Page 5
1. Introduction
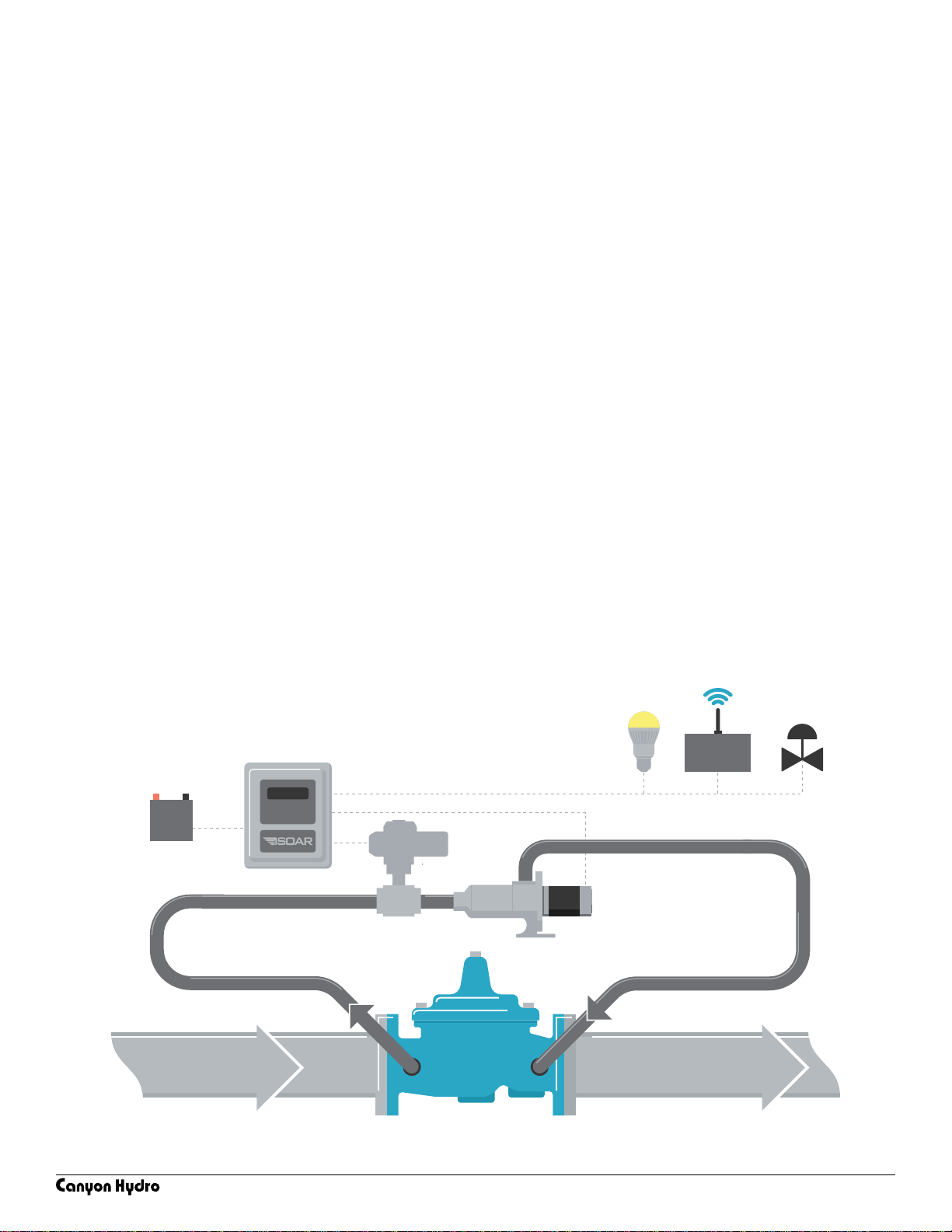
The M300 Pico-Hydro is a water-driven power generation and storage system.
Commonly installed in remote or unpowered locations the M300 system provides
electrical power to run a variety of equipment. Power generated is often used
for data aquisition and transmission and powering local devices.
Common equipment powered by the M300 Pico-Hydro system include Remote
Terminal Units (RTUs) for SCADA systems, pressure or ow control devices, radios,
blowers, fans, sump pumps, and LED lighting.
Unlike wind or solar, the M300 Pico-Hydro operates efciently in any kind of
weather and can be installed out of sight in secure locations. Because power
generation is readily available at all times smaller energy storage components
are required thereby reducing system cost.
This manual is intended to help with installation, operation, and maintenance
operations for the M300 Pico-Hydro System.