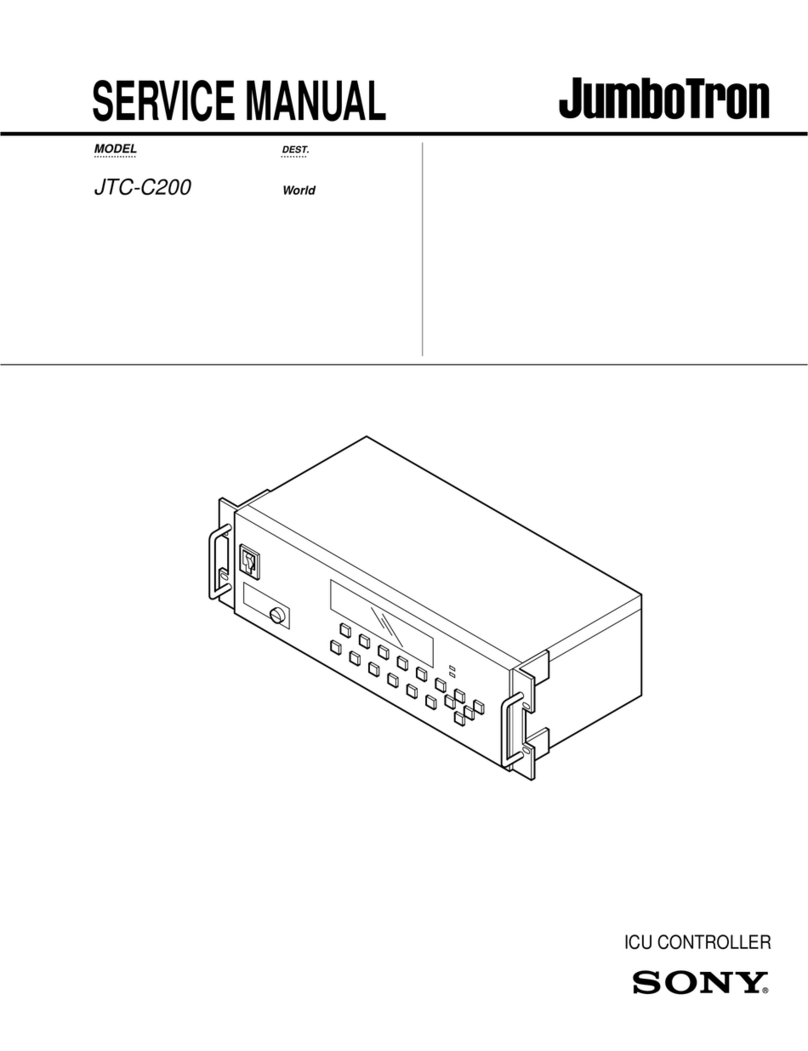
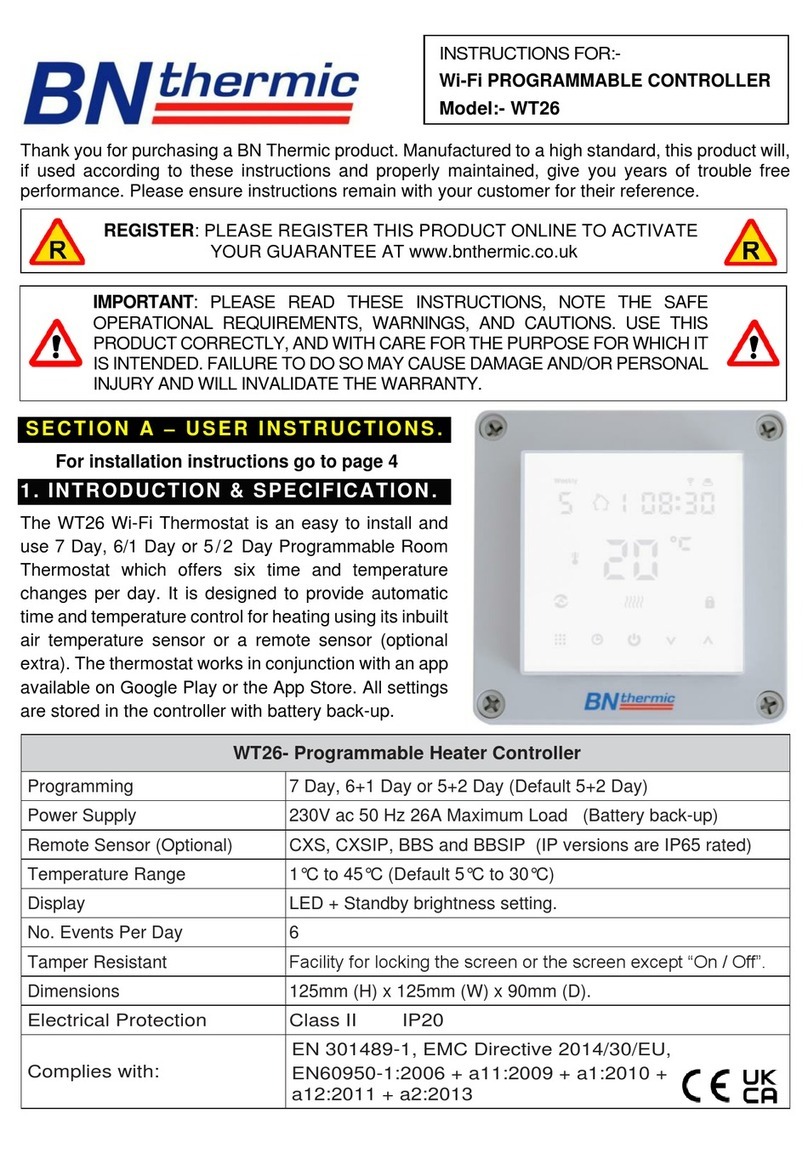
BEWATOR COTAG 4101-2 System manual

