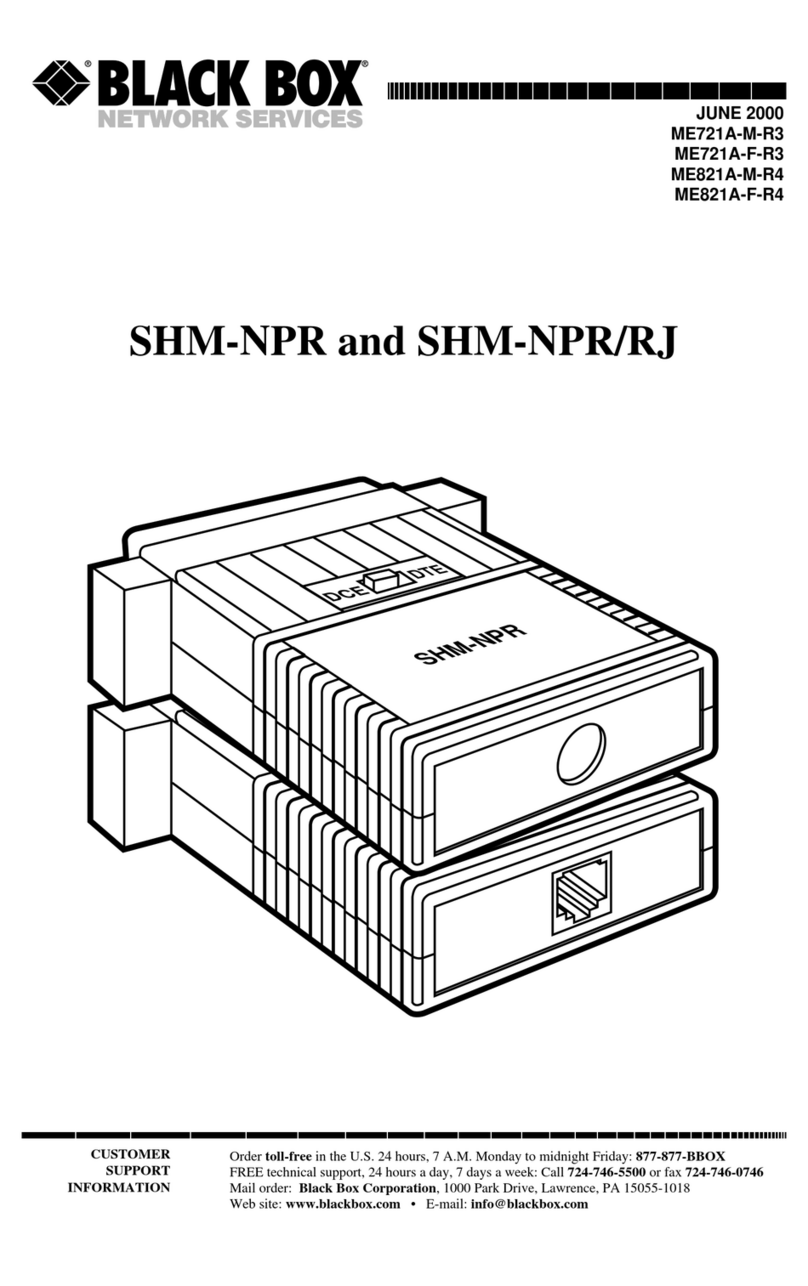
TX+
TX-
RX+
RX-
J1
RS-232
CONNECTOR
SPECIFICATIONS:
Interface: RS-232-C (DCE) to attached local device;
Proprietary balanced 4-wire to line.
Protocol: Synchronous
Clock Source: Local internal (each SHM-B Sync unit
independently generates it's own clock.
Operation: 4-wire, Full Duplex, point-to-point.
Flow Control: Hardware (RTS and/or DTR), local only (control
signals are not passed across the 4-wire line;
transparent to software (X-ON/X-OFF).
Data Rate: 19,200, 9600, 4800, 2400, 1200, or 600 bps.
Loopback: Simultaneous local loopback to attached RS-232
device and remote loopback to remote SHM-B Sync
(user-controllable)
User Controls: (1) Front-mounted push-button to turn loopback
ON and OFF. (6) Internal pairs of jumper posts for
setting the data rate. (3) Internal pairs of jumper posts
for setting CTS delay.
