Christ ALPHA 1-2 LDplus User manual

Translation of the original operating manual
sb-dc
Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020
Alpha 1-2 LDplus; ;
Version 11/2006
Alpha 1-2 LDplus
part no. 101521, 101470
Freeze-dryer
Operating Manual
Please retain for later use!

Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
2 / 94
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
Translation of the original operating manual

Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
3 / 94
Translation of the original operating manual
In case of inquiries, please state the following numbers:
Order number:
Serial number:
© Copyright by
Martin Christ Gefriertrocknungsanlagen GmbH
An der Unteren Söse 50
37520 Osterode am Harz
Germany
Tel.: +49 (0) 5522 / 5007-0
Fax: +49 (0) 5522 / 5007-12
Web: www.martinchrist.de
E-mail: info@martinchrist.de

Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
4 / 94
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
Translation of the original operating manual

Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
Table of contents
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
5 / 94
Translation of the original operating manual
1General information.............................................................................................................9
1.1 Importance of the operating manual..................................................................................9
1.2 Intended use.....................................................................................................................9
1.3 Warranty and liability.......................................................................................................11
1.4 Copyright........................................................................................................................12
1.5 Explanation of symbols...................................................................................................12
1.6 Standards and regulations..............................................................................................12
1.7 Scope of supply..............................................................................................................12
2Layout and mode of operation..........................................................................................13
2.1 Layout of the freeze-dryer...............................................................................................13
2.1.1 Functional and operating elements............................................................................13
2.1.2 Name plate................................................................................................................15
2.2 Mode of operation...........................................................................................................16
2.2.1 General information on freeze-drying.........................................................................16
2.2.2 Freeze-drying process...............................................................................................18
2.2.2.1 Preparation........................................................................................................18
2.2.2.2 Freezing.............................................................................................................19
2.2.2.3 Main drying........................................................................................................19
2.2.2.4 Final drying........................................................................................................19
2.2.2.5 End of drying and aeration.................................................................................20
2.2.2.6 Defrosting ..........................................................................................................20
3Safety..................................................................................................................................21
3.1 Marking of the unit..........................................................................................................21
3.2 Explanation of the symbols and notes.............................................................................22
3.3 Responsibility of the operator..........................................................................................23
3.4 Operating personnel .......................................................................................................24
3.5 Informal safety notes.......................................................................................................24
3.6 Safety notes concerning the transport, set-up and connection and initial start-up of the
freeze-dryer...............................................................................................................................24
3.6.1 General hazards........................................................................................................24
3.6.2 Hazards caused by improper transport......................................................................25
3.6.3 Hazards caused by improper set-up..........................................................................25
3.6.4 Hazards caused by improper connection...................................................................26
3.7 Safety notes concerning the operation............................................................................26
3.7.1 Hazards caused by electricity ....................................................................................26
3.7.2 Hazards caused by the refrigeration system (natural, flammable refrigerants)...........27
3.7.3 Hazards caused by the refrigeration system (non-flammable refrigerants).................27
3.7.4 Hazards caused by harmful products.........................................................................28
3.7.5 Hazards caused by solvents in the products..............................................................28
3.7.6 Hazards caused by acids in the products...................................................................28
3.7.7 Hazards caused by contaminated condensate (defrosting water)..............................29
3.7.8 Hazards caused by hot surfaces................................................................................29
3.7.9 Hazards caused by cold surfaces..............................................................................29

Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
Table of contents
6 / 94
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
Translation of the original operating manual
3.8 Safety devices ................................................................................................................29
3.8.1 System check............................................................................................................29
3.8.2 Earth conductor check...............................................................................................29
3.9 Procedures in the event of hazards and accidents..........................................................30
3.10 Maintenance and cleaning of the freeze-dryer................................................................30
3.11 Measures to be taken to ensure safe operation of the freeze-dryer.................................31
3.12 Remaining hazards.........................................................................................................32
4Storage and transport ....................................................................................................... 33
4.1 Dimensions and weight...................................................................................................33
4.2 Storage conditions..........................................................................................................33
4.3 Notes on transport..........................................................................................................34
4.4 Packaging.......................................................................................................................35
4.5 Transport safety device...................................................................................................35
5Set-up and connection ......................................................................................................36
5.1 Location of use ...............................................................................................................36
5.2 Power supply..................................................................................................................37
5.2.1 Type of connection ....................................................................................................37
5.2.2 Customer-provided fuses...........................................................................................37
5.3 Aeration and media drain valve.......................................................................................38
5.4 Vacuum sensor...............................................................................................................38
5.5 Vacuum pump.................................................................................................................40
5.6 Pressure control valve ....................................................................................................41
5.7 Rubber valves.................................................................................................................42
6Operation............................................................................................................................ 43
6.1 Initial start-up..................................................................................................................43
6.2 Installation of accessories...............................................................................................43
6.3 Preparation.....................................................................................................................43
6.4 Switching the freeze-dryer on .........................................................................................43
6.5 LDplus control system.....................................................................................................44
6.5.1 User interface............................................................................................................44
6.5.2 Mode .........................................................................................................................47
6.5.3 Main menu.................................................................................................................49
6.5.3.1 Changing set values ..........................................................................................49
6.5.3.2 Special functions................................................................................................51
6.5.3.3 Process and equipment information...................................................................52
6.5.3.4 Options..............................................................................................................53
6.5.3.5 Tutorial...............................................................................................................55
6.6 Switching the freeze-dryer OFF......................................................................................56

Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
Table of contents
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
7 / 94
Translation of the original operating manual
7Malfunctions and error correction....................................................................................57
7.1 General malfunctions......................................................................................................57
7.1.1 Power failure..............................................................................................................57
7.1.2 Insufficient vacuum....................................................................................................57
7.1.2.1 Small flange connections...................................................................................57
7.1.2.2 Aeration and media drain valve..........................................................................58
7.1.2.3 Pressure control valve........................................................................................58
7.1.2.4 Rubber valves....................................................................................................59
7.1.2.5 Vacuum sensor..................................................................................................59
7.1.3 Insufficient ice condenser temperature ......................................................................59
7.2 Process and equipment messages.................................................................................60
7.3 Service contact...............................................................................................................61
8Maintenance and service................................................................................................... 62
8.1 Maintenance...................................................................................................................62
8.1.1 General......................................................................................................................62
8.1.2 Ice condenser chamber .............................................................................................63
8.1.3 Aeration valve, media drain valve..............................................................................64
8.1.4 Heat exchanger (only for air-cooled freeze-dryers)....................................................65
8.1.5 Electrical system........................................................................................................65
8.1.6 Vacuum pump ...........................................................................................................65
8.1.7 Exhaust filter (oil mist separator)................................................................................66
8.1.8 Refrigeration system..................................................................................................67
8.1.9 Vacuum sensor..........................................................................................................67
8.1.10 Accessories...............................................................................................................68
8.2 Disinfection of the drying chamber and accessories .......................................................69
8.3 Service ...........................................................................................................................70
8.4 Return of defective parts.................................................................................................70
9Disposal.............................................................................................................................. 72
9.1 Disposal of the freeze-dryer............................................................................................72
9.2 Disposal of the packaging...............................................................................................72
10 Technical data.................................................................................................................... 73
10.1 Ambient conditions .........................................................................................................74
10.2 Technical documentation................................................................................................74
11 Appendix............................................................................................................................ 75
11.1 Brief operating instructions .............................................................................................75
11.2 EC declaration of conformity in accordance with the EC Machinery Directive.................81
11.3 Declaration of conformity –China RoHS 2......................................................................83
11.4 EC declaration of conformity in accordance with the Pressure Equipment Directive .......85
11.5 Table of the sublimation pressure curve..........................................................................87
12 Glossary.............................................................................................................................89
13 Index................................................................................................................................... 91

Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
Table of contents
8 / 94
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
Translation of the original operating manual

Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
1 General information
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
9 / 94
Translation of the original operating manual
→
1 General information
→
1.1 Importance of the operating manual
A fundamental requirement for the safe and trouble-free operation of the
unit is to be familiar with the fundamental safety instructions and all
possible hazards.
The operating manual includes important information concerning the safe
operation of the freeze-dryer.
This operating manual, and in particular the notes on safety and hazards,
must be observed by all persons operating the unit.
In addition, the local rules and regulations for the prevention of accidents
must be complied with.
→
1.2 Intended use
The freeze-dryer has been exclusively designed for the freeze-drying of
solid or liquid products in ampoules, vials or dishes. It is, therefore, solely
intended for this application.
The freeze-dryer is suitable for freeze-drying solid substances and aqueous
solutions (e.g. bacteria and virus cultures, blood plasma, serum fractions,
antibodies, sera, vaccines and pharmaceutical products such as
chloramphenicol, streptomycin, vitamins, ferments and plant extracts for
biochemical tests).
Freeze-drying of solvent-containing products
(non-aqueous media)
With regards of corrosion resistance, the use of some organic solvents in
aqueous solutions with low concentrations is acceptable.
A freeze-dryer is designed to be chemically resistant to most compounds
that are commonly used in freeze-drying processes. However, by
necessity, the freeze-dryer is comprised of several different materials,
some of which may be attacked and degraded by certain chemicals.
The methods of fabrication and/or conditions of exposure of an acrylic door,
as well as the way the chemicals are applied, can influence the results.
Some of these factors are listed below:
•Fabrication: Stress generated while sawing, sanding, machining,
drilling, polishing, and/or forming.
•Exposure: Length of exposure, stresses induced during the life of the
product due to various loads, changes in temperature etc.
•Application of chemicals: by contact, rubbing, wiping, spraying etc.
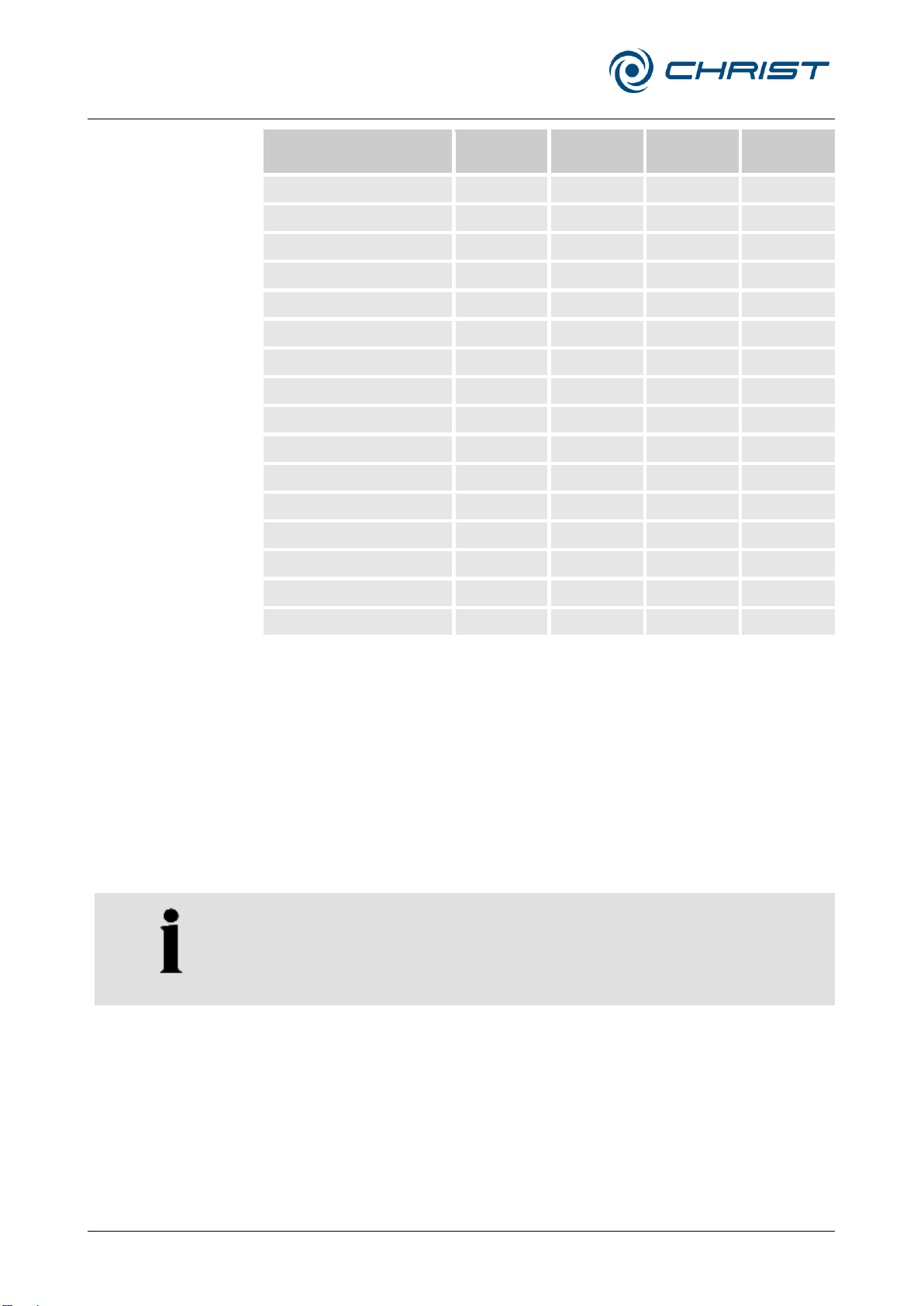
The following table can be used as a general guide for the expected
degradation during normal freeze-drying processes of organic solvents with
a total max. concentration of 10 vol-% in aqueous solutions.
Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
1 General information
10 / 94
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
Translation of the original operating manual
Solvent
Acrylic
glass
Stainless
steel
Silicon
rubber
EPDM
Acetic acid 20%
+
+
+
o
Formic acid
+
+
o
-
Trifluoracetic acid (TFA)
-
+
-
+
Calcium chloride
+
o
+
+
Sodium phosphate
+
+
-
+
Acetone
-
+
+
+
Acetonitrile
-
+
+
+
Carbon tetrachloride
-
+
-
-
Cyclohexane
+
+
-
-
Dioxane
+
+
-
o
Methyl-t-butyl ether
+
+
o
-
Pyridine
+
+
-
-
Methanol
-
+
+
+
Ethanol
o
+
+
+
tert-Butanol
-
+
o
o
DMSO
-
+
+
+
Legend:
+ No degradation to be expected
o Moderate degradation; limited use
- Severe degradation; infrequent use recommended;
immediate thorough cleaning required
The use of other solvents, e.g. ammonia, should be avoided.
The chemical attack on devices and accessory components can be
significantly reduced by immediate cleaning after the end of operation. All
parts of the freeze-dryer that have come in contact with the product must
be checked regularly for damages and replaced if necessary.
The following features are not permissible or must be deactivated:
•omission of product temperature sensors of the PT100 or LyoRx type or
of specially connected PT100 sensors (with a cable connection),
NOTE
Solvents that are not listed in the table above, or the listed solvents in a
concentration higher than 10% by volume, must not be used!
Freeze-drying of acid-containing products
Freeze-drying of products containing acids is only permissible if special
protective measures and equipment-related precautions are taken. Other-
wise, there is a risk of damage to property and personal injury. Consultation
of Martin Christ Gefriertrocknungsanlagen GmbH is absolutely mandatory
in order to define the measures that need to be taken!

Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
1 General information
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
11 / 94
Translation of the original operating manual
Any other use beyond this area of application is regarded as improper use.
Martin Christ Gefriertrocknungsanlagen GmbH cannot be held liable for any
damage resulting from such improper use.
The intended use also includes:
•observation of all the notes and instructions included in the operating
manual;
•compliance with the inspection and maintenance instruction.
The following operations are regarded as NOT PERMISSIBLE:
•operation of the freeze-dryer if it is not properly installed
•use of the freeze-dryer if it is not in a perfect technical state;
•use of the freeze-dryer within hazardous locations where there is a risk
of explosions:
•use of the freeze-dryer with unauthorised additions or conversions
without the written approval by Martin Christ Gefriertrocknungsanlagen
GmbH;
•use of the freeze-dryer with accessories that have not been approved
by Martin Christ Gefriertrocknungsanlagen GmbH, with the exception of
commercially available freeze-drying vessels made of glass or plastic;
•use of the freeze-dryer with concentrated solvents;
•freeze-drying of products that may react during the freeze-drying
process following the supply of high amounts of energy, e.g. solvent-
containing products;
•freeze-drying of products containing azides;
•freeze-drying of products that may damage the material of the chamber
walls, shelves, pipes, or seals, or that may affect the mechanical
strength.
→
1.3 Warranty and liability
The warranty and liability are subject to our "General Terms and
Conditions" that were distributed to the operator upon the conclusion of the
contract.
Warranty and liability claims are excluded if they are due to one or several
of the following reasons:
•improper use
•non-compliance with the safety instructions and hazard warnings in the
operating manual
•improper installation, start-up, operation, and maintenance of the
freeze-dryer.

Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
1 General information
12 / 94
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
Translation of the original operating manual
→
1.4 Copyright The copyright concerning the operating manual remains with Martin Christ
Gefriertrocknungsanlagen GmbH.
The operating manual is solely intended for the operator and their
personnel. It includes instructions and information that may not be
•duplicated,
•distributed, or
•communicated in any other way neither in full nor in parts.
Non-compliance may be prosecuted under criminal law.
→
1.5 Explanation of symbols
In this operating manual, specialist terms that are explained in the glossary
(see chapter 12 - "Glossary") are marked by an arrow and printed in italics
(e.g. →sublimation).
→
1.6 Standards and regulations
EC declaration of conformity in accordance with the EC Machinery
Directive (see chapter 11.2 - "EC declaration of conformity in accordance
with the EC Machinery Directive")
→
1.7 Scope of supply
The scope of supply comprises:
•1 tube of high-vacuum grease
•1 drain hose 0.5 m (silicone 8 x 12 mm)
•1 open spanner (size 19)
•1 operating manual
In addition, if a vacuum pump is included:
•1 litre of vacuum pump oil
•1 hexagon socket key (size 6)
Accessories and commissioning
According to your order, our order confirmation, and our delivery note.

Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
2 Layout and mode of operation
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
13 / 94
Translation of the original operating manual
→
2 Layout and mode of operation
→
2.1 Layout of the freeze-dryer
→
2.1.1 Functional and operating elements
1 Ice condenser
chamber with an
internal ice condenser
2 Aeration and media
drain valve
Fig. 1: Left side of the freeze-dryer
3 Pipe connection of the
vacuum pump (behind
the cover plate)
4 Ice condenser
Fig. 2: Ice condenser chamber

Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
2 Layout and mode of operation
14 / 94
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
Translation of the original operating manual
5 User interface (see
chapter 6.5.1 - "User
interface")
6 Mains power switch
Fig. 3: Front and right side of the freeze-dryer
7 Power supply of the
pressure control valve
8 Name plate (see
chapter 2.1.2 - "Name
plate")
9 Power supply of the
vacuum pump
10 Equipotential bonding
screw
11 Mains connection
12 Vacuum connection
13 Connection of the
vacuum sensor
14 Option: data interface
for further
accessories
15 Heat exchanger of the
refrigeration unit
Fig. 4: Rear view of the freeze-dryer

Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
2 Layout and mode of operation
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
15 / 94
Translation of the original operating manual
→
2.1.2 Name plate
1 Serial number
2 Type
3 Refrigerant data of
the 1st stage
4 Nominal voltage
5 Year of manufacture
(month/year)
6 Part number
7 Rated current /
apparent power
Fig. 5: Example of a name plate

Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
2 Layout and mode of operation
16 / 94
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
Translation of the original operating manual
→
2.2 Mode of operation
→
2.2.1 General information on freeze-drying
What is freeze-drying?
Freeze-drying or lyophilisation is a procedure for the gentle drying of high-
quality products. The product is dried by →sublimation without passing
through the liquid phase.
What are typical applications for freeze-drying?
An important area of application is the drying of biotechnological and
pharmaceutical products, e.g. tissues and tissue extracts, bacteria,
vaccines, and sera. Products that would not keep well when they are
dissolved in water can be preserved by freeze-drying. During this process,
the biological properties of these sensitive substances are preserved. The
compounds remain unchanged from a qualitative and quantitative point of
view. After the addition of water, the products will have the same
characteristics as the original products.
How does freeze-drying work?
Freeze-drying is a very gentle procedure for the extraction of water from a
product in the frozen state. The drying process takes place through →
sublimation, i.e. the direct transition of a product from the solid phase to the
gas phase. This happens under vacuum.
The following section describes the process of sublimation based on the
example of water, since most products that are processed by freeze-drying
are aqueous solutions. Their behaviour is based on identical fundamental
principles.
The vapour pressure curve for ice and water (sublimation pressure curve)
describes the phase transition as a function of the pressure and
temperature. The higher the temperature is, the higher the vapour
pressure.
•If the vapour pressure is higher than 6.11 mbar (A), water passes
through all three phases: solid, liquid, and gas (see the illustration).
•At 6.11 mbar and 0.0098°C, the melting pressure curve, vapor pressure
curve, and sublimation pressure curve meet in one point, the so-called
triple point. In this point, all three phases coexist (simultaneously).
•If the vapour pressure is below 6.11 mbar (B) and energy is added, the
ice will be directly converted into water vapour once the sublimation
curve is reached. This transition is called “sublimation”. If thermal
energy is added to pure ice with a temperature of less than –30°C at a
pressure of 0.37 mbar, it will be converted into water vapour once it
reaches –30°C (see figure).
The vacuum prevents the melting of ice when energy is added. If thermal
energy is added to a frozen product under vacuum, thawing of the product
will be prevented and the water that is contained within the product will be
released in the form of water vapour.

Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
2 Layout and mode of operation
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
17 / 94
Translation of the original operating manual
Fig. 6: Vapour pressure curve for ice and water
From a physical point of view, the freeze-drying process covers three
phases (see figure below):
(1) Freezing: The product to be dried is frozen under atmospheric pressure.
This can be done either directly in the freeze-dryer or in a separate deep-
freeze. The freezing temperature should be approximately 10°C below the
solidification point of the product.
(2) Evacuation: When the product is sufficiently frozen, the vacuum pump is
activated. The pressure inside the drying chamber will be lowered to the
value that corresponds to the freezing temperature in accordance with the
vapour pressure curve for ice and water.
(3) Sublimation: Thermal energy is added to the product, thus starting the
sublimation process. Due to the added energy, the water in the product is
converted into water vapour. Since the ice condenser is much colder than
the product that is to be dried, the vapour pressure in the ice condenser is
considerably lower than above the product. As a result, the water vapour
that is released by the product streams to the ice condenser, where it
condenses on the condenser coils.
Once the free water has been extracted from the product during the main
drying phase, the last traces of bound water will also be removed at a final
pressure that is as low as possible and at higher temperatures. This takes
place by way of →desorption. This drying phase is also called final drying.

Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
2 Layout and mode of operation
18 / 94
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
Translation of the original operating manual
Fig. 7: Freeze-drying phases
NOTE
Please find further information about basic principles, optimum
procedures and applications in the brochure "Smart freeze-drying", which
can be downloaded at www.martinchrist.de →[Applications] →
[Lyophilisation].
→
2.2.2 Freeze-drying process
The main components of a freeze-dryer are:
•vacuum drying chamber or drying manifold,
•vacuum pump for generating a vacuum inside the drying chamber,
•ice condenser for binding the water vapour that is released by the
product.
→
2.2.2.1 PreparationThe ice condenser chamber must be clean and dry. Any water residues
from a preceding drying run must be removed.
The media drain valve and the aeration valve must be closed.
In the case of units that are equipped with a pressure control valve
(standard on LSCplus and LSCbasic units), the vacuum pump should be
warmed up (“warm-up”) for at least 15 minutes prior to the start of the main
drying phase. Do not subject the vacuum pump to condensable gases until
the operating temperature is reached. In this way, the service life of the
vacuum pump can be extended.
At the same time, the ice condenser is pre-cooled ("cool-down"). The ice
condenser temperature does not have any influence on the product
temperature. The sole purpose of the ice condenser is to bind the released
water vapour.

Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
2 Layout and mode of operation
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
19 / 94
Translation of the original operating manual
→
2.2.2.2 Freezing First, the product that is to be dried is frozen. Especially in the case of small
filling quantities, we recommend pre-cooling the shelves as well in order to
prevent the product from thawing during the evacuation.
Two very different structures of the frozen material can be distinguished:
•crystalline structures with clearly distinguishable crystals
•amorphous structures with no crystal junctions at all (e.g. glass)
The majority of the freeze-drying products have a crystalline form.
When freezing these kinds of products, one must take into consideration
that too deep and too quick freezing leads to smaller ice crystals, which has
a negative effect on the duration of the drying process.
For every product to be dried, the solidification point must be determined as
a first step. This is the point at which the water that is contained in the
product has completely crystallised. In order to ensure an optimum freeze-
drying process, the product temperature should be approximately 10°C
below the solidification point.
→
2.2.2.3 Main drying
When the product is frozen, the main drying phase commences. The
vacuum pump is switched on. The pressure inside the drying chamber will
be lowered to the value that corresponds to the freezing temperature in
accordance with the vapour pressure curve for ice and water (sublimation
pressure curve). At the same time, thermal energy will be added to the
product. In the case of products in round-bottom flasks, wide-neck bottles,
etc., this is realised through the environment that is considerably warmer
(direct contact heat), in the case of unheated shelves by way of thermal
radiation from the environment, and in the case of temperature-controlled
shelves directly via the shelves. As a result, the sublimation process starts.
At the beginning of the drying process, the maximum drying rate will be
reached. The more the sublimation area recedes into the product, the
further the produced water vapour must pass through the layers that have
already been dried.
Under certain conditions, it is possible that the vacuum inside the ice
condenser chamber increases during the main drying phase (e.g. from 0.63
mbar to 0.47 mbar) although the valve towards the vacuum pump is closed.
From a physical point of view, this is due to the pumping effect of the ice
condenser ("cryo-pumping effect").
The required drying time depends strongly on the drying vacuum. At 1.0
mbar, one gram of ice takes up a volume of 1 m3of vapour, at 0.1 mbar a
volume of 10 m3of vapour, and at 0.001 mbar a volume of 100 m3. The
closer the vacuum is to the solidification point, the smaller is the resulting
vapour volume. The drying rate increases and the drying time decreases.
→
2.2.2.4 Final drying
Final drying is an option whenever one requires a product with minimal
residual moisture. In the physical sense, this process is a desorption
process, i.e. the removal of adsorptively bound water. Final drying is
performed under the lowest possible final pressure that depends on the ice

Freeze-dryer Alpha 1-2 LDplus
2 Layout and mode of operation
20 / 94
Version 11/2006, Rev. 2.10 of 09/03/2020 • sb-dc
Translation of the original operating manual
condenser temperature in accordance with the vapour pressure curve for
ice and water as well as on the final vacuum of the vacuum pump that is
used. The process is supported by a higher shelf temperature.
→
2.2.2.5 End of drying and aeration
The end of the drying process is reached when both the product and shelf
temperature are clearly in the positive range (+15 to +20°C) and if their
difference is not greater than 5 K.
Another indication of the end of the drying process is the behaviour of the
vacuum and of the ice condenser temperature. The ice condenser is no
longer subject to load and reaches the final temperature of approximately -
55°C or -85°C. The pressure in the drying chamber decreases in
accordance with the ice condenser temperature.
The vacuum pump will be switched off and the drying chamber will be
aerated via a rubber valve or via the aeration valve. The aeration valve can
also be used to flood the unit with nitrogen or another inert gas instead of
ambient air.
Then, the product can be removed from the unit.
→
2.2.2.6 Defrosting Defrosting of the ice condenser is carried out at room temperature or with
warm water.
•At a maximum, the ice condenser chamber may be half filled with water.
•Ensure that no water gets into the pipe connection of the vacuum pump
and the vacuum sensor (behind the cover plate, see figure)
1 Cover plate
Fig. 8: Eis condenser chamber
•Drain the condensate through the media drain valve at the left side of
the freeze-dryer by attaching a hose on the nozzle (included in the
scope of supply) and placing a vessel underneath.
In order to avoid damage, the condensate must be removed directly after
the completion of the defrosting process. Then, any residual water must be
removed from the ice condenser chamber by way of a cloth.
Other manuals for ALPHA 1-2 LDplus
2
This manual suits for next models
2
Table of contents