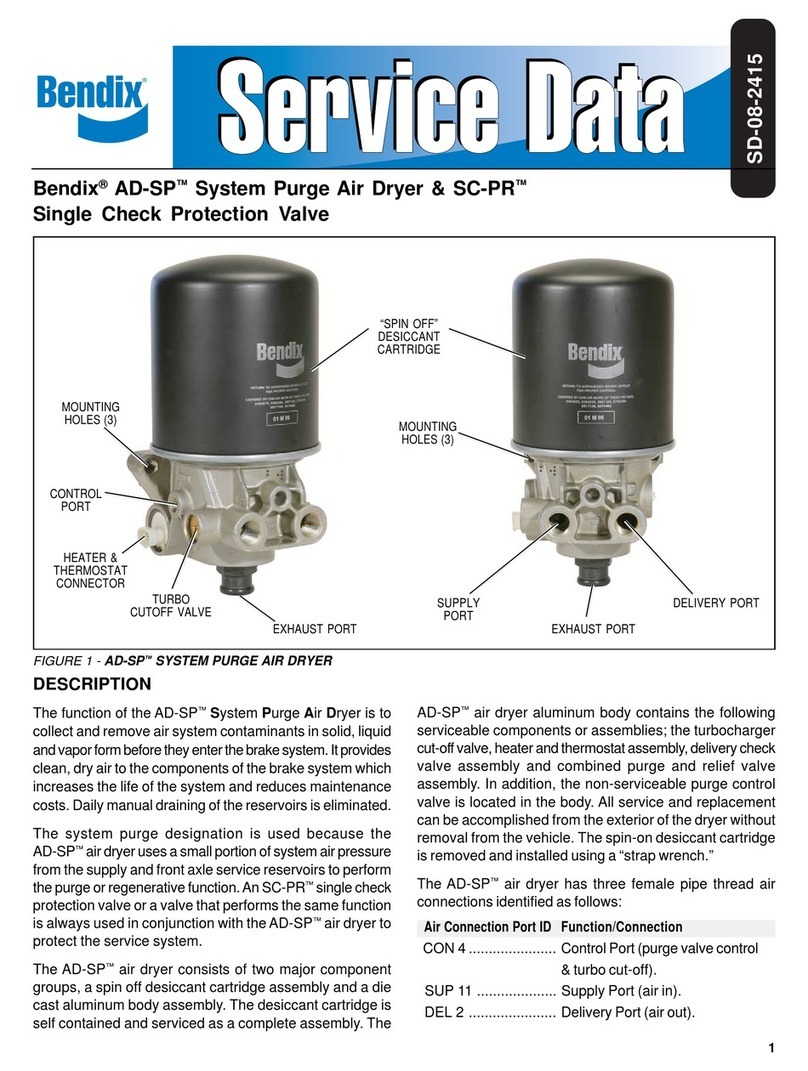
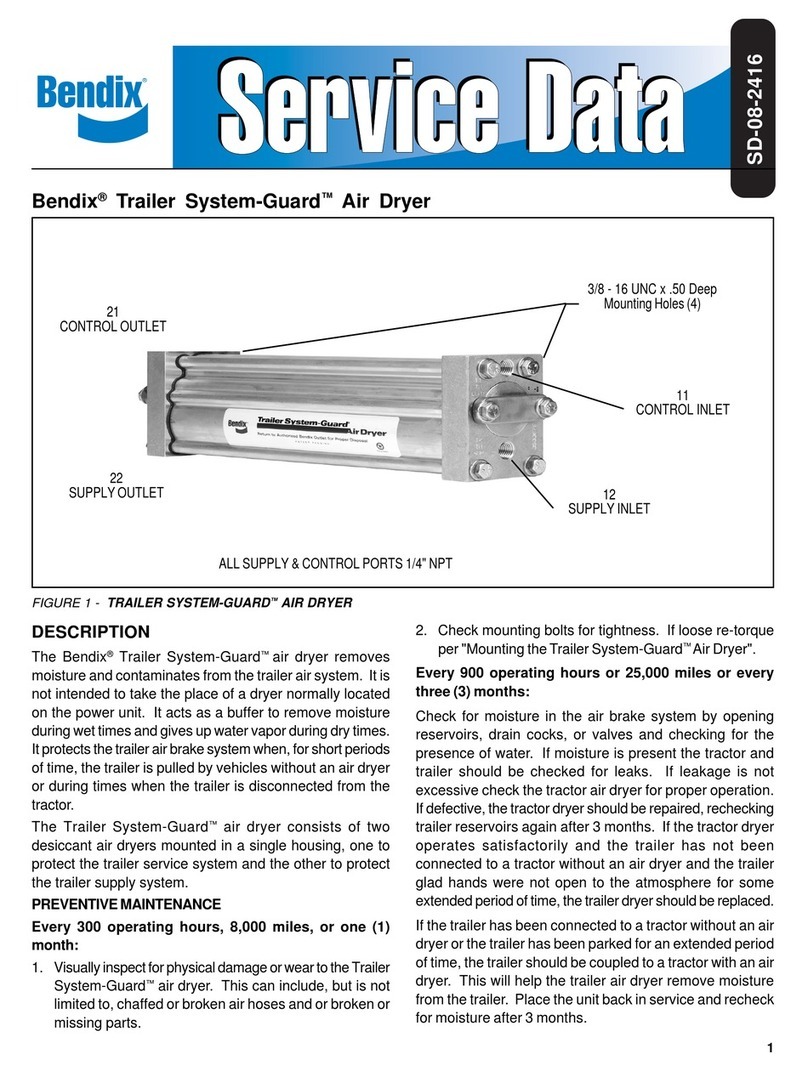
4
ofthe contaminants to condenseand drop to thebottom of
the air dryer and reservoir system purge valve assembly,
ready to be expelled at the next purge cycle. The air then
flowsintothedesiccantcartridge,where it flows through an
oilseparatorwhichremovesliquidoilandsolidcontaminants.
