Section III Basic structure of Carter 0.8T/1.0T excavators mechanical system
1 Power system
Carter 0.8T/1.0T excavator is equipped with single-cylinder air-cooling diesel engine.
2 Drive system
Carter 0.8T/1.0T excavator's drive system could transfer the output power from diesel engine through the
hydraulic system to work equipment, swing mechanism and traveling mechanism.
3 Swing mechanism
Swing mechanism could turn the work equipment and upper rotary leftwards and rightwards, so as to do the
excavating and the unloading. Carter 0.8T/1.0T excavator’s swing mechanism has to fix the rotary table onto
frame and has it swing flexibly, without any inclining risk. Therefore, Carter 0.8T/1.0T excavator is equipped with
a slewing support (supports) and a slewing drive (power of turntable slewing), which are called by a joint name as
swing mechanism.
3.1 Slewing support
Carter 0.8T/1.0T excavator has its rotary table supported with a rolling bearing, realizing the swinging of
upper rotary.
3.2 Rotary drive
Carter 0.8T/1.0T excavator adopts the direct drive type. Namely, the output shaft of low-speed high-torque
hydraulic motor is mounted with a driving pinion which meshes with the slewing gear ring.
4 Traveling mechanism
Traveling mechanism supports the complete weight of excavator and drives it to run.
Carter 0.8T/1.0T excavator has the crawler traveling mechanism similar to other crawlers, with one hydraulic
motor driving one track. This excavator adopts low-speed high-torque motor. When two hydraulic motors run in
the same direction, this machine goes straightly forward; when one motor is supplied with oil and the other is
braked, excavator steers around the braked track; when two motors runs reversely, excavator rotates in situ.
Each part of traveling mechanism is mounted on integral traveling frame. The pressure oil from hydraulic pump
goes through the multi-way directional valve and the central swing joint into the hydraulic traveling motor that
changes the pressure energy into output torque that then goes to sprocket, driving excavator to run.
Carter 0.8T/1.0T excavator’s sprockets are of integral castings and able to correctly engage with track, featuring
balance drive. Sprockets located at rear part of excavator, shortening the tensioner part and relieving the track
abrasion, wear and power consumption. Each track is equipped with a tensioner, adjusting the track tension and
reducing the track vibration noise, abrasion, wear and power loss.
5 Work equipment
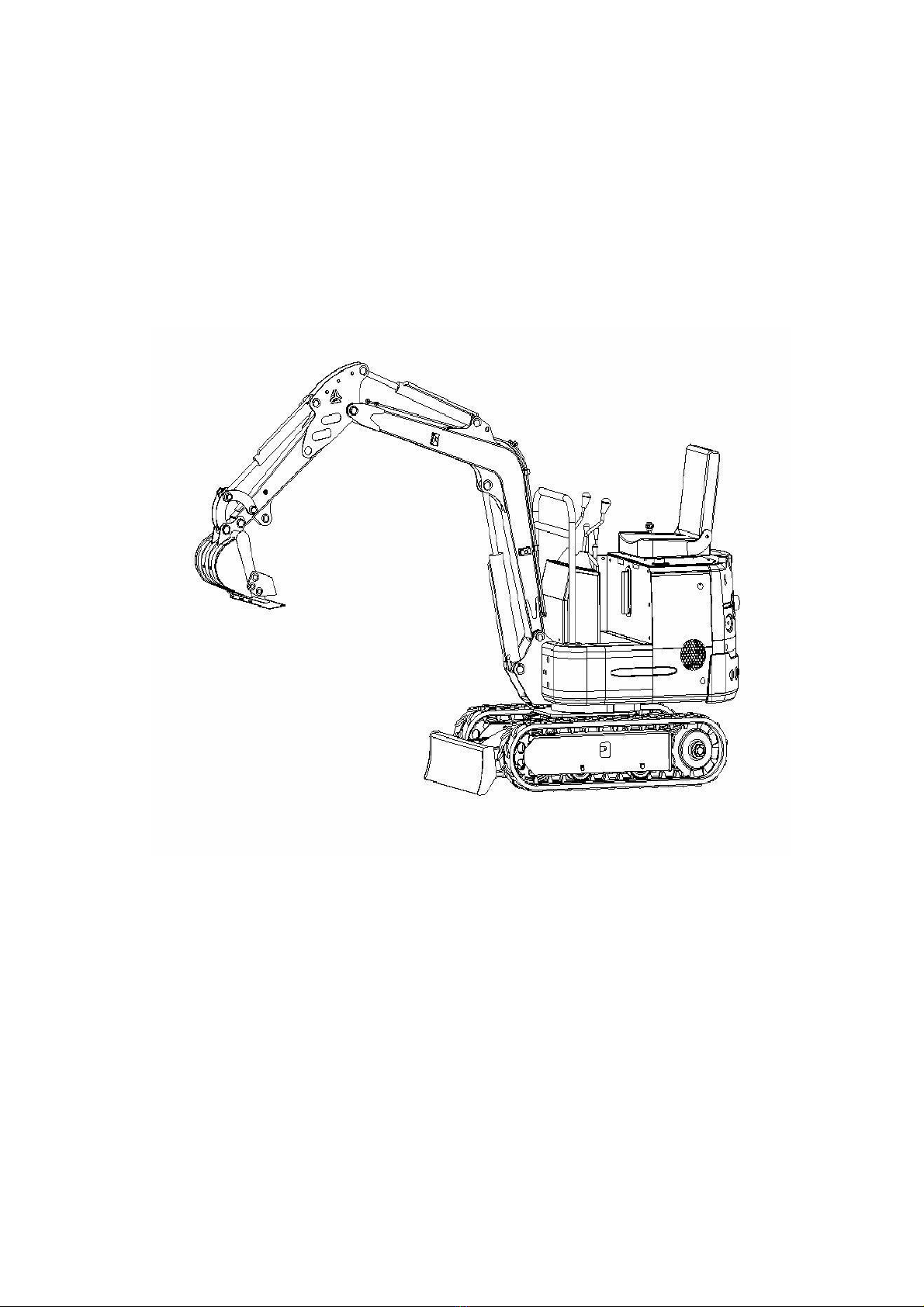
The hydraulic excavator could have multiple work equipment, up to dozens of varieties, with backhoe and ripper
most popular.
