-4- -5-
WTarget output and concentration
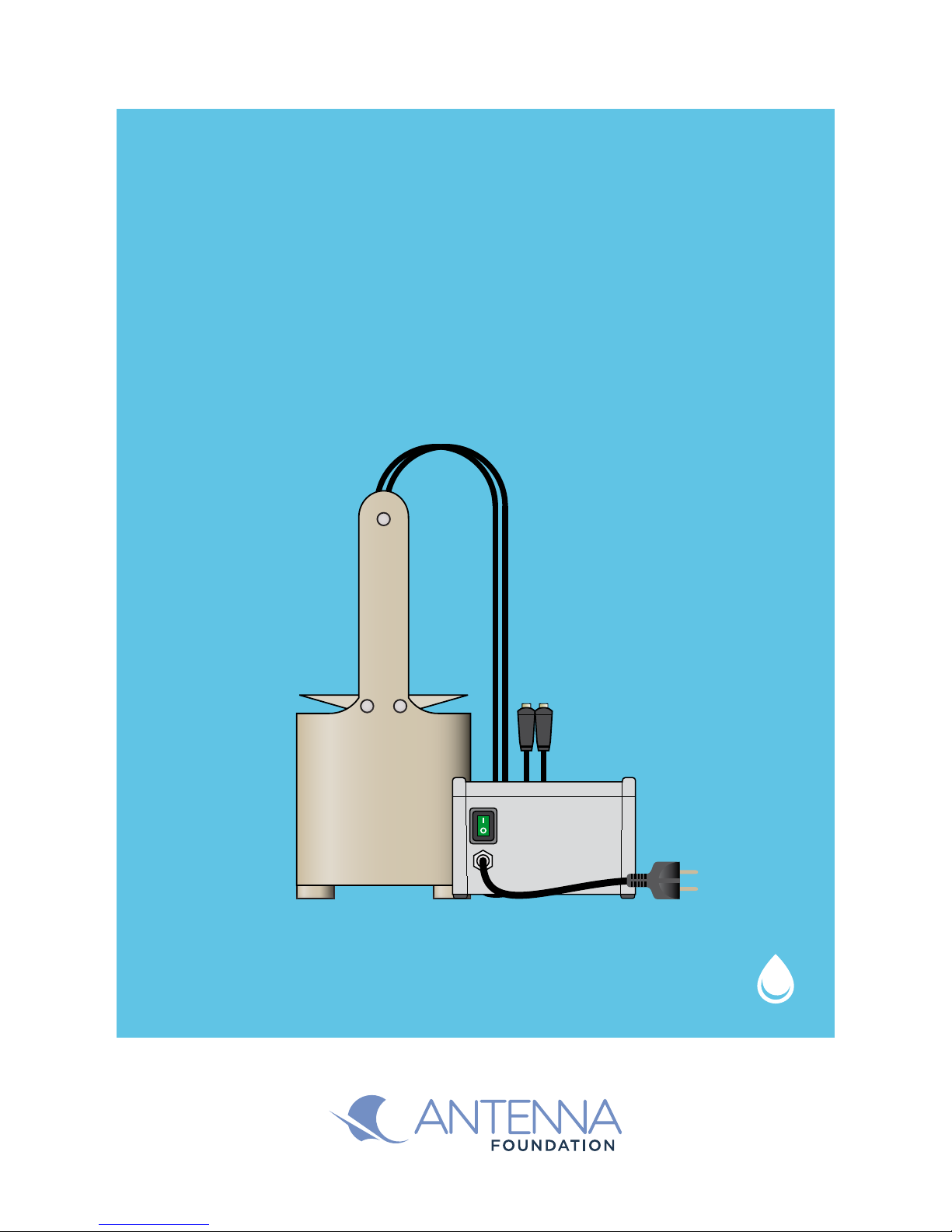
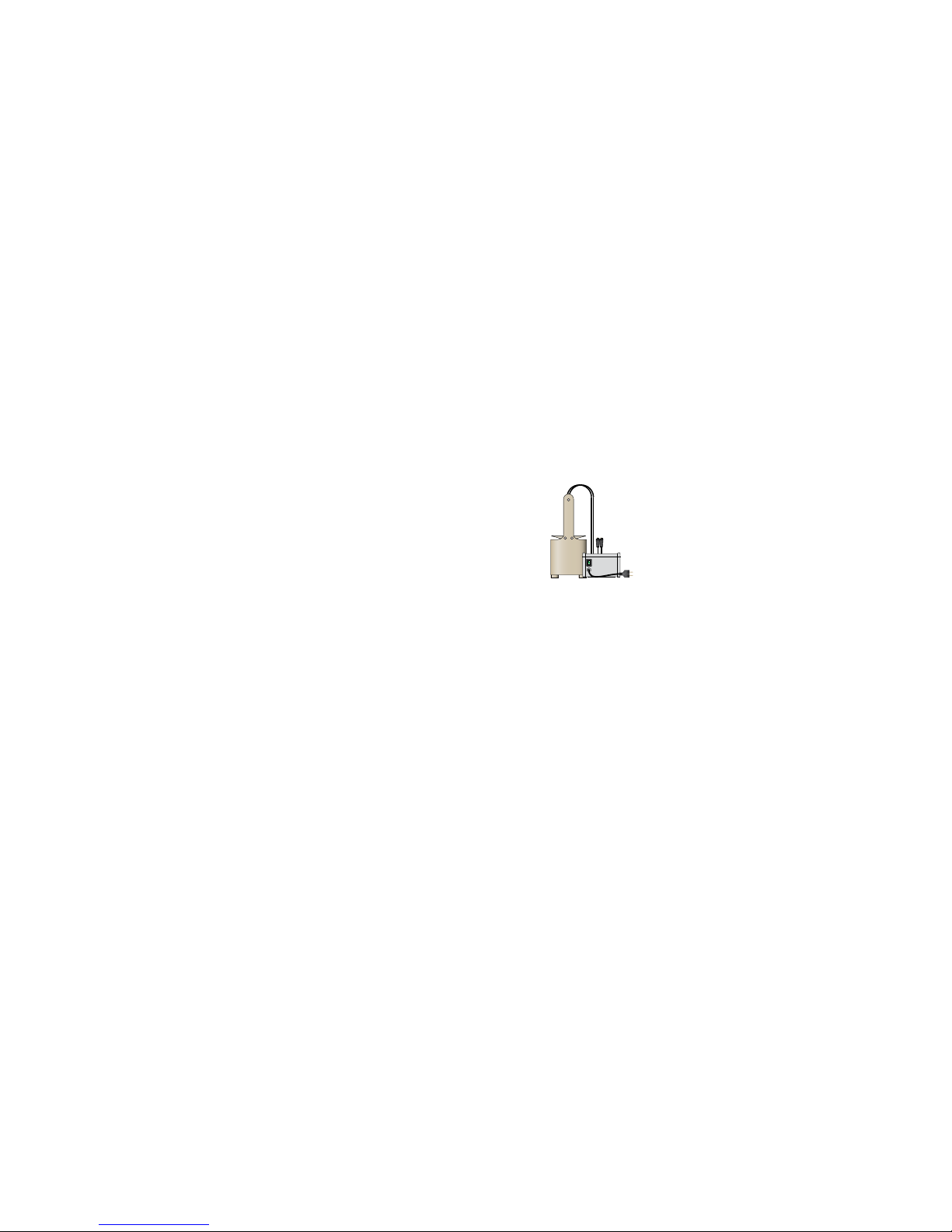
The WATA-Plus®uses electrolysis of salt water at 25 g/L (375 grams of salt per 15 litres
of water) to produce a sodium hypochlorite solution with a 6 g/L concentration of active
chlorine. Failure to follow these parameters could lead to a poor quality production or
a damaged power supply.
WIn case of unstable current, use a voltage regulator
If the power grid is subject to intermittent outages or sudden voltage dips and surges
(fluctuations in the intensity of light emitted by the bulbs provide sufficient evidence
that this is occurring), the power supply could be destroyed. If this is the case, use a
voltage regulator. Likewise, if a generator has a large variation in operating regimes, it
is advisable to use a voltage regulator.
WUse with a generator
The generator should not run out of fuel while the WATA-Plus®is in use. Ensure that the
tank is full before starting production. Wait until the generator is stable before plugging
in the WATA-Plus
®
.When the procedure is complete, first unplug the WATA-Plus
®
’s power
supply and then turn off the generator.
WRespect the prescribed production volumes.
The recommended volume of each production run is 15L.
WOverheating of the power supply
If overheating occurs, the power supply will automatically shut off and then restart when
its internal temperature falls below 70°C. However, it is advisable to stop the procedure
and allow the power supply to cool down for 15 minutes.
WRespect the 6 g/L concentration
The WATA-Plus®is designed to produce a sodium hypochlorite solution with a 1 to 6
g/L concentration of active chlorine.The concentration must not exceed 7 g/L. Prolonged
use or excessive salt will result in raising the temperature of the bath, not in increasing
concentration. If this occurs, there is a risk of damaging the power supply and/or not
achieving 6 g/L concentration. Use WataTest®to measure concentration once the
procedure is complete.
WWater temperature for production
To begin the procedure, use water with a temperature between 20 and 27°C. Check the
temperature using a clean thermometer.
WUse a log book
To facilitate the monitoring of chlorine production and to trace the origin of any problems
