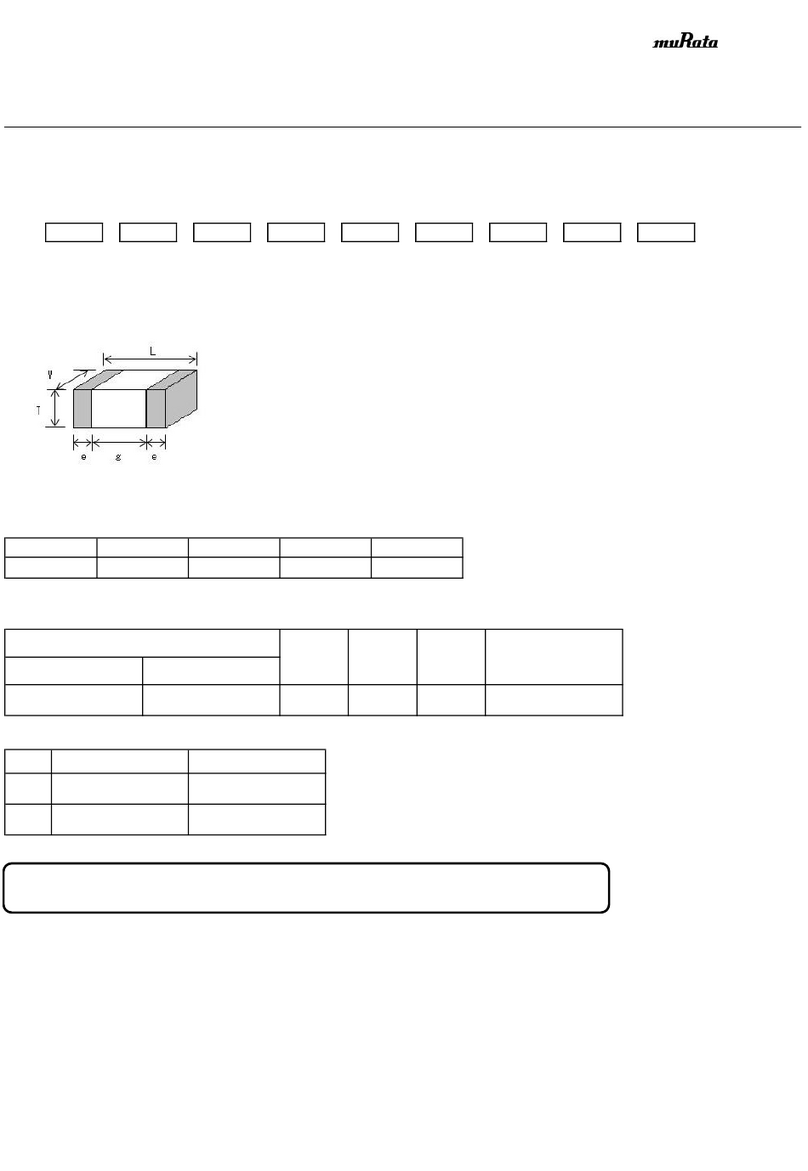
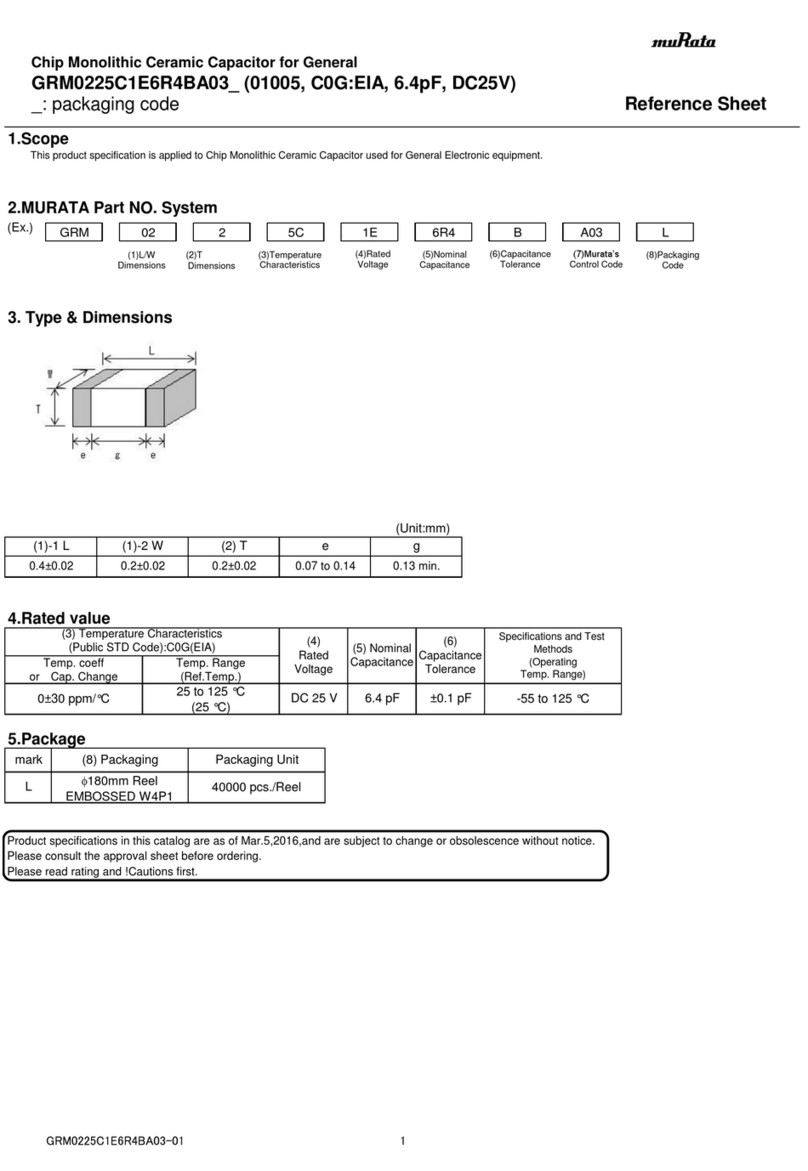
Introduction
Service Information S270-20-3 provides installation and
operation instructions for the Kyle Type GV and GW
Sectionalizers. Before installing and operating this sec-
tionalizer, carefully read and understand the contents of
this manual.
Read this Manual First
Read and understand the contents of this manual and
follow all locally approved procedures and safety prac-
tices before installing or operating this equipment.
Additional Information
These instructions can not cover all details or variations
in the equipment, procedures, or processes described
nor provide directions for meeting every possible contin-
gency during installation, operation, or maintenance. For
additional information, please contact your Cooper
Power Systems representative.
Acceptance and Initial
Inspection
Each sectionalizer is completely assembled, tested,
inspected, adjusted, and filled to the correct level with
insulating oil at the factory. It is in good condition when
accepted by the carrier for shipment.
Upon receipt, inspect the shipping container for signs of
damage. Unpack the sectionalizer and inspect it thor-
oughly for damage incurred during shipment. If damage
is discovered, file a claim with the carrier immediately.
Check for oil leakage, and tighten all bolts that may have
been loosened during shipment, especially the bolts
attaching the head to the tank.
Handling and Storage
Be careful during handling and storage of the sectional-
izer to minimize the possibility of damage. If the section-
alizer is to be stored for any length of time prior to instal-
lation, provide a clean, dry storage area. Locate the sec-
tionalizer so as to minimize the possibility of mechanical
damage. In particular, protect the bushings and keep the
operator cabinet closed to protect the electronic control
