3
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
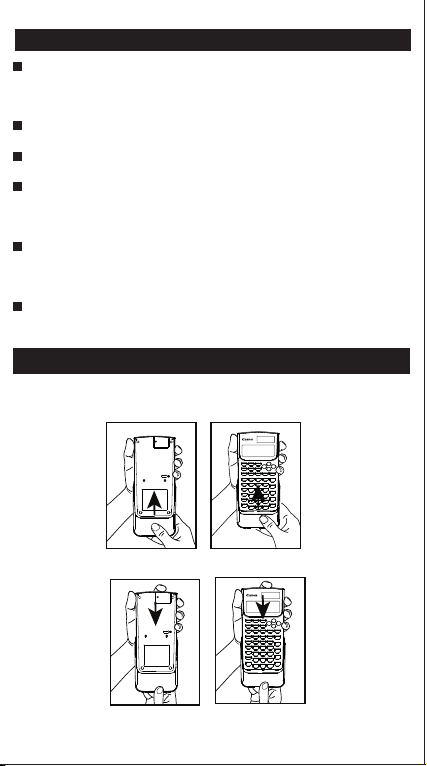
Slide the unit out of the protective case to open or close the
cover as shown in the figure.
USING THE PROTECTIVE SLIDE CASE
OPEN
CLOSE
This calculator contains precision components such as
LSI chips and should not be used in places subject to rapid
variations in temperature, excessive humidity, dirt or dust, or
exposure to direct sunlight.
Do not apply excessive pressure on the liquid crystal display
panel as it is made of glass.
Use a soft, dry cloth to clean the calculator. Do not clean with
a damp cloth or volatile liquid such as paint thinner.
Do not under any circumstances dismantle the device. If the
calculator is not functioning properly, please contact Canon
Service & Support or mail the device with the Warranty to a
Canon service location.
Do not improperly dispose of the calculator such as in an
incinerator as it may cause personal injury or harm.
Please dispose of the product in accordance with
National regulations
It is recommended to replace the battery once every two
years.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS .....................................................P.3
USING THE PROTECTIVE SLIDE CASE .............................P.3
DISPLAY (2-LINE DISPLAY) ................................................P.4
TO GET STARTED
Power On and Off .............................................................P.5
Input Capacity ..................................................................P.5
Display Format Setting (Notation – Fix, Sci, Eng) ............P.5
Inputting and Editing Calculations ....................................P.6
Order of Operations ..........................................................P.7
Input Ranges.....................................................................P.8
Error Messages and Error Locator..................................P.11
BASIC CALCULATIONS
Arithmetic Calculations....................................................P.12
Memory Calculations.......................................................P.13
Fraction Operations.........................................................P.15
Percentage Calculations .................................................P.15
Degrees-Minutes-Seconds Calculations .........................P.15
Angle Unit Conversion ....................................................P.16
FUNCTIONAL SCIENTIFIC CALCULATIONS
Square, Root, Power, Power Root, Reciprocal and Pi ...P.17
Trigonometry Calculations .............................................P.17
Logarithm, Natural Logarithm, and Antilogarithm ...........P.18
Coordinate Conversion ..................................................P.18
Base-n Calculations and Logical Calculations ...............P.19
Permutations, Combinations Factorials and
Random Number Generation ..........................................P.21
STATISTICAL CALCULATIONS ........................................P.22
BATTERY REPLACEMENT ...............................................P.25
BATTERY CAUTION ...........................................................P.26
SPECIFICATIONS ...............................................................P.26
Mantissa
minus sign