4101-2 Controller
Installation Handbook
HB02/105-EN Iss B
Applicability
This handbook applies to the 4101-2 Modular Controller,
the 4910 Power Supply Unit and all available modules.
© BEWATOR COTAG MAY 2000
ThishandbookisbasedonthebestinformationavailabletoBewatorCotagatthetimeofpublication.
Althougheveryeffortismadetokeepourdocumentationuptodate,smallchangeswhicharisefrom
the Company's policy of continuing product improvement are not necessarily incorporated. Some
products are not available in all countries. All orders are accepted only on the Company's standard
Conditions of Sale, copies of which are available on request.
Bewator Cotag, a division of Bewator Group Ltd, Mercers Row, Cambridge CB5 8EX, UK
Tel: +44 (0)1223 321535 Fax: +44 (0)1223 366799


Other documents you may need
The Access Control Software is described in handbook HB02/100.
Loop antenna installation is described in handbook HB02/106.

Safety
Thisequipmentmustbepoweredbyasupplywhichissuitablyinsulated
from the mains. The supply should be classed as SELV under the terms
of EN60950. You are recommended to use a 4910 or 4911 Power Supply
Unit.
The power supply must be connected to safety earth. A mains isolation
switch should be provided by the installer. Any third party equipment
connected must also be suitably insulated from the mains supply.
We also recommend that the 4101-2 Controller is connected to safety
earth via the power supply.
Controller relay outputs must not be connected to mains voltages.
Any fuses which are replaced must be of the recommended rating and
type.
Wiring connected by the installer must be adequate. The use of
inadequate wiring may present a fire hazard.
Except where specified the equipment is not suitable for outside use.
Some of the circuit boards provided contain lithium cells. These must
not be short circuited, dismantled or disposed of in fire. Consult local
regulations on disposal.
Lead acid batteries can present a variety of hazards. Use of batteries
other than those recommended should only be attempted by skilled
personnel. Lead acid batteries must not be short circuited, dismantled
or disposed of in fire. Consult local regulations on disposal.
Except where specified this equipment is not for use in safety critical
applications.
EMC Directive
4101-2Controllersand4910/4911PowerSupplyUnitsareindependently
tested to the harmonized standards (for emission and immunity) of the
EuropeanCommunity, permitting affixingof the CEmark. The CE mark
symbolizes the fact that the person responsible for the marking has
verified that the product conforms to all the provisions that apply to it.
The signature of the responsible person appears on our declaration of
conformity.
• The incorporation of non-tested components or equipment may
render the purchaser responsible for obtaining their own EMC
Certification for the resulting system.

