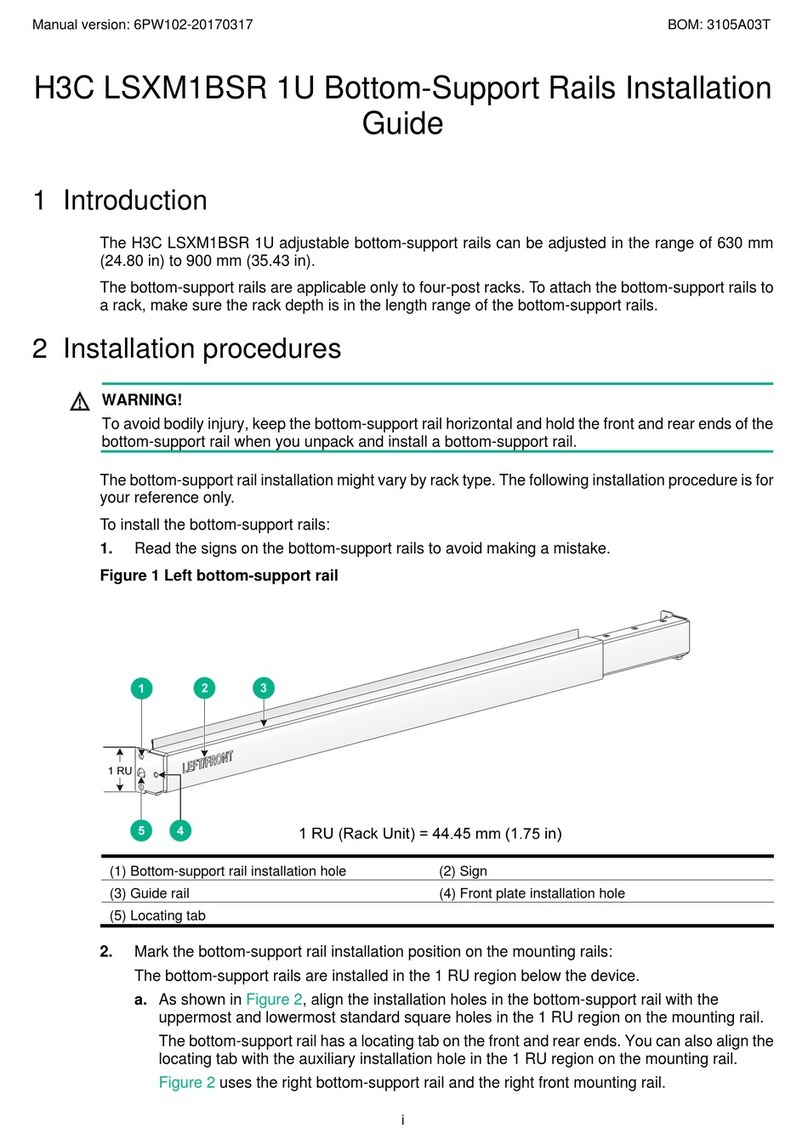
Clepsydra NTS-3000 User manual

1
USER MANUAL
NTP/PTPv2 Network Time Servers
NTS-3000
NTS-4000
NTS-5000
Updated: 17-Jul-15

2
SAFETY INSTUCTIONS 3
TRADEMARKS, ACKNOWLEGMENT & CONTACTS 3
GLOSSARY TIME TERMS 4
1. QUICK START 6
2. PRODUCT INTRODUCTION 9
3. STANDARD SERVER HARDWARE 10
4. EXTRA OPTIONS. EXTENDED MODULES. 14
5. MULTISOURCE. NEW CONCEPT OF TIME SOURCE 16
6. TARGET UTC. THE TRUE OUTPUT TIME 17
7. MOUNTING GPS ANTENNA 22
8. POWERING UP NTS 25
9. BASIC DEVICE CONFIGURATION 26
10. ERROR MESSAGES 28
11. NTP – NETWORK TIME PROTOCOL 29
12. NTP ON TIME FAILURE TOLERANCE NETWORK 32
13. NTS SOFTWARE SETUP 34
14. SECURITY AND NTP AUTHENTICATION MODE 44
18. ON-LINE SUPPORT 57

