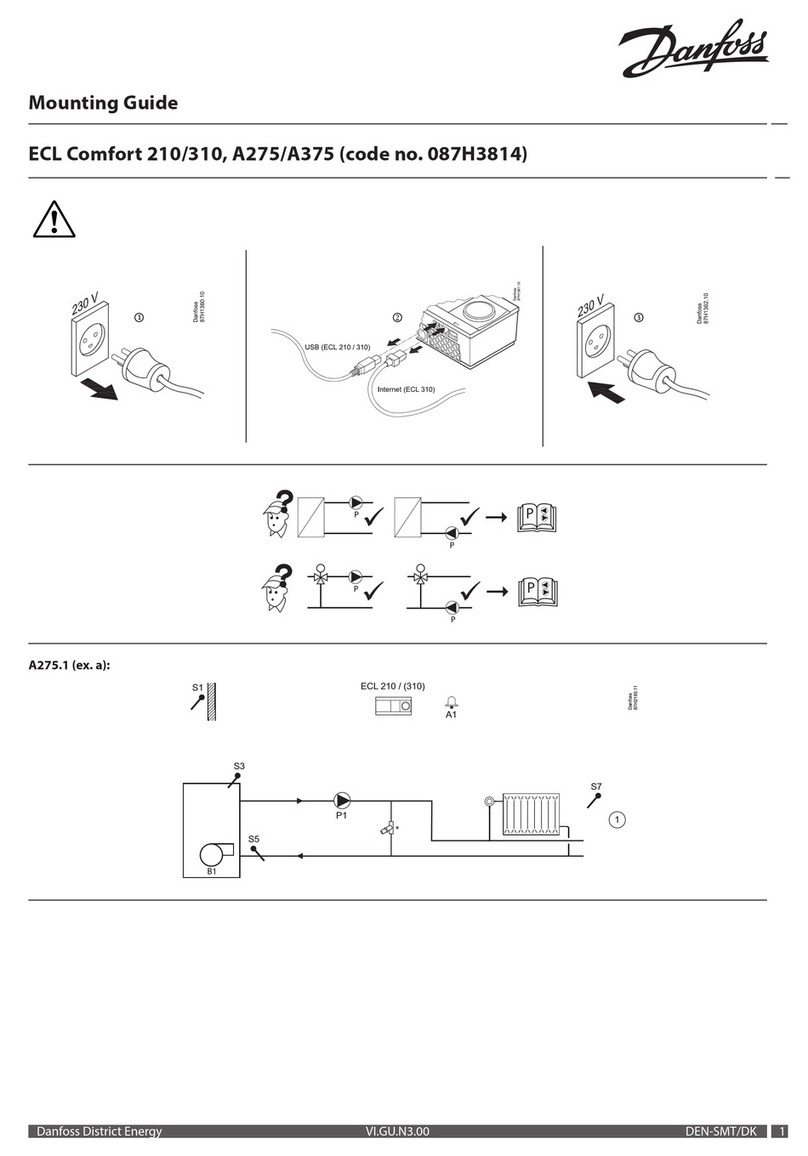
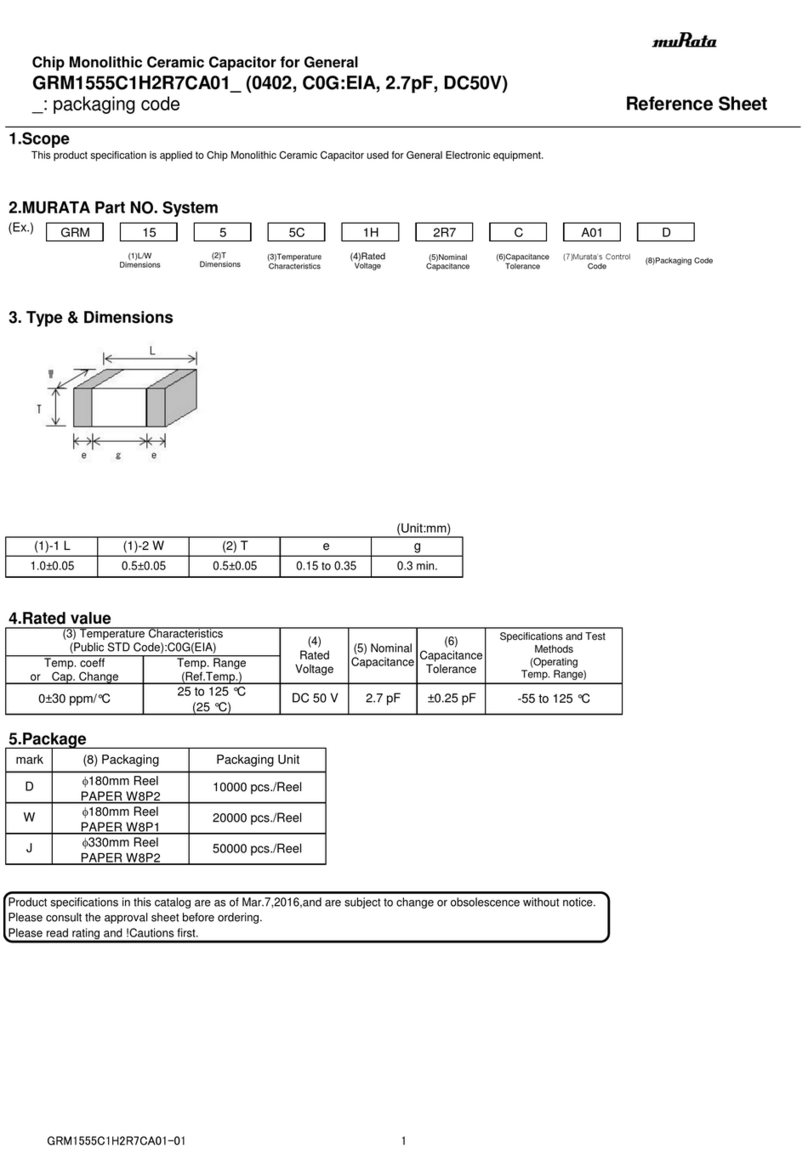