components.
Standards
Kyle sectionalizers are designed and tested in accor-
dance with ANSI standard C37.63 where applicable.
Quality Standards
ISO 9001:2000 Certified Quality Management System
Description
The sectionalizer is a self-contained, circuit-opening
device used in conjunction with source-side protective
devices such as reclosers or circuit breakers, to auto-
matically isolate faulted sections of electrical distribution
systems. The sectionalizer senses current flow above a
preset level, and, when the source-side protective
device opens to de-energize the circuit, the sectionalizer
counts the overcurrent interruption. Depending upon the
coordination scheme, the sectionalizer will open during
the first, second, and third open interval of the fault inter-
rupting device to isolate permanent faults and confine
outages to smaller sections of line.
The sectionalizer does not interrupt fault current but can
be closed into a faulted line. It opens during the open
interval of the backup device. For this reason, it must
always be used in series with a fault-interrupting backup
protective reclosing device. Also, it will reset counts that
do not reach the counts-to-open setting within the
selected reset time due to clearing of temporary faults.
A minimum of 0.5 A of load current flowing through the
sectionalizer will block the generation of a count pulse.
This count-restraint feature prevents the sectionalizer
from counting overcurrents interrupted by down-line
devices.
The sectionalizers are also equipped with an inrush-current
restraint feature which distinguishes between inrush cur-
rents and fault currents. If it is determined that the over-
current through the sectionalizer is inrush current, the
phase and ground current levels of the sectionalizer are
blocked for a duration of 3 seconds upon current detection.
3
S270-20-3
PRODUCT INFORMATION