3
SAFETY INSTUCTIONS
ATTANTION!
These are the important Safety Instructions that should be followed during
installation and maintenance of the Elproma NTS-3000/4000/5000 timeserver family
product.
IMPORTANT NOTE
This equipment contains hazardous AC and DC voltages. Do not handle any metallic
part until the power has been disconnected. Do not assemble, disassemble set when
the power is ON. Making wiring and touching cables is strongly prohibited when
power is ON. Please refer to your RACK’19 safety instruction to learn more about
connecting power to equipment. The NTS-protection system requires PE line to be
connected into RACK’19 din rails.
Elproma safety advises:
1. Safety first! Never work alone under hazardous voltage conditions
2. High short circuit current trough conductive materials can cause server burns
3. Check that the power cord(s), plug(s), and sockets are in good conditions
4. Always use qualified service personnel to install permanently wired equipment
5. Do not handle any metallic part before the power has been disconnected
6. Take care your power lines and rack’19 frame is properly PE grounded
TRADEMARKS, ACKNOWLEGMENT &
CONTACTS
© CLEPSYDRA is trademark of Elproma Elektronika Sp.z o.o.
© ELPROMA is trademark of Elproma Electronics BV & Elproma Elektronika Sp.z o.o.
© TELEORIGIN is trademark of Elproma Elektronika Sp. z o.o.
EU Factory:
ELPROMA Electronics Poland Sp. z o.o.,
Szymanowskiego Str. 13 PL05092 Lomianki/Warsaw POLAND (EU)
Phone: +48 227517680
Fax: +48 227517681
Internet: http://www.clepsydratime.com
Internet: http://www.teleorigin.com
Internet: http://www.elpromagroup.com http://www.elproma.com.pl
E-mail: info@clepsydratime.com