i
Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction
Who should read this handbook...............................................................1-1
What the chapters describe......................................................................1-1
Chapter 2 The access control system
Introduction.............................................................................................2-1
Access control..........................................................................................2-1
Access tokens ...................................................................................2-2
Readers and Reading Heads ..............................................................2-3
Controllers........................................................................................2-3
The computer....................................................................................2-3
Door hardware..................................................................................2-4
4101-2 Modular Controllers.....................................................................2-5
Configurations - linking Controllers to a host computer ............................2-7
One 4101-2 Controller only............................................................2-7
Two 4101-2 Controllers configured as master and slave..................2-7
Several 4101-2 Controllers on one branch......................................2-8
Several 4101-2 Controllers on more than one branch......................2-8
Hardware Systems ............................................................................2-9
Local Hardware Systems................................................................2-9
Remote Site Hardware Systems ......................................................2-9
Chapter 3 4101-2 Modular Controller
Description..............................................................................................3-1
Connectors, switches and LEDs ...............................................................3-2
Module slots............................................................................................3-4
Siting.......................................................................................................3-5
Mounting.................................................................................................3-5
Connecting ..............................................................................................3-7
CONN1 .............................................................................................3-7
Connection to computer serial port.................................................3-7
Connection to Radio Controlled Clock.............................................3-8
CONN2 .............................................................................................3-8
CONN3 .............................................................................................3-9
CONN4 ...........................................................................................3-10
CONN5 ...........................................................................................3-10
Installing the RF module and teaching the Controller its
Distributor Code....................................................................................3-10
The Controller can only learn the Distributor Code once -
you cannot change it once learned................................................3-11
Setting up the Controller........................................................................3-12
Installing a system - noting the addresses of readers, inputs and
outputs..................................................................................................3-12
Motherboard LEDs.................................................................................3-13
Operating ..............................................................................................3-14

4101-2 Controller Installation Handbook
ii
Chapter 4 4322 Cotag Reader module
Description..............................................................................................4-1
Transmit and receive (Tx and Rx) ...................................................4-1
LEDs: red, amber and green (
R
,
A
and G)...................................4-1
Warning outputs (for local buzzer when door is left open
or forced).......................................................................................4-1
Relay connections: normally open (NO), normally closed (NC)
and common (Com)........................................................................4-1
Door exit control inputs (egress inputs - EG)...................................4-2
Door open monitoring inputs (door open and door forced
functions - DO)..............................................................................4-2
Connectors, jumpers and LEDs................................................................4-2
JU7...............................................................................................4-2
LEDs.............................................................................................4-3
Connecting ..............................................................................................4-3
280 Reading Head.............................................................................4-4
090 Reading Head.............................................................................4-4
Local warning bleepers......................................................................4-5
Relays (for door lock mechanisms).....................................................4-5
Using a relay to switch inductive DC loads .....................................4-5
Door open and door exit control (egress) inputs..................................4-6
Operating ................................................................................................4-6
Board LEDs ......................................................................................4-6
Reading Head LEDs ..........................................................................4-6
Green............................................................................................4-7
Red ...............................................................................................4-7
Amber ...........................................................................................4-7
Chapter 5 4422 Swipe Card Reader module
Description..............................................................................................5-1
Wiegand and Magnetic Stripe inputs (DØ and D1)...........................5-1
LEDs: red, amber and green (
R
,
A
and G)...................................5-1
Warning outputs (for local buzzer when door is left open or
forced)...........................................................................................5-1
Relay connections: normally open (NO), normally closed (NC)
and common (Com)........................................................................5-1
Door exit control inputs (egress inputs - EG)...................................5-1
Door open monitoring inputs (door open and door forced
functions - DO)..............................................................................5-2
Cdk...............................................................................................5-2
Connectors, jumpers and LEDs................................................................5-2
JU3/JU6.......................................................................................5-2
JU2/JU5.......................................................................................5-2
JU1/JU4.......................................................................................5-3
LEDs.............................................................................................5-3
Connecting ..............................................................................................5-3
Wiegand card reader or 5000 series reader ........................................5-4
Magnetic Stripe.................................................................................5-4
LEDs ................................................................................................5-5
Local warning bleepers......................................................................5-5