Connectors: (1) DB25 Female connector; (1) 4-screw
terminal block.
Indicators: (2); (1) TD and (1) RD.
Leads/Signals Supported: RS-232: TD, RD, RTS, CTS, DSR,
SGND, DCD, TC, RC, DTR. Pins 1 thru 8, 15, 17,
and 20.
Surge Protection: Internal opto-isolators (effective up to
20 VDC) on transmit and receive lines.
Power: Power is supplied by a wall-mounted power transformer.
Primary 230VAC +/- 10%, 50 Hz, 5 watts.
Secondary: 17 VAC, 700 ma
External Power Supply Part # = PS008E
S2
Loopback
TD
RD
TERMINAL
BLOCK
GND
LONG
SHORT
NONE
CTS-DELAY
SELECTION
600
1200
2400
4800
9600
19200
DATA RATE
SELECTION
Data Rate
in bps Distance
in miles Distance
in km
19,200
9,600
4,800
2,400
1,200
600
.75
.9
1
2
3.5
5
1.2
1.4
8
5.6
1.6
3.2
INTRODUCTION:
The Short-Haul Modem-B Sync (SHM-B Sync for short) is a synchronous full-duplex 4-wire line
driver and receiver that makes it possible for two RS-232-C devices to communicate across
distances up to 5 miles (8 km), at data rates up to 19,200 bps. In addition to its transmitter and
receiver circuits, the SHM-B Sync also features status LED's a loopback switch, and support for
RS-232 clock and control signals.
The SHM-B Sync is designed to operate with 4-wire cable. It is also designed for maximum
operator safety. There are no voltages greater than 12 VDC or 17 VAC present on the unit's circuit
board. Opto-isolation circuits protect both the transmit and receive lines against voltage surges (up
to 20 VDC) such as those caused by lightning.
The SHM-B Sync is available in either a 120-VAC (ME801A) or 220-VAC (ME801A-E)
standalone version or a card version (ME801-C) that will fit in our ME810 or RM007 card chassis.
CONFIGURATION:
Before you install a pair a SHM-B Sync units, you should set their configuration jumpers as
necessary. Caution!
If you have the card version, make very sure that the SHM-B
Sync card is not installed in a powered chassis when you
configure it. If you have the standalone version, make sure
that it is unplugged and is disconnected from any other devices.
No voltages greater than 17 VAC are ever present on the board
even when it is powered, but the possibility of electric shock
should always be avoided.
When you handle the SHM-B Sync's circuit board, take every
reasonable precaution against damaging the board with static
electricity. At the very least, discharge yourself by touching a
fixed metal surface before handling the board; if possible, stand
on an anti-static mat and wear a grounding strap or anti-static
gloves.
There are two sets of jumper posts mounted on the SHM-B Sync's circuit board.
1. Six pairs of posts are used to set the SHM-B Sync's data rate. They're at the front of
the left-hand side of the board. The six possible data-rate settings are 600, 1200,
2400, 4800, 9600, and 19200 bps. The factory-default value is 9600 bps; if your
RS-232 equipment is using one of the other data rates, set the jumpers in both units
accordingly by moving the jumper to the appropriate pair of posts. (The SHM-B Sync
units must both be set to the same data rate, which they will generate internally; the
attached devices must be set to accept clock from them).
2. Three pairs of posts are used to set the SHM-B Sync's CTS delay. They are at the
rear of the right-hand side of the board. The CTS delay is the amount of time that the
SHM-B Sync waits after detecting that the attached device has raised RTS before it
responds by raising CTS. The possible settings are LONG (53 ms), SHORT (7 ms)
or NONE. Factory default is NONE, but if your RS-232 device needs to see a CTS
delay in order to function properly, move the jumper to the appropriate post in that
SHM-B Sync only. INSTALLATION:
1. Open the case of one of the SHM-B Sync units.
2. Thread the bare ends of the four wires into the four screw terminals on the SHM-B
Sync's board marked RX+, RX-, TX+, and TX-. Refer to drawing on the next page for
proper wiring of the terminal blocks.
3. Plug one end of an RS-232 cable into the DB25 female connector on the rear of the
unit. Avoid running this cable farther than 50 ft.
4. Plug the other end of the RS-232 cable into a powered-down device whose serial
communication you want to extend.
5. Repeat steps 1 thru 4 with the remote site's SHM-B Sync unit.