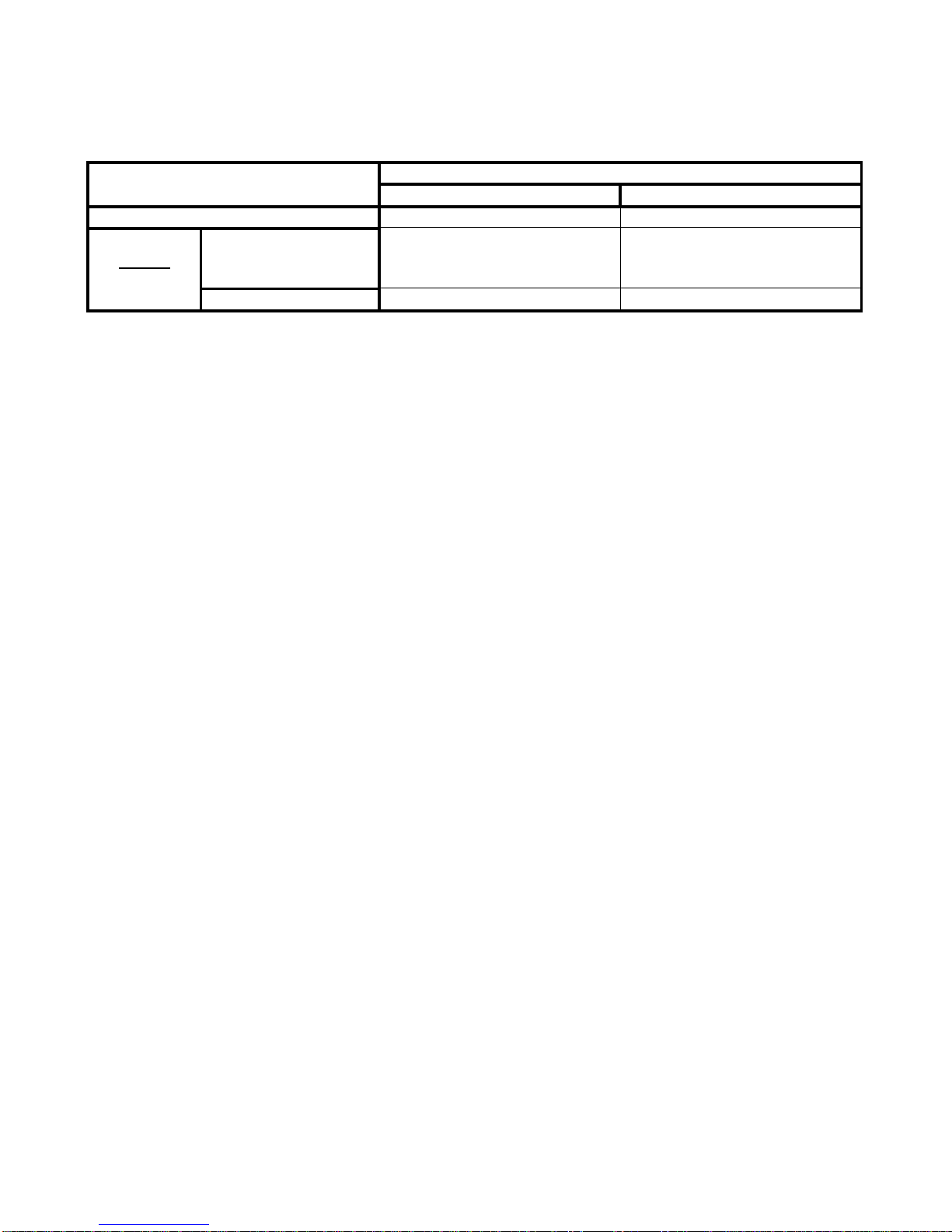
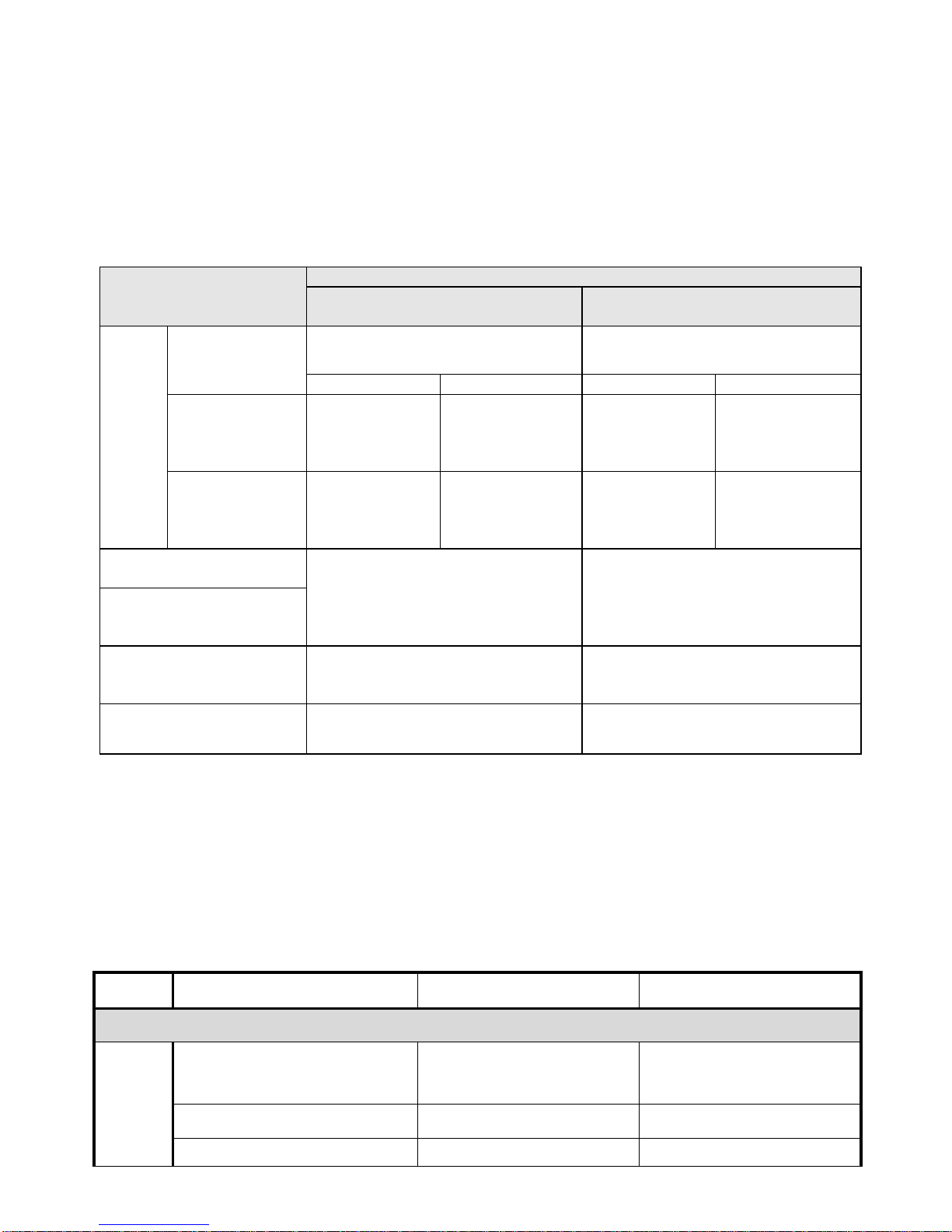
10
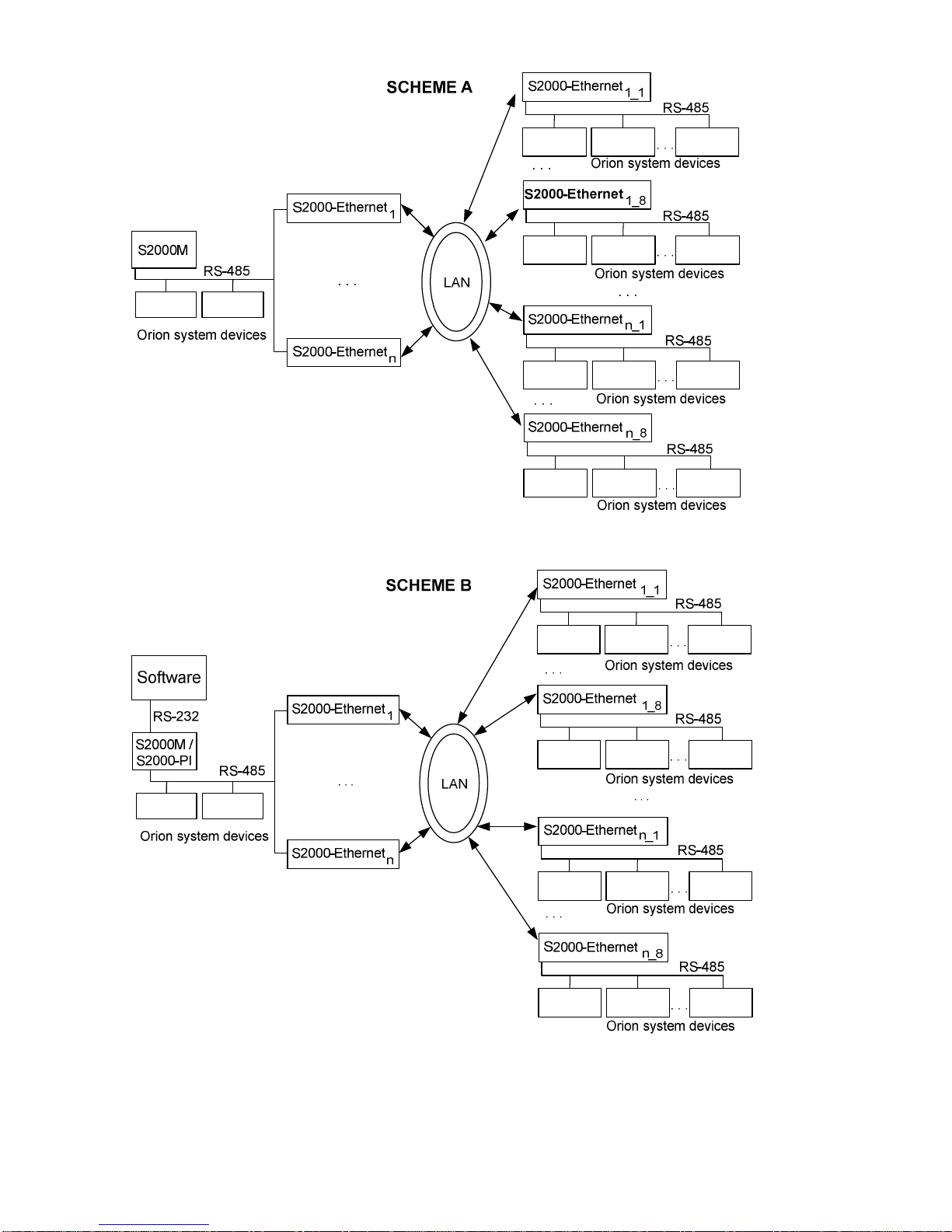
Figure 3. Common Diagrams for Using the S2000-Ethernet as a Component of an Orion System
1.4.4 Preparing the S2000-Ethernet for Operation
1.4.4.1 Configuring the S2000-Ethernet
Editing configuration parameters of the S2000-Ethernet is to be performed by means of UProg
Configuration Tool. The last version of UProg is available at the site http://bolid.com in Software
Section. Configuration parameters of the S2000-Ethernet along with their ranges and default values
are shown in Table 5. Devices S2000-Ethernet of v.2.52 and higher support two ways to change
device configuration: over the RS-232 interface (as before) and over the LAN (new). The relevant
way to configure the S2000-Ethernet is to be selected by means of UProg (such selecting is
supported for UProg of v.4.1.0.52 and higher; configuring the S2000-Ethernet via a PC COM
