8
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
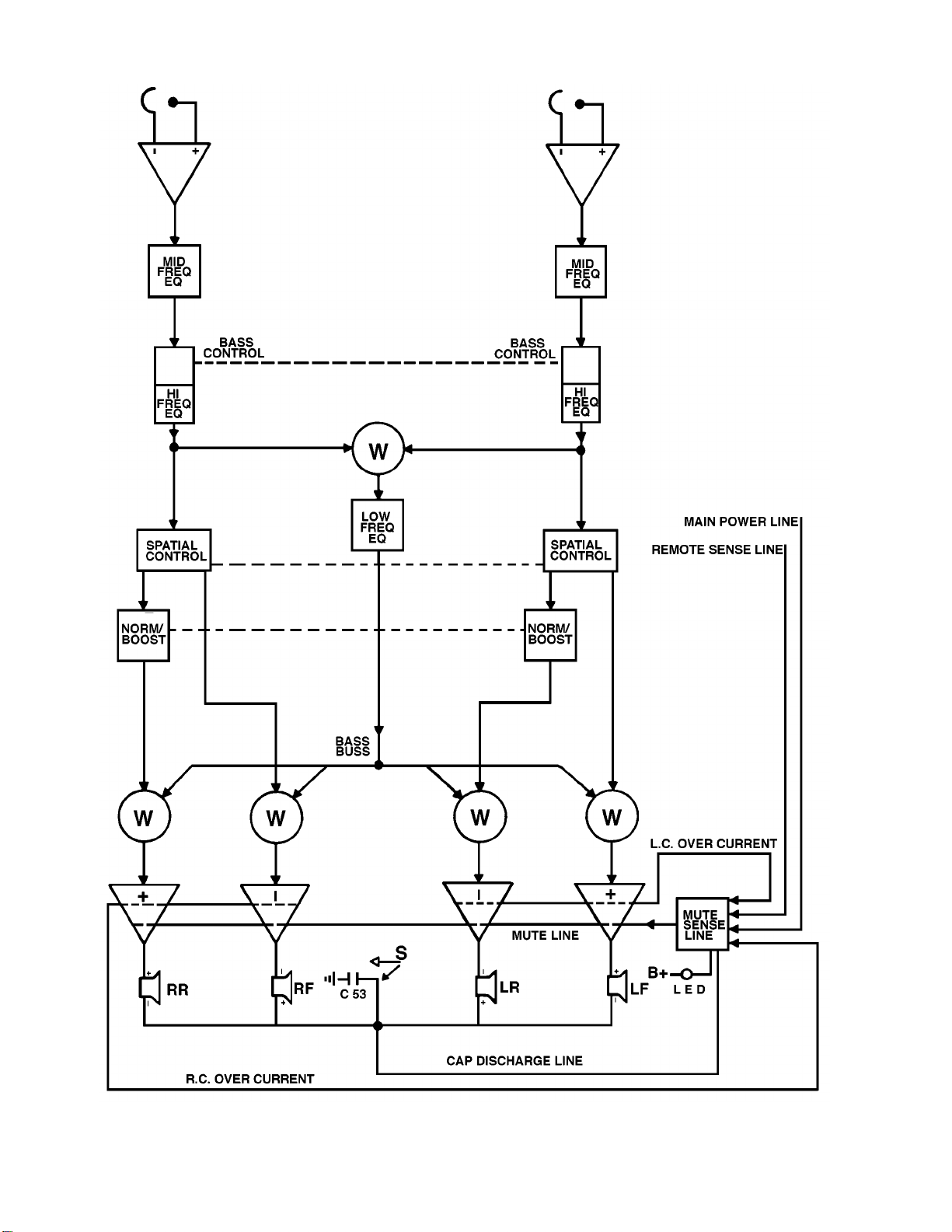
The Bose®1201 Booster/Equalizer is a two speaker system similar to the 1401™ II. In gen-
eral, the same troubleshooting rules apply to both units. The RCAand high level inputs are the
same, as well as the connectors for the power and speakers. The 1201 also has mute and
short circuit protection circuits.
The 1201 has two amplifiers instead of four. The system has switchable equalization for the
4.5" driver or the new 6"x 9" speakers. The equalizer attenuates frequencies above 1kHz in the
4.5" position and turns off the bass equalization in the 6"x 9" position. The 1201 does not have
Spatial Control™ or frequency controls.
A new feature for the 1201 is an input level control that provides the ability to interface with a
variety of front ends. The input level control adjusts the amp gain for a power sensitivity of
approximately 100-1000 mV (low level) and 1-10 Volts (high level) to produce 25 Watts of
power per channel at full output at 1 kHz.
Also new in the 1201 amplifier is a compressor circuit. The compressor monitors the power
amplifiers and reduces the input gain when the power amplifier begins to clip. Comprised of
1/2 of U1 and U3, U3 acts as a current controlled resistor across R109/209 whose equivalent
resistance is inversely proportional to the current into pins 3/6. With no control current, U3
looks like an open circuit. As the current into pins 3/6 increases, the net resistance of R109/
209 goes down and reduces the compressor amp gain. Control current is provided by
detector/driver circuit of Q601-603. The outputs of the power amps (U4, U5, pin 6) pulses
when the amp begins to clip. These pulses are detected by Q602, 603 and is filtered. The DC
voltage is converted to control currents by R302, 402.