4
GLOSSARY TIME TERMS
In alphabetic order:
Accuracy - The degree of conformity of a measured or calculated value to its definition or with respect
to a standard reference time. In the meaning of NTP (Network Time Protocol) the accuracy determines
how close the PC clock is to UTC reference (GNSS or external atomic clock).
Atomic Time Scale (TA) - a time scale based on atomic or molecular resonance phenomena. Elapsed
time is measured by counting cycles of a frequency locked to an atomic or molecular transition. Earlier
time scales were based on the rotational rate of the earth.
GBEIDOU– (see COMPASS)
Calibration - The process of identifying and measuring time or frequency errors, offsets, or deviations
of a clock/oscillator relative to an established standard, such as UTC(NIST).
Clock - a device for maintaining and displaying time.
GOMPASS (BEIDOU)– is Chinese satellite navigation system. It consists of two separate satellite
constellations – a limited test system that has been operating since 2000, and a full-scale global
navigation system that is currently under construction. The first BeiDou system, officially called the
BeiDou Satellite Navigation Experimental System.
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) - a coordinated time scale, maintained by the Bureau International
des Poids et Mesures (BIPM), which forms the basis of a coordinated dissemination of standard
frequencies and time signals. A UTC clock has the same rate as a Temps Atomique International (TAI)
clock or international atomic time clock but differs by an integral number of seconds called leap
seconds. The UTC scale is adjusted by the insertion or deletion of leap seconds to ensure
approximate agreement with UT1.
Drift (frequency) - the linear (first-order) component of a systematic change in frequency of an
oscillator over time.
Frequency - the rate at which a periodic phenomenon occurs over time. Frequency drift - see drift.
Frequency offset - the frequency difference between the measured value and the defined value.
Frequency shift - change in frequency from a standard reference. Frequency stability - statistical
estimate of the frequency fluctuations of a signal over a given time interval.
Frequency standard - an oscillator such as a rubidium (Rb), cesium (Cs), or hydrogen (H) maser who’s
output is used as a frequency.
GALILEO – is a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) currently being built by the European Union
(EU) and European Space Agency (ESA). One of the aims of Galileo is to provide a high-precision
positioning system upon which European nations can rely, independently from the Russian
GLONASS, US GPS, and Chinese COMPASS (BEIDOU) which can be disabled in times of war or
conflict. Galileo is compatible to US GPS (see GPS).
GLONASS – acronym for Globalnaya navigatsionnaya sputnikovaya sistema or Global Navigation
Satellite System, is a space-based satellite navigation system operated by the Russian Aerospace
Defence Forces. It provides an alternative to Global Positioning System (GPS) and is the only
alternative navigational system in operation with global coverage and of comparable precision.
Glonass use L1-1575.42MHz with additional frequency margin between 1597.50-1609.50Mhz.
GPS (Global Positioning System) - a highly accurate, global satellite navigation system based on a
constellation of at 24 satellites orbiting the earth at a very high altitude 20000 km. GPS signals
are: L1-1575.42MHz;L2-1227.6MHz;L3-1381.05 MHz
GMT (Greenwich Mean Time) - a 24 Hour system based on mean solar time plus 12 hours at
Greenwich, England. Greenwich Mean Time can be considered approximately equivalent to
Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), which is broadcast from all standard time and frequency radio
stations. However, GMT is now obsolete and has been replaced by UTC.
International Atomic Time (TAI) - an atomic time scale based on data from a worldwide set of atomic
clocks. It is the internationally agreed upon time reference conforming to the definition of the second,
the fundamental unit of atomic time in the International System of Units (SI). It is defined as the
duration of 9 192 631 770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between two

5
hyperfine levels of the ground state of the cesium - 133 atom.
Synchronization - The process of measuring the difference in time of two time scales such as the
output signals generated by two clocks. In the context of timing, synchronization means to bring two
clocks or data streams into phase so that their difference is 0 (see time scales in synchronism).
Synchronization - Relative adjustment of two frequency sources with the purpose of canceling their
frequency difference but not necessarily their phase difference.
Stability (frequency) - statistical estimate of the frequency fluctuations of a signal over a given time
interval: Long term stability usually involves measurement averages beyond 100s. Short term stability
usually involves measurement averages from a few tenths of a second to 100s.
Stratum - indicates how fare from cesium ref. the clock is in the chain of synchronization.
Time code - a system of symbols (digital or analog) used for identifying specific instants of time. An
information format used to convey time information. IRIG-B is example of Time Code.
Time interval - The duration between two instants read on the same time scale.
Time scale - a system of unambiguous ordering of events. A time scale is meant to be stable and
homogeneous.
Time standard - a continuously operated device used for the realization of a time scale in accordance
with the definition of the second and with an appropriately chosen origin.
Time step - a discontinuity in a time scale at some instant. A step is positive (+) if the time scale
reading is increased and negative (-) if the reading is decreased at that instant.
Difference between Accuracy and Stability in Time Synchronization
STABLE & ACCURATE STABLE - NOT ACCURATE ACCURATE - NOT STABLE DRIFT