Contents
iii
Relays (for door lock mechanisms).....................................................5-6
Using a relay to switch inductive DC loads .....................................5-6
Door open and door exit control (egress) inputs..................................5-6
Setting up the Swipe Card Reader module ................................................5-7
Operating ................................................................................................5-7
Board LEDs ......................................................................................5-7
Door indicator LEDs..........................................................................5-8
Green............................................................................................5-8
Red ...............................................................................................5-8
Amber ...........................................................................................5-8
Chapter 6 4922 Dual PINpad Data Adapter and 4988 PINpad Data
Converter
Description..............................................................................................6-1
Installing the 4922 Dual PINpad Data Adapter on a 4322 or
4422 Reader module................................................................................6-1
Mounting the 4988 PINpad Data Converter...............................................6-2
4922/4988 connectors and LEDs.............................................................6-2
Connecting ..............................................................................................6-2
Connecting the 4922 Dual PINpad Data Adapter to one or
two 4988 PINpad Data Converters .....................................................6-2
Connecting the PINpad to the 4988 PINpad Data Converter................6-3
Connecting the PINpad LEDs.............................................................6-3
Testing ....................................................................................................6-3
LED outputs available from CONN1 of 4988 PINpad Data Converter .........6-4
Using the PINpad.....................................................................................6-4
PINpad types.....................................................................................6-5
Using your PIN for normal entry ........................................................6-5
Entering your PIN for the first time ....................................................6-5
Duress PIN........................................................................................6-6
Activating a trigger event under PIN control........................................6-6
Chapter 7 4253 Input/Output module 16/8 & 4953 I/O Status Display
module
Description..............................................................................................7-1
Supervised inputs..........................................................................7-1
Relay outputs ................................................................................7-1
Connectors and jumpers on the 4253 module...........................................7-2
Connecting the 4253 I/O module .............................................................7-2
Inputs...............................................................................................7-3
Configuring inputs.........................................................................7-4
Outputs............................................................................................7-5
Using a relay to switch inductive DC loads .....................................7-5
Setting up the 4253 I/O module...............................................................7-5
Inputs ...........................................................................................7-5
Outputs.........................................................................................7-6
Installing the 4953 Status Display module ...............................................7-6
LEDs and jumpers on the 4953 module....................................................7-7
Setting up the 4953 I/O Status Display module........................................7-7
4953 I/O Status Display module LED indications.....................................7-7
Input indications ...........................................................................7-7

4101-2 Controller Installation Handbook
iv
Output indications.........................................................................7-7
Chapter 8 4230/4232/4235 Communications modules
Hardware Systems...................................................................................8-1
Local Hardware Systems................................................................8-1
Remote Site Hardware Systems ......................................................8-1
Which Comms module do you need? ........................................................8-1
One or two Controller system .........................................................8-2
Controllers at remote sites..............................................................8-3
4-wire RS485 multidrop comms ...............................................................8-3
RS232/RS485 conversion and baud rate conversion.................................8-3
Maximum of two Comms modules in any one 4101-2 Controller ...............8-3
Connectors, jumpers, switch and LEDs ....................................................8-4
Comms layouts........................................................................................8-6
The most common system - 1 Comms module ................................8-6
Expanded system using two Comms modules.................................8-7
Expanded system - at least three Comms modules..........................8-8
Extending the length of a branch....................................................8-8
Using a leased-line and modems to operate the system
across sites....................................................................................8-9
Using one or more dial-up modems to communicate with
Controllers at remote sites............................................................8-10
Summary of upstream and downstream connections to a Comms
module..................................................................................................8-11
Connecting ............................................................................................8-11
Connecting the Comms module to the computer and Controllers ......8-12
Connecting the host computer to the Comms module....................8-13
Connecting Controllers to a Comms module..................................8-14
Connecting downstream Comms modules........................................8-15
Connecting a Comms module to a modem at a remote site ...............8-16
Setting up Comms modules....................................................................8-17
Notes about installing Comms modules ..................................................8-18
LEDs.....................................................................................................8-18
Power up (Comms modules with DIR/DIAL link set to DIR)...........8-18
Power up (Comms modules with DIR/DIAL link set to DIAL) .........8-19
Running ......................................................................................8-19
Chapter 9 4105-2 Memory Expansion module
Description..............................................................................................9-1
Installation..............................................................................................9-1
Installing a 4105-2 Memory Expansion module in a 4101 Controller ..9-2
Chapter 10 4210 RF module
Description............................................................................................10-1
Installing the RF module and teaching the Controller its
Distributor Code....................................................................................10-1
The Controller can only learn the Distributor Code once -
you cannot change it once learned................................................10-2