that might arise, use a log book to record, each time the WATA-Plus®is used, the name
of the person responsible for production, the starting and finishing times of production
and a short description of the procedure. You’ll find examples in the «tool kit» on our
website, www.antenna.ch.
2. NECESSARY MATERIALS
`WATA-Plus®kit
`Ordinary salt
`Clear water
`Funnel
`Plastic container holding approximately 25L
`Wooden/plastic table
3. RECOMMENDATIONS FOR THE
PRODUCTION OF SODIUM HYPOCHLORITE
WChoose one or several people to be responsible for production
These persons should be trained and possess a general knowledge of chemistry.
Production with the WATA-Plus®involves more than just adding salt to water. Failure to
follow indicated procedures will lead to excessive energy consumption that will adversely
affect the proper functioning and life span of the power supply.
WSome precautions at the electrical level
The box containing the power supply should be put in a dry area away from splashing
water and should always remain closed, especially when the WATA-Plus®is in use. It
should be placed as far as possible from the chlorine vapours and never placed
at ground level. It should be opened only by qualified persons with electrical training
after the power supply has been unplugged. The electrical voltage in the electrolysis
bath involves no risk of electrocution for the user. However, precautions should be
taken regarding access to the device only by authorized persons. Furthermore, salt and
chlorine are not good for electrical devices, so rinse your hands/gloves before handling
the power supply.
WChoose an appropriate area and time for production
Only those persons specially trained in using the WATA-Plus®should use it. Owing to
significant emissions of hydrogen (a highly flammable gas) produced during electrolysis,
when the WATA-Plus®is in use, the device should be kept far from fire, flame and
sparks. In addition, it is advisable not to inhale the chlorine emissions, which are also
produced during electrolysis, and to work in a well-ventilated room. Production should
be carried out in a ventilated area with a temperature between 25 and 30°C,
protected from dust and the sun’s rays. In countries with a hot climate, it is best to work
early in the morning or in the evening, when temperatures are lower.