port is supported by all versions of UProg). Detailed instructions how to configure devices over
the local network with the help of UProg is available at the site http://bolid.com (Section
“Software”).
Configuring the S2000-Ethernet over the RS-232. To configure the S2000-Ethernet over the
RS-232, connect the S2000-Ethernet to a COM port of the PC and switch the device in the
configuration mode (jumper position: Config) – see Figure 1.
Configuring the S2000-Ethernet over the LAN (with the help of Orion 2 Device Interface
Protocol Service). The factory value of the IP address of the S2000-Ethernet is 192.168.127.254.
The device can be configured over the LAN in all operation modes (including Config). To have an
access to the device configuration over the LAN, do the following in UProg:
•Set Orion 2 service access parameters (for communicating with devices using the Orion 2
protocol): specify the IP address of the PC where the service has been installed and the
service port.
•Select the Orion 2 Service branch in the Device Tree and add a new line specifying the
parameters as shown in Table 4.
Access to reading and changing of the device configuration is granted if:
•IP address of the PC with the service «Orion 2 - Device Interface Protocol» is specified in
Remote Device List in S20000-Ethernet configuration. In this case, to have an access to the
S2000-Ethernet the following configuration parameters of the S2000-Ethernet are required:
UDP port (with the default value of 40000) and the Master key of the relevant record of
Remote Device List;
•IP address of the computer where the driver has been installed is not specified in the list of
remote devices, but connection with the unknown address is permitted in the device
configuration (it is permitted by default) and this connection is not occupied by anybody at
the moment. In this case, to access the S2000-Ethernet the following configuration
parameters are required: UDP port of the S2000-Ethernet for unknown address (factory
value 40001) and Master key for unknown address.