Carrier 50ZP036300 User manual
Other Carrier Air Conditioner manuals

Carrier
Carrier PGD4 Instruction Manual

Carrier
Carrier MOTORMASTER 48/50P3 User manual

Carrier
Carrier Modu-Pac 50DF034 Dimensions and installation guide

Carrier
Carrier 73KCA051D User manual

Carrier
Carrier 40GXC User manual
Carrier
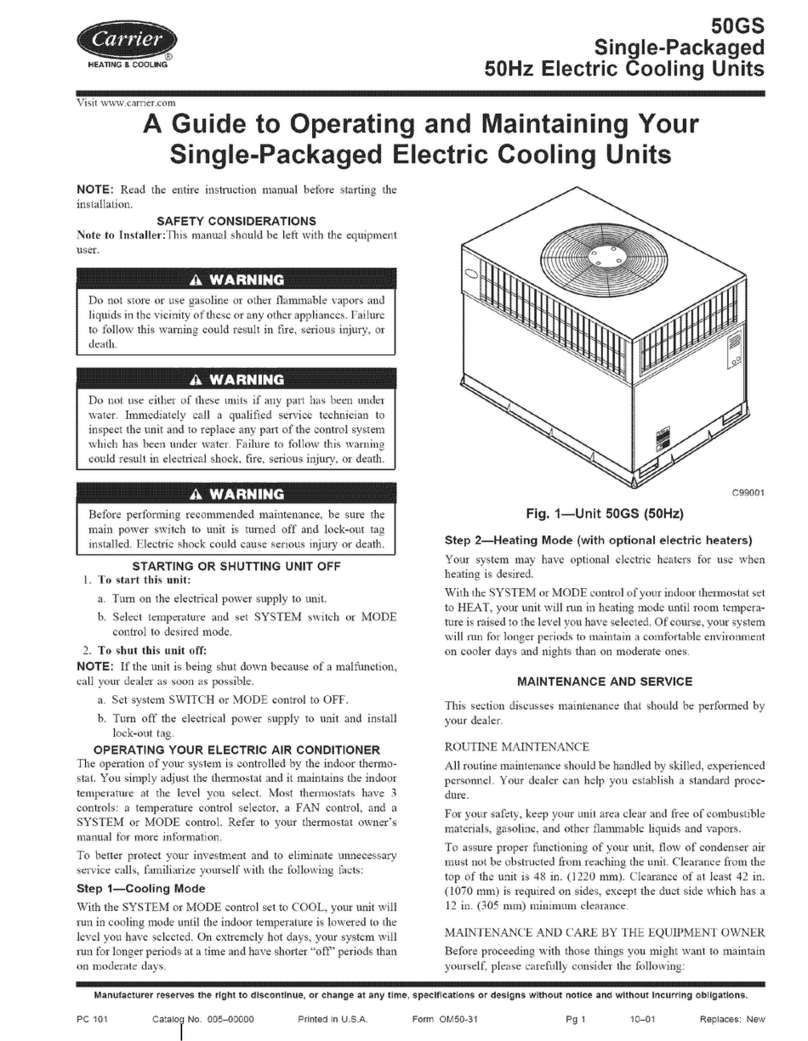
Carrier SINGLE PACKAGED ELECTRIC COOLING UNITS 50GS Assembly Instructions
Carrier
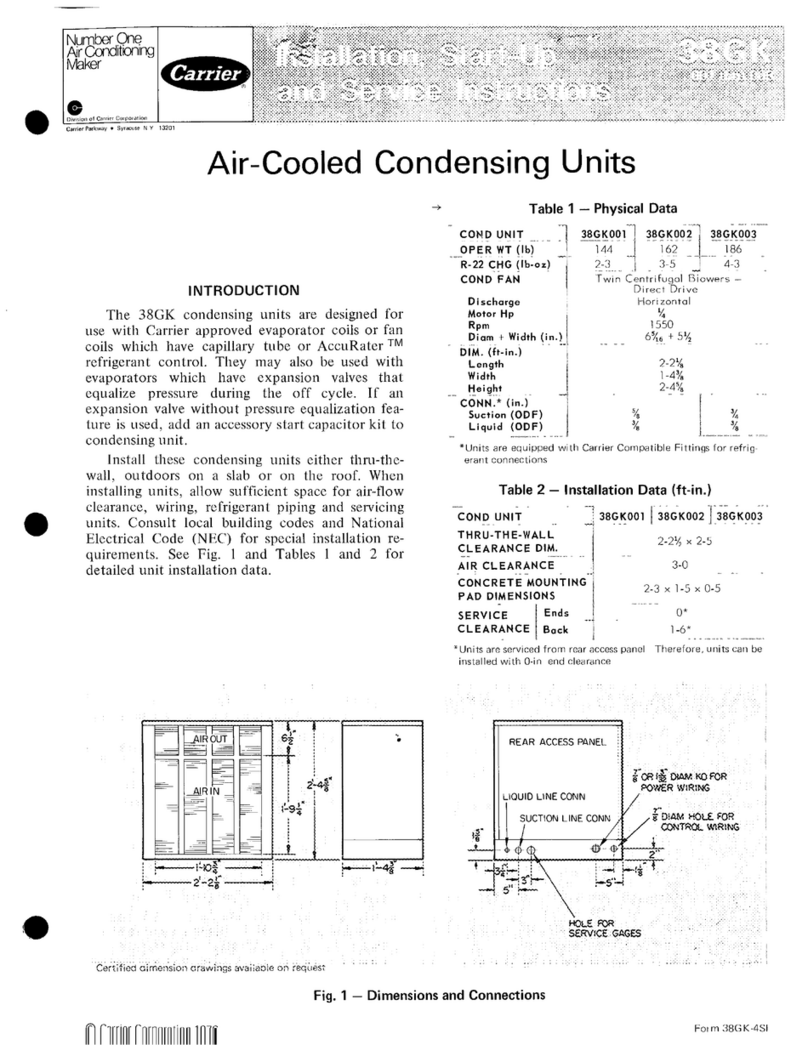
Carrier 38GK Dimensions and installation guide

Carrier
Carrier WeatherMaster 50HCQ 04 Series User manual

Carrier
Carrier WEATHERMASTER 50HJQ004 Dimensions and installation guide
Carrier
Carrier 42XPP050 User manual

Carrier
Carrier Gemini 38AU 16-28 Series Dimensions and installation guide

Carrier
Carrier 39CQ Manual
Carrier
Carrier 50GL 024-060 Assembly Instructions

Carrier
Carrier 42HQV025 User manual

Carrier
Carrier 38QHP09E8S series Repair manual

Carrier
Carrier Allegro 51AKE075 User manual

Carrier
Carrier LUVH025N User manual

Carrier
Carrier 42NQ009N User manual

Carrier
Carrier 42GCVBE010-703 User manual

Carrier
Carrier 50FC Series User manual
Popular Air Conditioner manuals by other brands

CIAT
CIAT Magister 2 Series Installation, Operation, Commissioning, Maintenance

Bestron
Bestron AAC6000 instruction manual

Frigidaire
Frigidaire FFRE0533S1E0 Use & care guide

Samsung
Samsung AS09HM3N user manual

Frigidaire
Frigidaire CRA073PU11 use & care

Soleus Air
Soleus Air GB-PAC-08E4 operating instructions