CONTENT
DOCUMENTS INFORMATION................................................ERROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
1. PHRASE AND REFERENCE LITERATURE................ERROR! BOOKMARK NOT DEFINED.
1.1 Breviary........................................................................................... Error! Bookmark not defined.
1.2 Phrase.............................................................................................. Error! Bookmark not defined.
1.3 Reference literature ......................................................................... Error! Bookmark not defined.
2. INTRODUCTION................................................................................................................................4
2.1 Compile Objective ............................................................................................................................4
2.2 Project Background...........................................................................................................................4
3. LIFE 8 SUMMARIZE.........................................................................................................................5
3.1 LIFE 8 product description ...............................................................................................................7
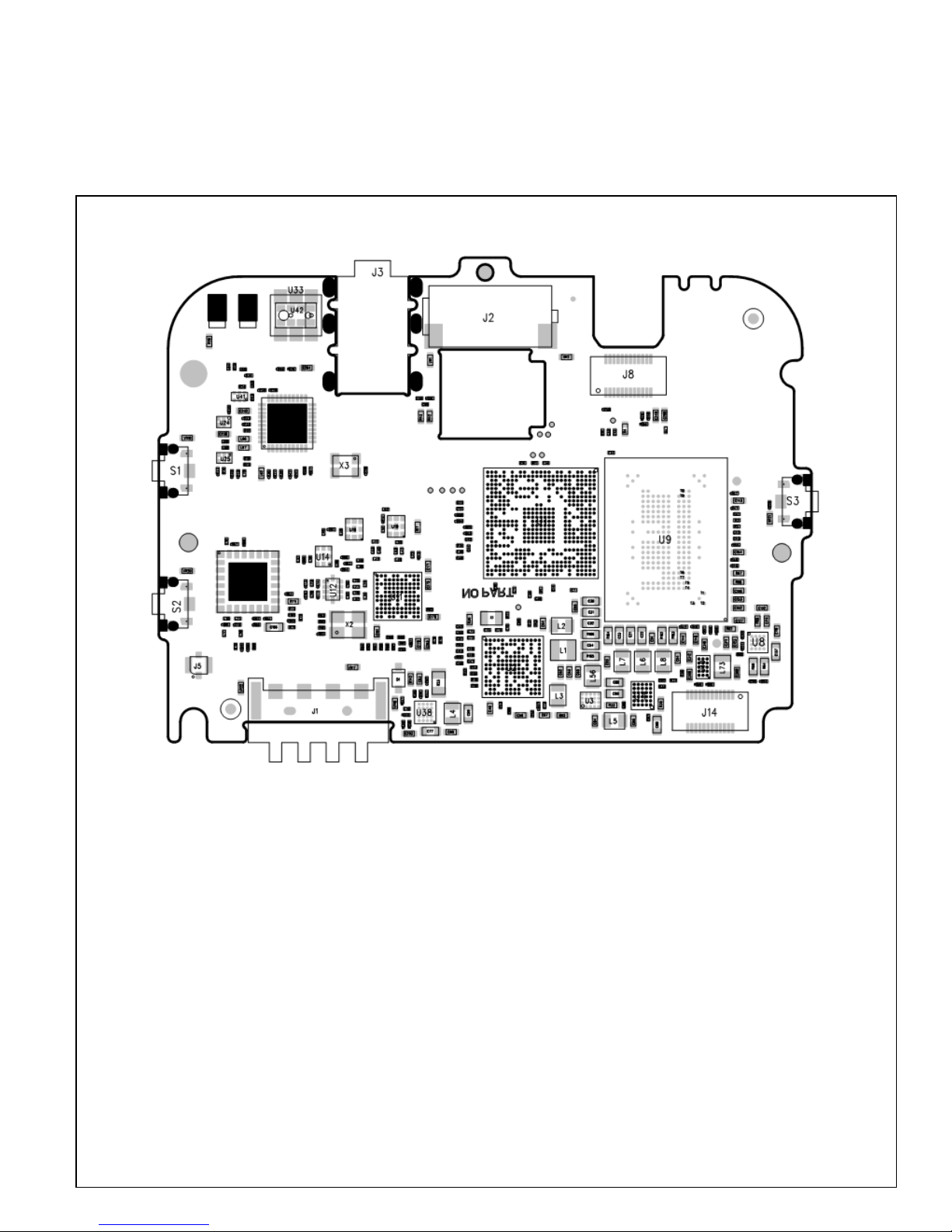
3.2 Assembly components on TOP layer as follow.................................................................................8
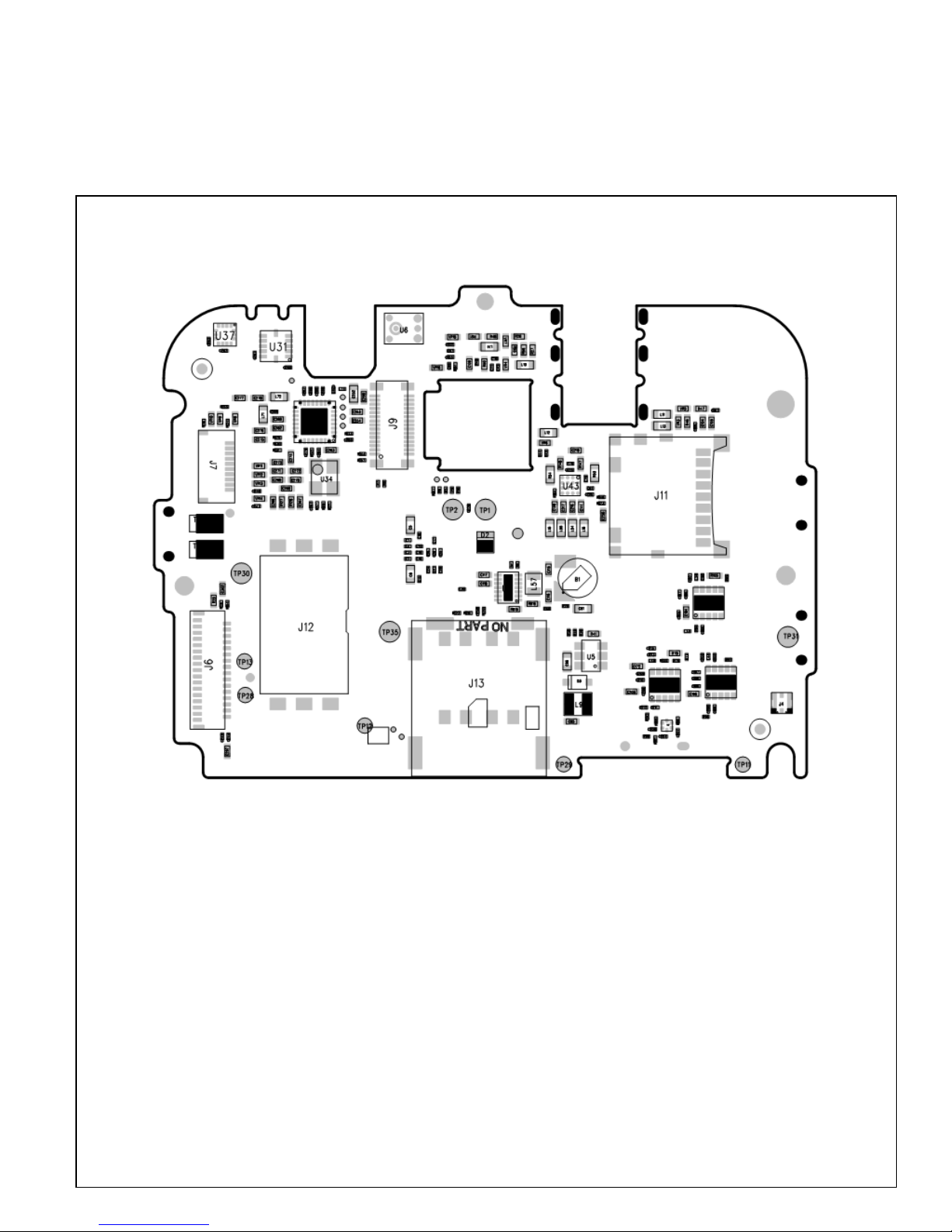
3.3 Assembly components on Bottom layer as follow:........................................................................9
3.4 LIFE 8 Hardware Diagram..............................................................................................................10
4. RF PARTS..........................................................................................................................................12
4.1 Basic diagram:.................................................................................................................................12
4.2 TX Part troubleshooting.................................................................................................................13
4.2.1 TX process analysis..............................................................................................................13
4.2.2 TX circuit troubleshooting.....................................................................................................14
4.2.3 TX circuit examine and repair flow chart ..............................................................................15
4.3 RX Circuit troubleshooting .............................................................................................................16
4.3.1 RX circuit analysis.................................................................................................................16
4.3.2 RF Part examine and Repair..................................................................................................17
4.3.3 RX examine and repair flow chart........................................................................................19
5. BASEBAND PARTS..........................................................................................................................20
5.1 Power Management Part Diagram ..................................................................................................20
5.2 Power on .........................................................................................................................................21
5.2.1 Normal Power On..................................................................................................................21
5.2.2 Schedule Power On/OFF .......................................................................................................21
5.2.3 Charge Power On...................................................................................................................22
5.2.4 Phone can not power on troubleshooting:...........................................................................22
5.3 Audio Part troubleshooting .............................................................................................................22
5.3.1 Speaker Circuit ......................................................................................................................22
5.3.2 MIC Circuit............................................................................................................................22
5.3.3 Earphone Circuit....................................................................................................................23
5.3.4 Receiver Circuit.....................................................................................................................23
5.4 Vibration issue: ...............................................................................................................................24
5.5 Download process...........................................................................................................................25
5.5.1 NAND Flash Download ........................................................................................................25
5.6 LCD Part .........................................................................................................................................25
5.7 CTP Part..........................................................................................................................................26
5.8 Camera part.....................................................................................................................................26
5.9 SIM card issue:................................................................................................................................26