6
1. Quick Start
Switch ON power and following screen sequence will appear on 2x20 front panel green color LCD:
When booting the following message will be displayed (depends on server model
NTS3000/4000/5000) while dots will be counted up booting progress in the lower line:
After approximately 1 minute the following sequence of messages are displayed in loop:
Press & hold [OK] for 5s to entrance SETUP. The LAN1 IP address will appear on LCD. Use arrow
keys [] to select column position, and [] to assign requested 0-9 values for each IP address
position separately.
Press [OK] to switch to next screen (or press & hold [OK] for 5s to
save entered configuration). You can always interrupt and quit SETUP at any moment by pressing
& holding [C]. Exiting SETUP in [C] (CANCEL) mode disregards all changes and last saved settings
will be restored. Repeat above sequences to setup LAN2 IP address:
LAN1 & LAN2 are isolated (not routed) and therefore they can serve different TCP/IP sub-networks,
both with independent GATEWAY. If you use single LAN (#1 or #2) please leave another one filled by
Loading NTS-3000
…………
Loading NTS-4000
…………
Loading NTS-5000
…………
Press & hold [OK]
to enter setup
…………
Press & hold [OK] [C]
to reset to defaults
…………
LAN1: no carrier
LAN2: no carrier
LAN1: (disabled)
LAN2: (disabled)
LAN1 IP address:
192.168.001.002
LAN1 netmask:
255.255.255.000
LAN1 gateway:
192.168.001.001
LAN2 IP address:
010.000.000.002
LAN2 netmask:
255.255.000.000
LAN2 gateway:
010.000.000.001
© 1992-2014 CLEPSYDRA
TIME SYSTEMS
Boot loader V7.05.29
Loading

7
zero digits (000.000.000.000). Once IP address is set following screen request your confirmation to
save IP data:
and your NTS-3000/4000/5000 timeserver is ready to communicate via LAN1/LAN2 interface.
Unless you wish to provide more advance settings above configuration fine to start working now.
If the GNSS (GPS/Glonass/Galileo) Multi-SAT receiver remains asynchronous the following
information will be displayed on LCD indicating a part of process called –“warm” start:
Once number of satellites are in view receiver lock to GNSS and synchronization process is pending.
Starting from now your server is READY and following message is displayed:
If you use 2 receivers (A & B), additional information from Mulit-SAT GNSS (B) will be displayed too:
It is possible and very probable both GNSS receivers can show different volume of GNSS satellites.
In standard operation mode above screen is displayed to present each satellite system data using
format: XX/YY where XX are number of visible satellites for specific system; YY - total #amount of
available SAT channels at receiver). Following additional information can be provided at any time:
Environmental DATA is provided periodically using time zone settings:
Plugging Ethernet cable to LAN1 will trig following message on LCD
Are you sure?
[OK] - Yes [Cancel] - No
03-05-2014 INIT
12:00:01
03-05-2014 OK
12:01:00 sat A= 18/32
03-05-2014 OK
12:01:00 sat B= 19/32
03-05-2014 GPS 11/32
12:01:00 GNSS 9/32
Firmware release
NTS-3000 04/02/2014
Firmware release
NTS-4000 09/03/2014
Firmware release
NTS-5000 05/03/2014
CPU temperature [C]
+41.5 +36.8 +25.1
Onboard voltage [V]
+3.32 +5.03 +15.54
CPU temperature [F]
+106,7 +98,2 +77,1
LAN1: active
LAN2: no carrier
LAN1: 192.168.1.2
LAN2: (disabled)
LAN1: no carrier
LAN2: no carrier

8
display:

