Charger 6 / Charger 12 rel. 1.3c -E- english, page 3 of 22
table of contents
0. table of contents..............................................................................................................................3
1. Technical Description ....................................................................................................................4
1.1 Intended use....................................................................................................................................4
1.2 construction ....................................................................................................................................4
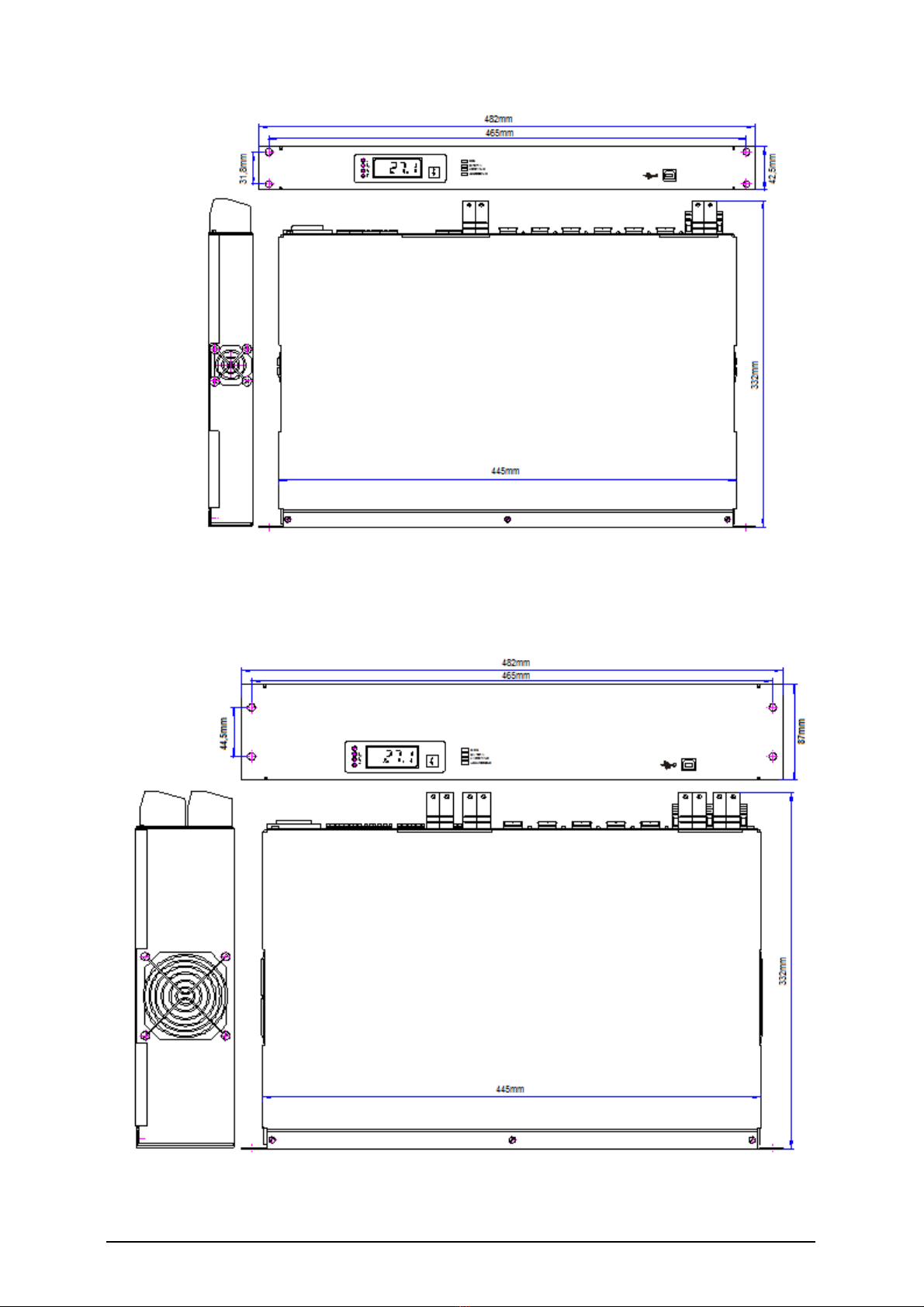
1.2.1 Battery charger CHARGER 6 ...................................................................................................6
1.2.2 Battery charger CHARGER 12 ...................................................................................................7
1.3 Basic electrical parameters............................................................................................................9
1.4 Recommended working conditions...............................................................................................9
2 Operation principle...................................................................................................................... 10
3. Installation and connection .........................................................................................................13
3.1 Installation ....................................................................................................................................13
3.2 Connection ....................................................................................................................................13
4. Operation ......................................................................................................................................15
4.1 General information ....................................................................................................................15
4.2 Operation safety ...........................................................................................................................15
4.3 Digitale display ............................................................................................................................. 15
4.4 Digitale communication...............................................................................................................15
4.5 Operation state signaling.............................................................................................................16
4.6 Maintenance .................................................................................................................................17
5 Servicing........................................................................................................................................18
5.1 Circuit breakers ...........................................................................................................................18
5.2 Detecting faults and troubleshooting.......................................................................................... 19
6 Additional information ................................................................................................................ 19
6.1 Remarks of the manufacturer..................................................................................................... 19
6.2 List of indicated error codes........................................................................................................19
6.3 Handling packagings and used products ...................................................................................21