The mute circuit is different than in the 1401 II. It contains two comparators that serve as
voltage and time delay sensors. U6, pins 1-3, senses the ANT SW control voltage and goes
low if the ANT SW input or supply falls below 9-10 Volts. When U6, pin 1, goes high, C510
charges through R516. When C510's voltage exceeds that of U6, pin 6, (after approximately
2.5 seconds) pin 7 goes high and unmutes the amplifier. If U6, pin 1 goes low, C510 dis-
charges immediately through D501 and mutes the amplifier. During short-circuit conditions,
Q503 turns on and pulls U6, pin 2, high causing pin 1 to go low, starting the mute cycle.
The over-current protection network is Q54 and Q55. If the unit draws substantial current
across either or both R137 or R139 the voltage approaches .6 volts, creating the same chain
of events as previously mentioned in the turn off section. The over-current protection circuit will
attempt to recycle a turn on approximately every three seconds. If the over-current conditions
are still present, the unit will not turn on.
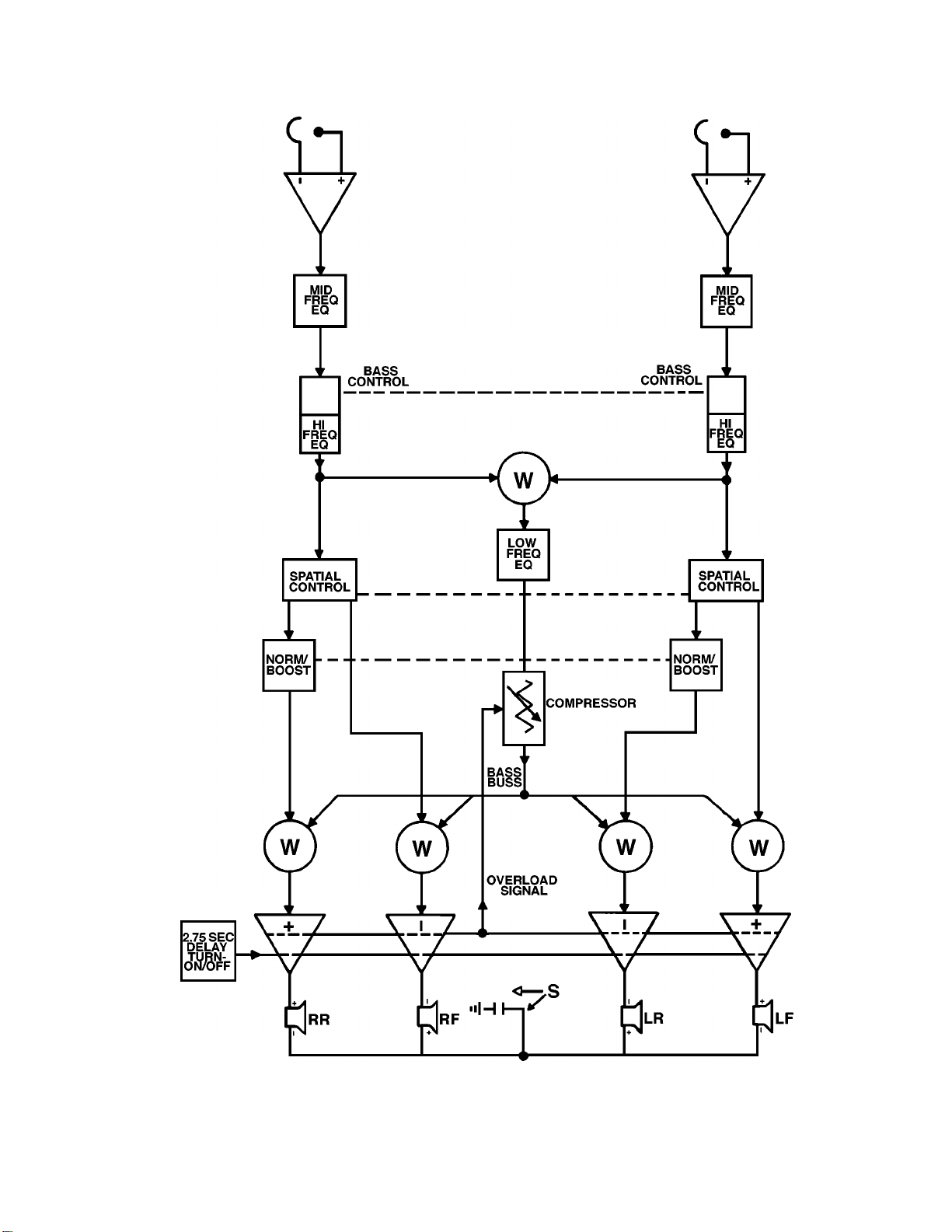
The 1401™ series Ihas a compressor circuit. This circuit contains two sections. IC U53, (pins
5, 6, and 7) is the clipping detector, and Z50, is used as a variable attenuator. The compressor
affects only the common bass buss signal. Pin 6 of each of the differential amplifiers is tied to
an overload signal buss, which is fed to Pin 5 of IC U53. Pins 5, 6, and 7 of IC U53 comprise a
voltage comparator network. The voltage at Pin 6 of U53 is the threshold voltage of the com-
parator. When the voltage at Pin 5 goes negative with respect to Pin 6, due to any amplifier
being over driven, the voltage of pin 7 will go negative, with respect to speaker reference (SR).
When the voltage of pin 7 goes negative, it turns on the LED, which is inside Z50, its resis-
tance goes down, which attenuates the bass signal. In effect, if any amplifier begins to be over
driven, the compressor circuitry is activated and will reduce the amount of common bass signal
to the power amplifiers, thereby reducing the bass gain, preventing the amplifier from clipping,
reducing potential distortion.
1201 Technical Description