9
2. Product Introduction
This manual is common for all Clepsydra Time server models available from Elproma:
NTS-3000, NTS-4000 and NTS-5000 also shortly indicated as NTS-3000/4000/5000. Therefore it use
following convention of NTS-4000/5000 to present functionality what us not available for NTS-3000.
Unless it is clearly indicated in the manual the assuming for functionality is valid for all 3 above
models.
The NTS-3000/4000/5000 Clepsydra Time Server provides a high precision time directly to TCP/IP
Ethernet networks using: NTP (Network Time Protocol), SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol). It is
compatible to all available versions of NTP/SNTP available on market. Optionally NTS-4000/5000
servers can extra support PTPv2 (Precision Time Protocol IEEE1588), IRIG-B and IBM SYSPLEX
synchronization standards in configuration depends on ordered options.
The NTS-3000/4000/5000 supports all majority of current popular operating systems (OS) including:
Microsoft Windows, Mac OS/X, Linux, FreeBSD, HPUX, IBM AIX, IBM AS/400, ORACLE SUN, CISCO
and other UNIX family systems. It can synchronize simultaneously ten of thousands servers,
workstations, routers, telecom stations (BTS), industrial and power distributions controllers.
Standard product provides accurate time via 2xLAN ports. Optionally the configuration can be
extended up to 6xLAN both: 100Base-T and GE. The Fiber Optic (FO) Ethernet communiocation is
possible via special converter available separatelly.
The NTS-4000/5000 has several extra I/O synchronization standards including optionally interface for:
IRIG-B, 1PPS, 10MHz, SYSPLEX, PTPv2/IEEE1588, E1/T1. Special fast sync startup mode of NTP
has been implemented to reduce unsynchronized time after powering up products that has no battery
powered up RTC clocks. Server NTS-5000 can be extra equipped with additional 8x IRIG-B (AM)
output distribution panel.
The accurate target UTC time is calculated as weighted average of numerous time sources including
double A/B redundant GNSS (GPS/Glonass/Galileo) receiver with build-in active antenna. Servers
NTS4000/5000 can use external clocks as reference too. The target UTC time is produced on way of
comparing settings of maximum available time references including: GNSS, 1PPS, 10Mhz, IRIG-B,
SYSPLEX etc. Special DCF77 RF-AM receiver is available on request for Central Europe & Germany.
Unit status information can be traced on front panel 2x20 characters LCD display. More detailed
statistic is available by remote NTP software utilities (ntpq, ntpdc) and setup utility via: WWW,
TELNET, SSH, SNMP. There is more software utility available FREE to download from
www.clepsydratime.com: ClepsydraNTPmonitor, ClepsydraNTPconfig, ClepsydraNTPclock etc.
All Clepsydra Time Servers can operate in standard or special NTP authentication mode protected by
MD5 algorithms and PKI infrastructure. Unit supports broadcast, manycast, multicast and client/server
modes of NTP. A true novelty is an option to create cascade of servers where one can simulate an
NMEA (GPS) antenna for the other. This functionality enables time synchronization of secured LANs
with official time from NTP servers available publicly on line in Internet.
All servers are ready to work with any external SYSLOG or SNMP (MIB2) server. Error messages can
be traced on local (2x20) LCD or remotely over wall LED NTP display from Elproma. It let friendly
warn on any unexpected situation that may happen. Messages can be also sent via E-MAIL directly
from any NTS-3000/4000/5000 timeserver.
Servers are designed to operate without ventilators and fans. Metal housing is an important part of
natural cooling system designed in such way that unit can be located in the neighborhood of any
device working inside rack19 mount frame.

10
3. Standard Server Hardware
NTS-3000/4000/5000 (standard version) has similar front panel architecture and components location.
There is 2x20 characters LCD Status Display (green color). All devices come with 6-key keyboard for
quick setup. The RS232 (DSUB-9 mail) connector is preserved for value added functionality (e.g.
cesium clock connection etc.). There is 2xUSB2.0 interface for firmware upgrade or backup purpose.
There is LAN2 connector located on the front panel too. It contains 2x LEDs: green - indicates cable
connection, yellow - flashes while data is being transmitted.
Standard Front Panel
The back panel of NTS-3000/4000/5000 (standard version) is organized on way there are several I/O
referential time sections. :
Standard Back Panel