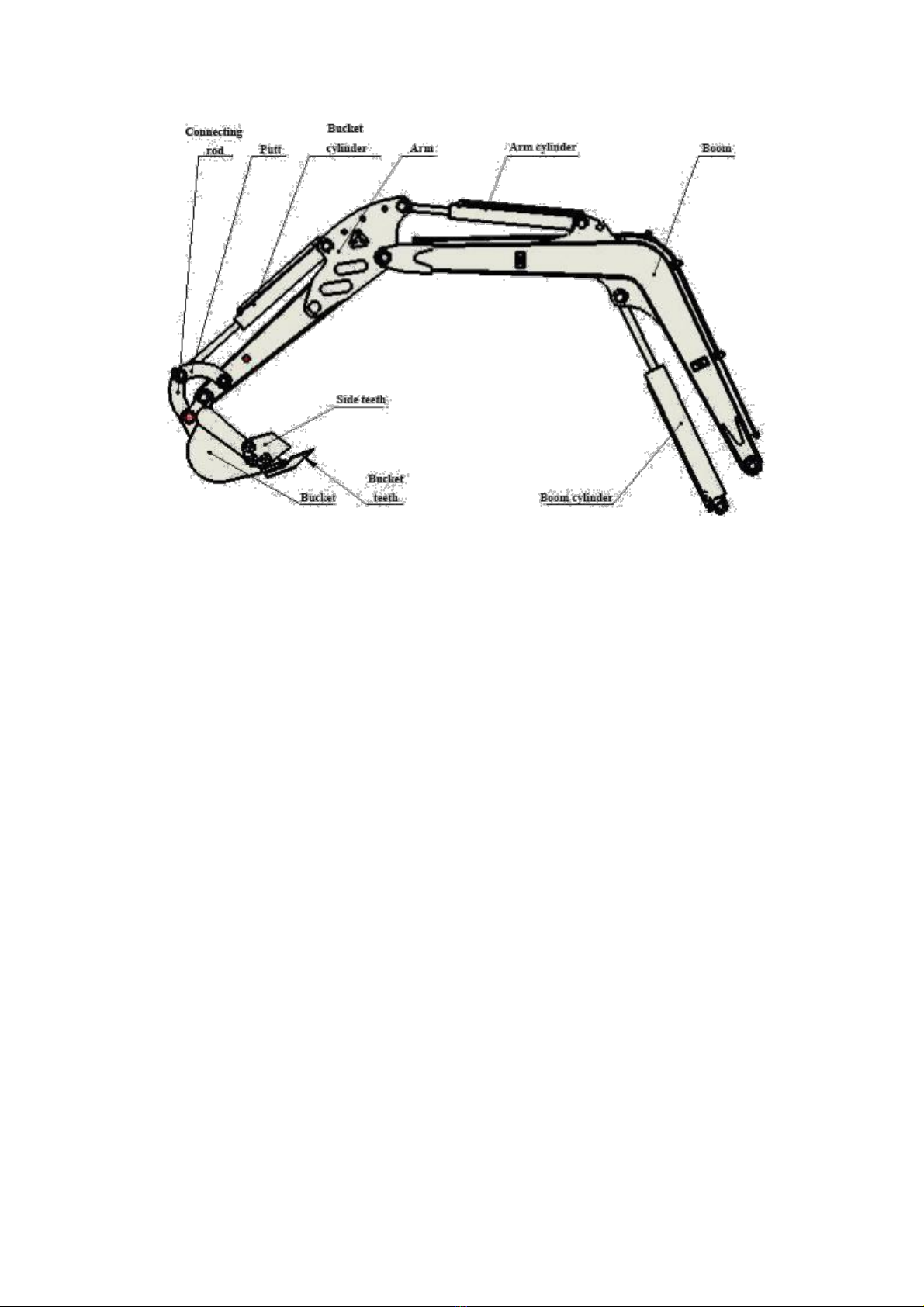
Carter 0.8T/1.0T excavator has the boom, arm and bucket articulated with each other, as shown in figure and
swing around their articulated points respectively with aid of the hydraulic cylinder, finishing the excavating,
lifting and unloading.
5.1 Boom
As the main component of backhoe work equipment, the integrated skewed boom is adopted on Carter 0.8T/1.0T
excavator.
Being of the most popular type at present, skewed boom could allow excavator to dip deeper and to lower the
unloading depth, satisfying the backhoe requirements.
9