface).
Table of contents
Other AETA Conference System manuals