11
NTS-3000 (Standard Version)
NTS-3000 (standard) Front Panel
NTS-3000 (standard) Back Panel
Table describe connectors it’s availability and related into it functions:
Name
Connector
Standard
Purpose
Availability
Antenna (A)
RJ-45
RS-485
Antenna connector (main antenna)
+
Antenna (B)
RJ-45
RS-485
Antenna connector (backup antenna)
+
IRIG-B IN*
BNC
IRIG-B
IRIG-B source signal (optionally)
-
IRIG-OUT*
BNC
IRIG-B
IRIG-B output signal (optionally)
-
10 MHz
BNC
10MHz
10 MHz output reference signal
-
1 PPS IN
BNC
1pps
1 PPS (pulse per second) source signal
+
1 PPS OUT
BNC
1pps
1 PPS (pulse per second) output signal
-
TIMER IN
DSUB9
RS-232
2xPPS (pulse per second) input signal
-
TIMER OUT
DSUB9
Various
Extra feature (not available yet)
-
LAN1
RJ-45
TCP/IP
Local Area Network (back panel)
+
LAN2
RJ-45
TCP/IP
Local Area Network (front panel)
+
RS-232
DSUB9
RS-232
For technical and service purpose
+
USB
KUSB
USB
For technical and service purpose
+
NTS-3000 (standard) Back Panel picture
NTS-3000 (standard) Front Panel picture

12
NTS-4000 OCXO (Standard Version)
NTS-4000 OCXO (Standard Version) 1U rack’19 mount Front Panel
NTS-4000 OCXO (Standard Version) Back Pane
Table describe connectors it’s availability and related into it functions:
Name
Connector
Standard
Purpose
Availability
Antenna (A)
RJ-45
RS-485
Antenna connector (main antenna)
+
Antenna (B)
RJ-45
RS-485
Antenna connector (backup antenna)
+
IRIG-B IN
BNC
IRIG-B
IRIG-B source signal (optionally)
+
IRIG-OUT
BNC
IRIG-B
IRIG-B output signal (optionally)
+
10 MHz
BNC
10MHz
10 MHz output reference signal
+
1 PPS IN
BNC
1pps
1 PPS (pulse per second) source signal
+
1 PPS OUT
BNC
1pps
1 PPS (pulse per second) output signal
+
TIMER IN
DSUB9
RS-232
2xPPS (pulse per second) input signal
+
TIMER OUT
DSUB9
Various
Extra feature (not available yet)
+
LAN1
RJ-45
TCP/IP
Local Area Network (back panel)
+
LAN2
RJ-45
TCP/IP
Local Area Network (front panel)
+
RS-232
DSUB9
RS-232
For technical and service purpose
+
USB
KUSB
USB
For technical and service purpose
+
NTS-4000 OCXO (Standard Version) Back Panel picture
NTS-4000 (Standard Version) Front Panel pictur

13
NTS-5000 Rubidium+OCXO (Standard Version)
NTS-5000 RUBIDIUM+OCXO (Standard Version) 2U rack’19 mount Front Panel
NTS-5000 RUBIDIUM+OCXO (Standard Version) 2U rack’19 mount Back Panel
Table describe connectors it’s availability and related into it functions:
Name
Connector
Standard
Purpose
Availability
Antenna (A)
RJ-45
RS-485
Antenna connector (main antenna)
+
Antenna (B)
RJ-45
RS-485
Antenna connector (backup antenna)
+
IRIG-B IN
BNC
IRIG-B
IRIG-B source signal (optionally)
+
IRIG-OUT
BNC
IRIG-B
IRIG-B output signal (optionally)
+
10 MHz
BNC
10MHz
10 MHz output reference signal
+
1 PPS IN
BNC
1pps
1 PPS (pulse per second) source signal
+
1 PPS OUT
BNC
1pps
1 PPS (pulse per second) output signal
+
TIMER IN
DSUB9
RS-232
2xPPS (pulse per second) input signal
+
TIMER OUT
DSUB9
Various
Extra feature (not available yet)
+
LAN1
RJ-45
TCP/IP
Local Area Network (back panel)
+
LAN2
RJ-45
TCP/IP
Local Area Network (front panel)
+
RS-232
DSUB9
RS-232
For technical and service purpose
+
USB
KUSB
USB
For technical and service purpose
+
NTS-5000 RUBIDIUM+OCXO (Standard Version) 2U rack’19 mount Front Panel
NTS-5000 RUBIDIUM+OCXO (Standard Version) 2U rack’19 mount Back Panel