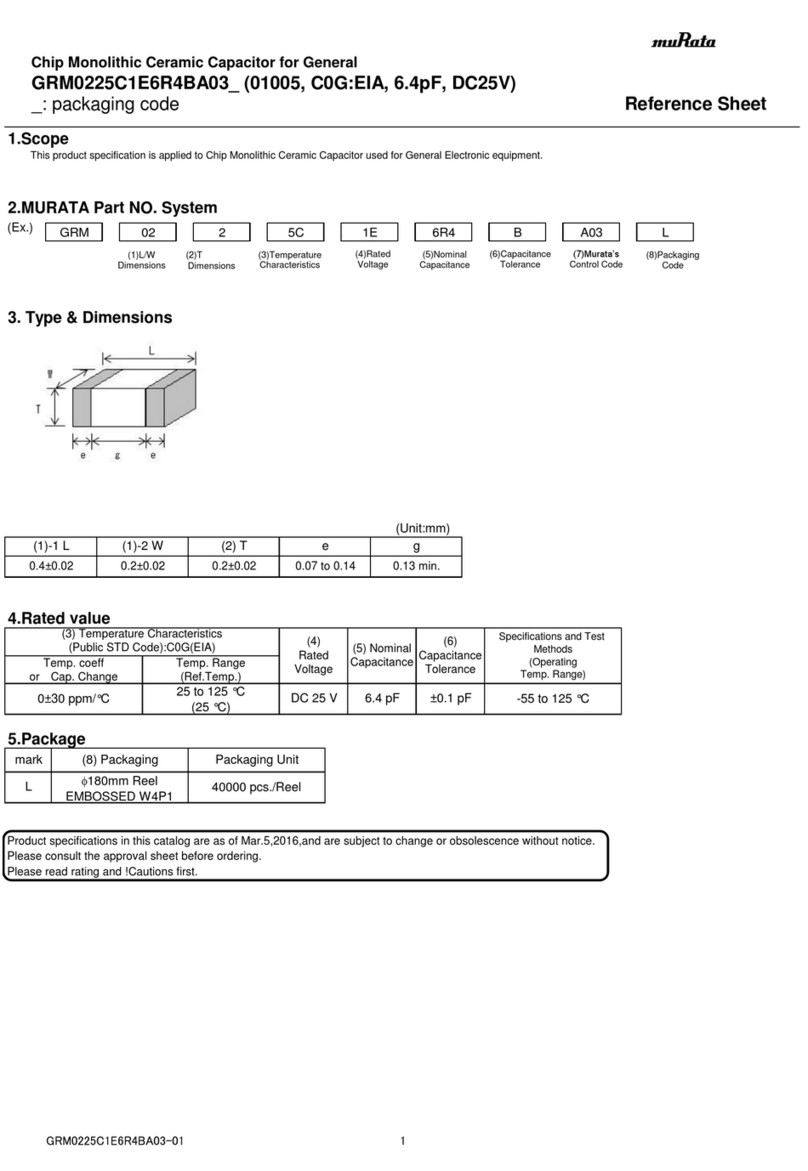
3.5 What are Bearing Currents and Shaft
Voltages?
