1. CONTENTS
1. CONTENTS ................................................................................................................................................... 1
2. SAFETY PRECAUTIONS.............................................................................................................................. 2
3. OVERVIEW.................................................................................................................................................... 3
4. INSTALLATION.............................................................................................................................................. 5
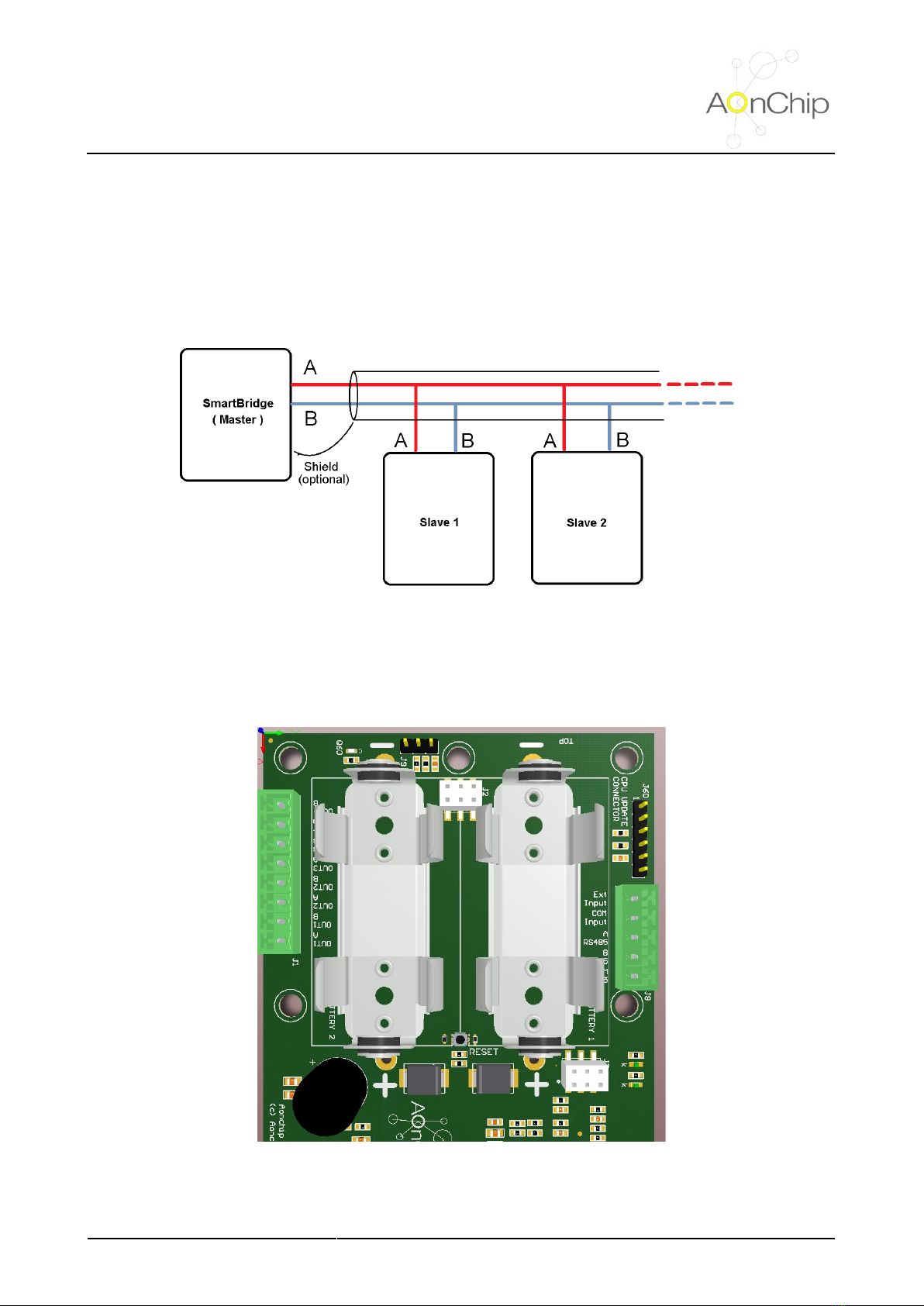
4.1. Electrical diagram .................................................................................................................................. 5
4.2. Connectors ............................................................................................................................................ 5
5. COMMISSIONING......................................................................................................................................... 7
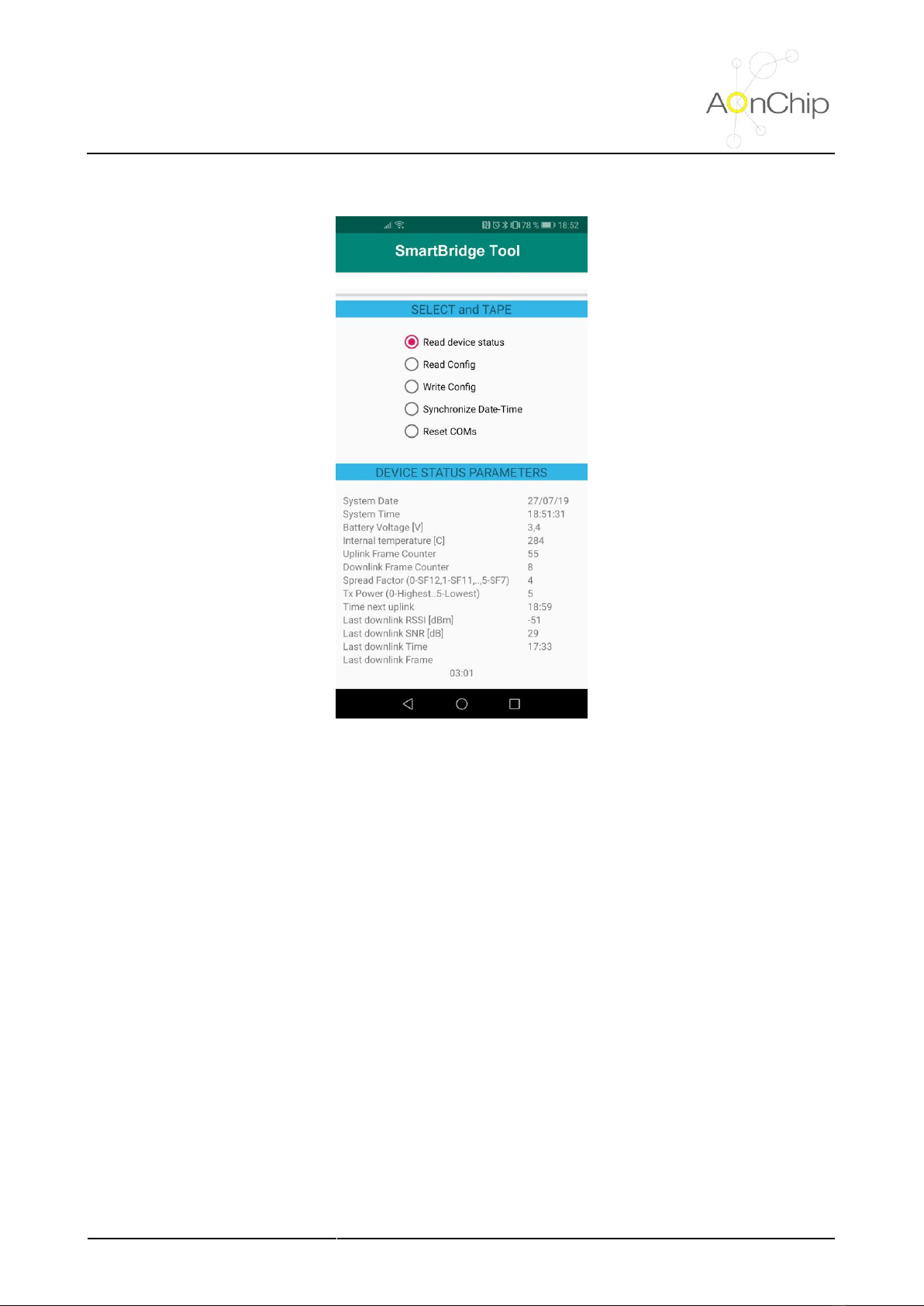
5.1. NFC connectivity ................................................................................................................................... 7
5.2. Setting LoRaWAN communication parameters ..................................................................................... 8
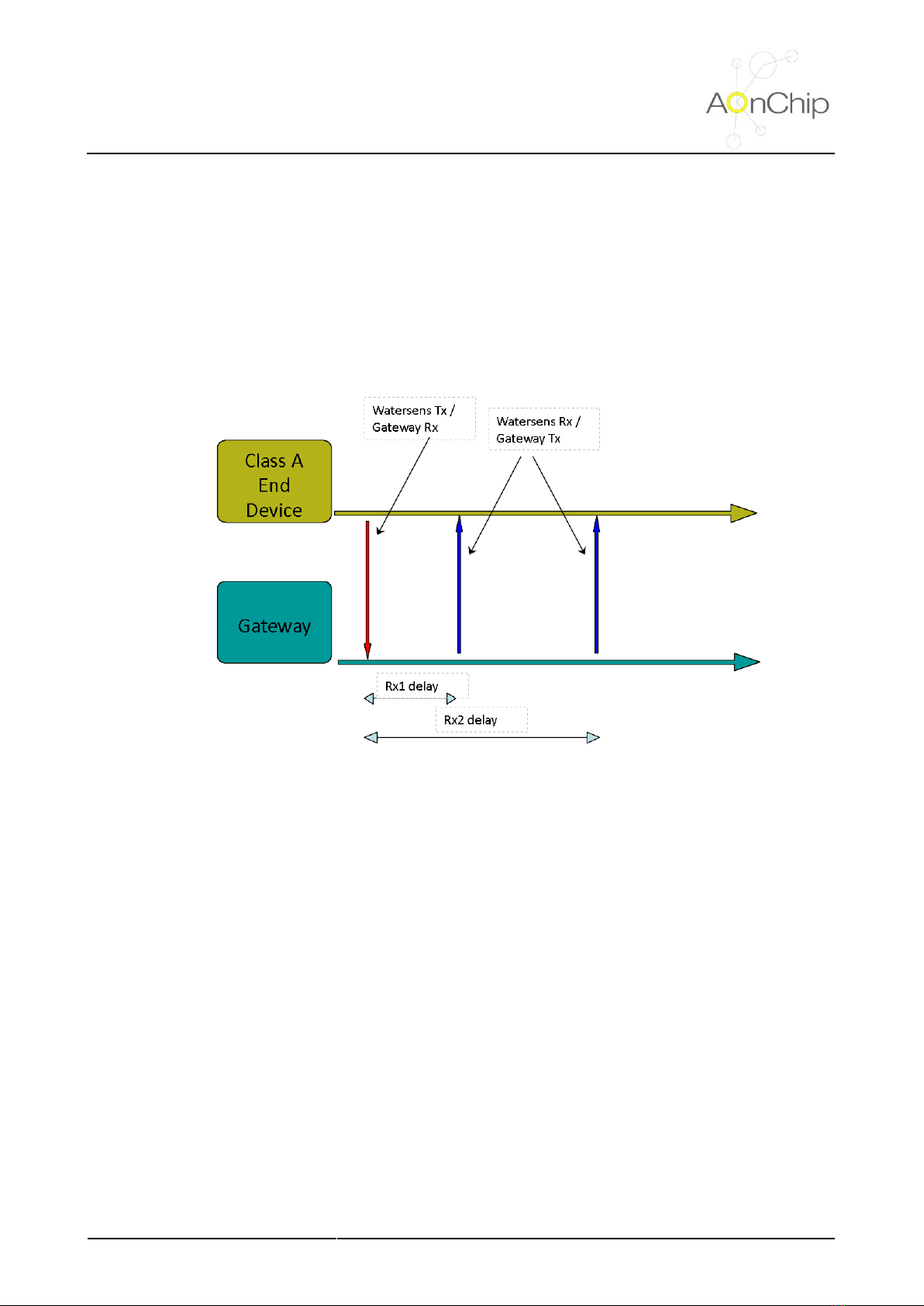
5.2.1. Understanding SmartBridge LoRaWAN profile class....................................................................... 8
5.2.2 LoRaWAN communication parameters ............................................................................................. 8
5.3 Modbus parameters settings .................................................................................................................11
5.3.1 Modbus serial RTU protocol overview..............................................................................................11