14
4. Extra options. Extended modules.
Extra options and product extensions can make a difference to std. panel component location:
Double Redundant Power Supply
Custom NTS-3000 or NTS-4000ocxo with redundant A+B dual power supply
Custom NTS-5000 Rb+OCXO with redundant A+B dual power supply
Direct Cesium 5071A (Custom) Time Server
Custom NTS-3000 with special direct cesium 5071A interface (1PPS+RS232)
Dial-Up GSM/PSTN/ISDN Time Server
Custom NTS-3000 Dial-Up with built-in GSM & PSTN (or ISDN) modem
6xLAN (NTP) Time Server
Custom NTS-3000 with 6x LAN (NTP) interfaces /also available as NTS-4000/
Custom NTS-5000 Rb+OCXO with 6x LAN (NTP) interfaces

15
IEEE1588/PTPv2 Master Clock
NTS-4000OCXO PTPv2 Master Clock (IEEE1588 Server on LAN5)
NTS-5000 Rb+OCXO PTPv2 Grand Master Clock (IEEE1588 Server on LAN5)
IEEE15888/PTPv2 Slave Clock with E1/T1 outputs
NTS-4000OCXO PTPv2 Slave Clock (IEEE1588 Client on LAN4) with T1/E1 outputs
NTS-5000Rb+OCXO PTPv2 Slave Clock (IEEE1588 Client on LAN4) with T1/E1 outputs
IEEE15888/PTPv2 Grand Master Clock with E1/T1 (SSU) in/out
NTS-4000OCXO Grand Master PTPv2 Clock (LAN4 PTP-client LAN-5-PTP-server) with T1/E1 in/out
NTS-5000Rb+OCXO Grand Master PTPv2 Clock (LAN4 PTP-client LAN-5-PTP-server) with T1/E1 in/out
8x IRIG-B DISTRIBUTION SYNCHRONIZED TO 2x OPTO GNSS RECEIVER
NTS-5000Rb+OCXO w/ 8x IRIG-B output & 2x OPTO GNSS antenna

16
5. Multisource. New concept of Time Source
A true novelty of NTS-3000/4000/5000 is real multi source time concept. Product can take
simultaneously a reference time from its all available hardware inputs. Compering to other existing
solutions, it does not take “best” or “selected” source, but it is automatically and continuously
computing weighted average UTC output out of all available sources (clocks) including groups:
GNSS satellite systems (via GPS, Russian GLONASS, EU GALIELO, Chinese BEIDOU)
Remote TIME SERVERS (via NTP, PTP/IEEE1588, SYSPLEX)
Local external atomic clocks (via IRIG-B, 1PPS, 10MHz, RS-232),
Multisource concept. Server simultaneously receives time from all available time sources
Some other vendor products available on market use name “multisource” too. The following figure
presents difference between Clepsydra multisource meanings and other concepts:
Other product available on market Clepsydra Time (ELPROMA) Time Servers
(Switching between “best selected” sources) (Weighted arithmetic mean –calculating average UTC target)
Clepsydra Time Servers does not limit manual switching. Single source of reference UTC can be
achived by simple disabling all other sources.
The short philosophical digression on time and clocks says that if you have one clock you have to
trust it. Dealing with 2 different clocks means you don’t know what time is. Three or more clocks
enables considerations what time can be. Above philosophy still plays role today.