Air then flows into the desiccant drying bed and becomes
progressivelydrieraswatervaporadherestothedesiccant
material in a process known as “ADSORPTION.”
Dry air exits the desiccant cartridge through the center of
thebaseassembly. The air then flows to thedeliverycheck
valve and also through an orifice into the purge reservoir.
Thedeliverycheckvalveopens,supplyingairtothepressure
protectionvalves(A)through(D)simultaneously,thesafety
valve,andalsoto thereservoirportofthe attachedgovernor.
The purge reservoir fills, storing air that will be used to
reactivate the desiccant during the purge cycle. This air is
available to supply downstream components during the
chargemode.
When the air pressure reaches approximately 106 psi, the
four pressure protection valves will open and air will be
supplied to the primary reservoir, secondary reservoir and
accessories. Ifthepressureprotectionvalvesare preset to
differentvaluesthevalveswill openinorderoflowestsetting
to highest setting when charging a flat system.
Theairdryerandreservoirsystemwill remain in the charge
cycle until the air brake system pressure builds to the
governor cut-out setting of approximately 130 p.s.i.
PURGE CYCLE (Refer to Figure 3.)
Whenairbrakesystempressurereachesthe cut-out setting
ofthe governor, the governorunloadsthe compressor and
thepurgecycleoftheairdryerandreservoir system begins.
The governor unloads the compressor by allowing air
pressure to fill the line leading to the compressor unloader
mechanism - causing the delivery of compressed air to
theAD-IS®airdryerandreservoirsystem to be suspended.
Similarly, the governor also supplies air pressure to the
AD-IS®airdryerand reservoirsystempurgecontrolchannel.
The AD-IS®air dryer and reservoir system purge piston
moves down in response to this air pressure, causing the
purgevalvetoopentotheatmosphereandtheturbocut-off
valvetocloseoffthesupplyofairfromthe compressor (this
will be further discussed in the Turbo Cut-off Feature
section). Waterand contaminants whichhave collected in
the purge valve base are expelled immediately when the
purgevalveopens. Also,air which was flowing through the
desiccant cartridge changes direction and begins to flow
toward the open purge valve. Oil and solid contaminants
collected by the oil separator are removed by air flowing
from the purge reservoir through the desiccant drying bed
totheopenpurgevalve.
The initial purge and desiccant cartridge decompression
lasts only a few seconds and is evidenced by an audible
burst of air at the AD-IS®air dryer and reservoir system
exhaust.
The actual reactivation of the desiccant drying bed begins
as dry air from the purge reservoir flows through the purge
orifice into the desiccant bed. Pressurized air from the
purge reservoir expands after passing through the purge
orifice; its pressure is lowered and its volume increased.
The flow of dry air through the drying bed reactivates the
desiccantmaterialbyremovingthewatervaporadheringto
it. Approximately 30 seconds are required for the entire
contentsofthe purgereservoirofastandardAD-IS®airdryer
and reservoir system to flow through the desiccant drying
bed.
Thedeliverycheckvalveassemblypreventsairpressurein
thebrakesystemfromreturningtotheairdryerandreservoir
system during the purge cycle. After the purge cycle is
complete, the air dryer and reservoir system is ready for
the next charge cycle to begin.
TURBO CUT-OFF FEATURE (Refer to Figure 3.)
Theprimary function ofthe turbo cut-offvalve is to prevent
loss of engine turbocharger air pressure through the
AD-IS®air dryer and reservoir system when the dryer is in
theunloadedmode.
At the onset of the purge cycle, the downward travel of the
purgepistonisstoppedwhentheturbocut-off valve(tapered
portion of purge piston) contacts its mating metal seat in
thepurgevalvehousing. Withtheturbocut-off valve seated
(closed position), air in the compressor discharge line and
AD-IS®air dryerandreservoirsysteminletportcannotenter
theairdryerand reservoir system. In this manner the turbo
cut-off effectively maintains turbo charger boost pressure
to the engine.
PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE
Important: Review the warranty policy before performing
any intrusive maintenance procedures. An extended
warrantymaybevoidedifintrusivemaintenanceisperformed
duringthisperiod. Purgevalvemaintenanceis permissible
duringthewarrantyperiodonlywhen usingagenuineBendix
purgevalvekit.
Becausenotwovehiclesoperate underidenticalconditions,
maintenance and maintenance intervals will vary.
Experience is a valuable guide in determining the best
maintenanceintervalfor any one particularoperation.
Every 900 operating hours, or 25,000 miles or three (3)
months:
1. Check for moisture in the air brake system by opening
reservoir drain valves and checking for presence of
water. If moisture is present, the desiccant cartridge