5.3.2. Table parameter...............................................................................................................................11
5.4. Checking the setup and establishing first communication .................................................................. 13
6. OPERATION ................................................................................................................................................ 14
6.1. Internal alarm wakeup ......................................................................................................................... 14
6.2. NFC signal detection ........................................................................................................................... 14
6.3. Modbus values request management ................................................................................................. 14
7. DATA FRAME FORMATS............................................................................................................................ 16
7.1. UPLINK FRAMES (FROM NODE TO SERVER) ................................................................................ 16
7.1.1. UPLINK 00 (Reading Modbus parameters) ................................................................................... 16
7.1.2. UPLINK 01 (Reading data type and address of the requested group of Modbus registers) ......... 18
7.1.3. UPLINK 02 (Reading slave address and function of the requested group of Modbus registers) .. 19
7.1.4. UPLINK 03 (Serial Modbus RS485 settings) ................................................................................. 20
7.1.5. UPLINK 04 (SmartBridge status) ................................................................................................... 21
7.2. DOWNLINK FRAMES (FROM SERVER TO NODE).......................................................................... 22
7.2.1. DOWNLINK 01 (Configure Type data and Modbus Address register) ........................................... 22
7.2.2. DOWNLINK 02 (Configure enable parameter, Modbus slave address device and read function) 23
7.2.3. DOWNLINK 03 (Configure Modbus RS485 settings)..................................................................... 24
7.2.4. DOWNLINK 05 (Direct Modbus command to slave) ...................................................................... 25
7.2.5. DOWNLINK 06 (Configure Uplink period) ...................................................................................... 26
7.2.6. DOWNLINK 07 (Configure Time and Date for the SmartBridge) ................................................... 27
7.2.7. DOWNLINK 08 (Next data request for uplink) ............................................................................... 28
8. TROUBLESHOOTING................................................................................................................................. 29
9. MAINTENANCE AND TECHNICAL SERVICE ............................................................................................ 30
9.1. Battery replacement procedure ........................................................................................................... 30
9.2. Firmware update.................................................................................................................................. 30
10. TECHNICAL FEATURES........................................................................................................................... 32
11. PRODUCT REGULATIONS....................................................................................................................... 34
12. TRADEMARKS.......................................................................................................................................... 35
13. GUARANTEE ............................................................................................................................................ 36
14. DOCUMENT HISTORY ............................................................................................................................. 37
15. CONTACT INFORMATION........................................................................................................................ 38