Contents
v
Chapter 11 4910 Power Supply Unit
Description............................................................................................11-1
Safety....................................................................................................11-2
Siting.....................................................................................................11-2
Installing...............................................................................................11-3
Mounting........................................................................................11-3
Setting the mains input voltage........................................................11-4
Fitting the battery ...........................................................................11-5
Connecting ............................................................................................11-6
Connecting the mains cable.............................................................11-6
CONN1 ...........................................................................................11-7
CONN2 ...........................................................................................11-7
LEDs.....................................................................................................11-7
POWER .......................................................................................11-7
CHARGED...................................................................................11-7
CHARGING..................................................................................11-7
Fuses ....................................................................................................11-8
Chapter 12 4914 auxiliary 24 volt converter
Description............................................................................................12-1
Installation............................................................................................12-1
Connecting ............................................................................................12-2
Chapter 13 Radio Controlled Clock
Connecting ............................................................................................13-1
Chapter 14 Cables
812 cable...............................................................................................14-3
Description .....................................................................................14-3
Specification ...................................................................................14-4
Mechanical properties..................................................................14-4
Electrical properties.....................................................................14-4
Break-out box.................................................................................14-5
Chapter 15 Antennas
Introduction...........................................................................................15-1
Antenna summary .................................................................................15-1
Reading Heads.............................................................................15-1
Loop antennas.............................................................................15-1
280 Reading Head .................................................................................15-3
Advantages..................................................................................15-3
Installing the 280 Reading Head......................................................15-3
Removing the cover......................................................................15-3
Mounting.....................................................................................15-4
Connecting the 280 Reading Head...................................................15-5
090 Reading Head .................................................................................15-6
Advantages..................................................................................15-6
Installing the 090 Reading Head......................................................15-6
Connecting the 090 Reading Head...................................................15-8
Loop antennas.......................................................................................15-8

4101-2 Controller Installation Handbook
vi
Chapter 16 Connecting Bewator Cotag Readers to 4101-2 Controllers
5291 Proximity Reader...........................................................................16-1
Connections.................................................................................16-1
Controller/module configuration ..................................................16-1
5291 Reader configuration...........................................................16-1
5298 PIN & Proximity Reader.................................................................16-2
Connections.................................................................................16-2
Controller/module configuration ..................................................16-2
5298 Reader configuration...........................................................16-2
BC16 Mag Stripe Reader........................................................................16-3
Connections.................................................................................16-3
Controller/module configuration ..................................................16-3
BC16 Reader configuration ..........................................................16-3
Chapter 17 Earthing and screening
Earthing................................................................................................17-1
Connecting the cable screens (shields)....................................................17-2
Fitting the ferrite sleeves ........................................................................17-3
Chapter 18 Commissioning
Making a plan of the hardware...............................................................18-1
Setting the Controller and Comms module addresses..............................18-1
Testing the communications to each Controller in a Local
Hardware System...................................................................................18-1
With the host computer connected and on line..............................18-1
Without the computer connected..................................................18-3
Results of checking comms ..........................................................18-3
Testing the communications between the Comms module and the
modem at a remote site..........................................................................18-4
Testing the communications to each Controller at a remote site...............18-5
Teaching 4101-2 Controllers the Distributor Code ..................................18-5
Testing the readers ................................................................................18-5
Results of testing the readers .......................................................18-6
Chapter 19 Fault finding
System never worked .............................................................................19-1
Getting the comms working .............................................................19-2
RS485 connections betweem Comms module and Controllers .......19-2
RS232 connections between PC and Comms module or Controller.19-4
Entering a site code.........................................................................19-4
Downloading the data from the Software..........................................19-4
Checking the reader modules ..........................................................19-4
Reader not being polled................................................................19-4
Checking the antennas using the 922 Test Card ..............................19-5
No transmit signal .......................................................................19-5
Reduced transmit signal...............................................................19-5
Checking the receive range at the antenna.......................................19-5
Low receive range on a reading head ............................................19-5
Low receive range on a loop antenna ............................................19-5
Correct Tx and Rx range but card not unlocking door ...................19-5
Checking the Software (because no cards are working).....................19-6