Fast switching transistors in the frequency converter
combined with an inherent common-mode voltage (voltage
between phases and ground) generate high-frequency
bearing currents and shaft voltages. While bearing currents
and shaft voltages can also occur in direct-on-line motors,
these phenomena are accentuated when the motor is fed
from a frequency converter. The majority of bearing
damages in motors fed by frequency converters are because
of vibrations, misalignment, excessive axial or radial loading,
improper lubrication, impurities in the grease. In some cases,
bearing damages are caused by bearing currents and shaft
voltages. The mechanism that causes bearing currents and
shaft voltages is quite intricate and beyond the scope of this
Design Guide. Basically, two main mechanisms can be
identified:
•Capacitive coupling: the voltage across the bearing
is generated by parasitic capacitances in the motor.
•Inductive coupling: caused by circulating currents
in the motor.
The grease film of a running bearing behaves like isolation.
The voltage across the bearing can cause abreakdown of the
grease film and produce a small electric discharge (a spark)
between the bearing balls and the running track. This
discharge produces amicroscopic melting of the bearing ball
and running track metal and in time it causes the premature
wear-out of the bearing. This mechanism is called Electrical
Discharge Machining or EDM.
3.5.1 Mitigation of Premature Bearing Wear-
Out
There are a number of measures that can be taken for
preventing premature wearing and damage of the bearings
(not all of them are applicable in all cases – combinations
can be used). These measures aim either to provide a low-
impedance return path to the high-frequency currents or to
electrically isolate the motor shaft for preventing currents
through the bearings. Besides, there are also mechanical
related measures.
Measures to provide a low-impedance return path
•Follow EMC installation rules strictly. A good high-
frequency return path should be provided between
motor and frequency converter, for example by
using shielded cables.
•Make sure that the motor is properly grounded and
the grounding has a low-impedance for high-
frequency currents.
•Provide agood high-frequency ground connection
between motor chassis and load.
•Use shaft grounding brushes.
Measures that isolate the motor shaft from the load
•Use isolated bearings (or at least one isolated
bearing at the non-driving end NDE).
•Prevent shaft ground current by using isolated
couplings.
Mechanical measures
•Make sure that the motor and load are properly
aligned.
•Make sure the loading of the bearing (axial and
radial) is within the specifications.
•Check the vibration level in the bearing.
•Check the grease in the bearing and make sure the
bearing is correctly lubricated for the given
operating conditions.
One of the mitigation measures is to use filters. This can be
used in combination with other measures, such as those
presented above. High-frequency common-mode (HF-CM)
filters (core kits) are specially designed for reducing bearing
stress. Sine-wave filters also have a good effect. dU/dt filters
have less effect and it is recommended to use them in
combination with HF-CM cores.
Introduction to Output Filt... Output Filters Design Guide
MG.90.N5.02 - VLT®is a registered Danfoss trademark 9
33