17
6. Target UTC. True Output Server Time
For single reference source of time (i.e. GPS), the synchronization and output UTC is represented:
Single source of reference UTC time
The dispersion represents the maximum possible error on the offset of source time reference like
GPS. The current Timeserver time is represented by zero (0) offset. The “Offset” margin adjustment of
internal server’s clock is proceeding and it can be set to possible values between “Reference UTC”
plus “Dispersion” and the “Reference UTC” minus “Dispersion”. In case of single source servers the
target UTC accuracy can be then less or equal to it’s reference origin pattern. However using single
source of time avoids advance computing for target output UTC. Actually timeserver always provides
“best replica” of source reference parameters. In some cases like Institutes of Metrology this technique
can be very useful, especially when using local-external, high performance atomic clock - as primary
reference source of time. Using local atomic clocks let produce high accuracy and stable UTC output
for NTP/PTP.
.
Single source configuration of NTS-3000 connected to Cesium Primary Reference Std. 5071A Clock
To allow output UTC (clock) quickly achieve high accuracy, yet avoid overshooting the time with
large time adjustments, timeserver uses large adjustments (after power-up) occur quickly and small
adjustments occur over time for normal mode of operation. For small time differences (less than 128
ms) server uses a minimal-gradual adjustment. This is called slewing. For larger time differences (i.e
after powering up), the adjustment is immediate and large. This is called stepping. The different types
of time adjustment are shown in figure below.

18
Computing target output UTC time from multisource NTS-3000/4000/5000. Step adjustment is possible after Power-ON only.
For multisource the synchronization and output UTC is much more complicated. Several steps are
involved by NTS-3000/4000/5000 in determining the correct time on server’s inputs. Although some of
these steps are not necessary when synchronizing to a single source (i.e. GPS) it is essential for more
complex multisourcing.
Multi source reference of UTC
Increasing the number of independent reference UTC sources is good for two reasons: it allows for
more accurate output time, and reduces the chance of the time becoming unsynchronized from an
accidentally or intentionally misconfigured time source. These advantages are realized inside server in
special clustering algorithm and the clock combination algorithm. Server NTS-3000/4000/5000 not
only tries to synchronize to “true time”, it also computes an error range on all source inputs. The
maximum error in either direction is called the dispersion representing offset and maximum possible
time error. NTS-3000/4000/5000 server determines the best time sources based on several factors,
including offset, the delay (latency), and statistical error factors (represents errors related to clock
reading times and frequency tolerance etc).
Multisourcing can improve target output UTC accuracy by reducing final dispersion (thin gray interval)
Multisourcing also helps reduce risk of time manipulations. Input clocks that have error bars
(dispersion) that overlap this interval are in the majority. Input clocks that are in this majority are called
“Truechimers” and clocks that are outside this majority are called “Falsetickers.” In most cases, all the
clocks in a configuration will be Truechimers. If a clock at server’s input appears to be a Falseticker,
then it is important to investigate to see what the problem is. While in an ideal world, all Falsetickers

19
would be the result of incorrectly set clocks, it is possible (but very unlikely) that a Falseticker may
have a incorrectly set clock as the result of time manipulation (i.e. GPS spoofing). These kind of tricky
things are similar acting to “time machine”. Spoofing GPS is one of most popular, but unfortunately not
the only one. Multisourcing offers unique possibilities to detect and eliminate Falsetickers.

20
7. Time scales. UTC & LEAP second
The basic supported time scale is UTC. Universal Coordinated Time is the primary time standard by
which the world regulates clocks and time. It is one of several closely related successors to Greenwich
Mean Time (GMT) set according to astronomic observations. For most purposes, UTC is synonymous
with GMT, but GMT is no longer precisely defined by the scientific and IT community, therefore we
strongly suggest to not mismatch both names.
According to definition of UTC the formula of calculating time is: UTC = TAI + 35s.
The 35s represents amount of leap seconds added to Atomic Time Scale (TAI) in case of keeping UTC
balanced according to instability of Earth rotation. Only single leap second can be added (or deducted)
in one-step time correction. Leap Seconds may be introduced as the last second of a UTC month
(June and December – preferred; March and September – second choice).
Other manuals for NTS-3000
1
This manual suits for next models
2
Table of contents
Other Clepsydra Server manuals