Contents
vii
System stopped working ........................................................................19-6
Detailed fault finding .............................................................................19-7
Card(s)............................................................................................19-7
No cards working.........................................................................19-7
Few cards not working.................................................................19-7
Single card not working................................................................19-7
Reader/antenna..............................................................................19-7
No transmit range ...........................................................................19-7
Is the Controller polling the reader?..............................................19-7
Is there power to the Controller?...................................................19-8
Low transmit range .........................................................................19-9
Low receive range with a reading head.............................................19-9
Low receive range with a loop antenna...........................................19-10
Controller and reader modules ......................................................19-11
Is there power to the Controller?.................................................19-11
Is the Controller polling the reader?............................................19-11
Are the comms working? ...............................................................19-12
Is the correct software running? .................................................19-12
Is the correct Comms module fitted?...........................................19-12
Is the PC Com port OK? .............................................................19-13
Is the RS232/RS485 Selection OK?............................................19-13
Are the cables too long? .............................................................19-13
Checking the RS232 connections at the PC.................................19-13
One or two controller systems only -...........................................19-14
checking the RS232 connections at the controller .......................19-14
Multiple controller systems - ......................................................19-14
checking the RS232 connections at the Comms module..............19-14
Checking the RS485 Connections downstream from the
Comms module to the controllers ...............................................19-15
Appendix 1 Wiring diagrams................................................... A-1-1
Appendix 2 Programming cards.............................................. A-2-1
Appendix 3 Wiring and setting up a door for anti-passback..... A-3-1

4101-2 Controller Installation Handbook
viii

1-1
Chapter 1
Introduction
Who should read this handbook
Anyone who needs to understand the Access Control System
hardware so they can configure and install systems.
What the chapters describe
Chapter 2 is a general description of access control in general and the
system which uses 4101-2 Controllers in particular.
Chapters 3 to 12 describe the modular Controller and its modules.
Chapter 13 describes the cables you should use to wire up the
system.
Chapter 14 describes the different types of antenna you can use for
hands free and proximity reading of Cotag Cards.
Chapter 15 describes how to connect earths and screens so that the
system complies with international PTT and EMC regulations.
Chapter 16 describes how to get the system working after
installation.
Chapter 17 gives a guide to simple fault finding on the access control
system.
Appendix 1 shows wiring diagrams for connecting the system up.
Appendix 2 describes how to program Cotag cards and tags for use
with the access control system.
Appendix 3 describes how to connect anti-passback on a single door.

4101-2 Controller Installation Handbook
1-2

2-1
Chapter 2
The access control system
Introduction
The access control system is designed to be flexible in the way it is
configured for different applications and powerful in its function. Its
modular structure provides a cost-effective adaptable system.
The 4101-2 Controllers are at the heart of the system. They can be
used either with Cotag Access Control Software or with other
supervising software as part of an OEM system. They provide the
wide range of extra functions required by the users of modern access
control systems.
4101-2 Controller features include:
• the same controller for all tasks.
• up to eight access points per controller.
• a family of application modules to fit different application
requirements.
• distributed intelligence to provide system speed and integrity.
• fast and powerful communications structure.
• programmable logical control of input/output events.
• simple installation.
• automatic system configuration during commissioning.
Access control
An access control system uses an access token - usually a card - to
identify its holder and either grant or deny access to a door (or
“access point”). To achieve this, the number or code contained in the
card is read by a reader or reading head under control of an
electronic circuit known as a controller. The controller takes the
access decision (whether or not to let the cardholder through the
door) and operates the door using an electrical door lock mechanism

4101-2 Controller Installation Handbook
2-2
of some kind. One or more controllers are supervised by a computer,
usually a PC.
The diagram below shows a typical layout of the access control
system.
Computer
Printer
ControllerControllerController
Reading Head PINpad
Access tokens
The access control system can support all kinds of access token.
These will usually be proximity Cards or Tags using RF reading
technology to give Real Hands Free reading range.
Proximity Cards and Tags contain a custom micro chip and an
antenna system which enable the security codes stored in the chip to
be read by a reading head.
The system also supports the use of other card technologies such as
Wiegand, Magnetic Stripe or Bar Code and other identification
techniques such as PIN entry, fingerprint recognition or any other
biometric system.

The access control system
2-3
Readers and Reading Heads
Each different card or identification technology is associated with a
different reader.
The 4101-2 Controllers can drive the full range of Cotag Reading
Heads and Loop Antennas. The Reading Head consists of
transmitting and receiving antennas which are driven by a reader
module fitted inside the modular controller. When the cardholder
brings the card within range of the Reading Head the interrogation
signals from the Reading Head activate the card’s microchip. The
number stored in the card is then transmitted to the Reading Head.
4101-2 Controllers can also take inputs from any other card reader
or identification system which has a Wiegand or Magnetic Stripe style
of electrical interface. (Consult the chapter on swipe card modules or
call Technical Support if you need help with an interface.)
Controllers
The controller provides the intelligence and memory needed for the
access control decision, and the drive signals for the reader. It can
also receive input from monitored sensors and provide control of
other devices and systems via its relay outputs. This includes
activating a door lock and monitoring the door status.
One or more controllers are connected via a serial data link to the
supervising computer to make up the complete system.
The computer
The controllers in the system are all linked to a supervising
computer (or computers on a network). The computer is used to set
up the system database and download it to each controller. Most
decisions can then be taken by the controller without reference to the
computer. This means that the system can respond faster and will
continue to work even if the computer or its serial connections fail.
This technique is known as “distributed processing”.
The computer can also be used to monitor information about access
transactions, alarms and other messages from the controllers. Also, if
the computer is off-line, the controllers store this information for later
transmission.
4101-2 Controllers can be managed by a PC running the Access
Control Software or by any other computer system which has
software written to handle the Communications Protocol.

4101-2 Controller Installation Handbook
2-4
Door hardware
The access control system is completed by electric door locks and
sensors. Remarks here are confined to general observations.
Door locks must be carefully chosen to match the requirement and
the door structure itself. They are usually the only moving parts in
the whole system. Some designs of lock remain locked when the
power or the system fails (“fail secure”) and other designs unlock
when the power or the system fails (“fail safe”). It is very important to
ensure that the requirements of fire safety and the rules of the local
fire safety authority are taken into account.
Sensors can be used to show if a door is open or closed. They can
also be used to monitor almost any other part of a building or its
installed equipment to provide status information on the security of
the building or anything else.

The access control system
2-5
4101-2 Modular Controllers
Each controller is housed in a metal case with removable cover and
internal chassis for ease of installation and maintenance.
The chassis carries a motherboard and provides slots for five modules
plus a 4210 RF Module for proximity cards.
0
2
4
6
89
1
3
5
7
LEDs
Module
slots
Case Motherboard Chassis
Memory
expansion
connector Tamper
switch
The motherboard has a microprocessor circuit which manages the
modules, takes access control decisions and communicates with the
host computer. It also has enough RAM to retain all the access
control data needed for up to eight access points and 13,000
cardholders. An expansion connector for the 4105-2 Memory
Expansion Module enables the RAM to be increased to store up to
77,000 cards.
The 4210 RF Module is used in any 4101-2 Controller which also
contains Cotag reader modules. It occupies its own slot at the bottom
of the controller, smaller than all the other slots. If a controller is not
being used for Cotag readers (either because swipe cards are being
used or because the controller is only handling inputs and outputs)
then it does not need the RF Module.

4101-2 Controller Installation Handbook
2-6
The five other module slots can all take application modules
according to the needs of the installation:
Reader modules handling two readers (with PINpads if required) can
be fitted in any of the top four module slots. There are currently two
types of reader module:
• 4322 Cotag Reader module
• 4422 Swipe Card Reader module
Input/Output modules can be fitted in any of the top five slots. There
is currently one type of I/O module:
• 4253 Input/Output module 16/8 (provides 16 inputs and 8
outputs)
Up to two Communications modules can be fitted in any of the top
five slots. These are used to manage the controller communications -
see later for different configurations. There are currently three types
of Comms module:
• 4230 Communications module (the first Comms module in
systems with 17 to 64 Access Points)
• 4232 Communications module (for general use anywhere in
the system, and the first Comms module in systems with 1 to
16 Access Points)
• 4235 Communications module (the first Comms module in
systems with more than 64 Access Points)
Table of contents
Popular Controllers manuals by other brands

Nordson EFD
Nordson EFD ValveMate 7197PCP operating manual

HM Digital
HM Digital PS-202 user guide

Pixsys
Pixsys DRR460 Series user manual

ActronAir
ActronAir QTW-1000 Installation and commissioning manual

Siemens
Siemens TE7291-0A Series Installation, operation & maintenance instructions

National Instruments
National Instruments AT-GPIB/TNT Getting started