Deif MTR-3 User manual

QUICK START GUIDE
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
Document no.: 4189300022C
SW version 3.0X.X or later
Multi-transducer, MTR-3

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 2 of 51
Table of contents
1. ABOUT THIS DOCUMENT ................................................................................................... 3
GENERAL PURPOSE......................................................................................................................3
CONTENTS/OVERALL STRUCTURE.................................................................................................. 3
2. WARNINGS AND LEGAL INFORMATION........................................................................... 4
LEGAL INFORMATION AND RESPONSIBILITY..................................................................................... 4
ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGE AWARENESS .....................................................................................4
SAFETY ISSUES............................................................................................................................4
DEFINITIONS ................................................................................................................................4
SAFETY WARNINGS AND INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE ...........................................................................5
WASTE........................................................................................................................................5
3. BASIC DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION OF THE MTR-3................................................. 6
INTRODUCTION.............................................................................................................................6
USER INFORMATION ..................................................................................................................... 7
DESCRIPTION OF THE PRODUCT ....................................................................................................7
PURPOSE AND USE OF MEASURING TRANSDUCER........................................................................... 8
4. CONNECTION..................................................................................................................... 10
INTRODUCTION...........................................................................................................................10
MOUNTING.................................................................................................................................10
CONNECTION OF INPUT/OUTPUT MODULES...................................................................................12
COMMUNICATION CONNECTION ................................................................................................... 12
CONNECTION OF AUXILIARY POWER SUPPLY ................................................................................14
5. SETTINGS ........................................................................................................................... 15
INTRODUCTION...........................................................................................................................15
M-SET SOFTWARE......................................................................................................................15
SETTING PROCEDURE.................................................................................................................16
GENERAL SETTINGS ...................................................................................................................16
CONNECTION.............................................................................................................................18
COMMUNICATION .......................................................................................................................18
SECURITY..................................................................................................................................19
ENERGY ....................................................................................................................................19
ANALOGUE OUTPUTS..................................................................................................................20
ALARMS.....................................................................................................................................23
RESET OPERATIONS...................................................................................................................23
6. MEASUREMENTS............................................................................................................... 24
INTRODUCTION...........................................................................................................................24
SUPPORTED MEASUREMENTS.....................................................................................................24
AVAILABLE CONNECTIONS...........................................................................................................24
EXPLANATION OF BASIC CONCEPTS.............................................................................................26
CALCULATION AND DISPLAY OF MEASUREMENTS..........................................................................26
PRESENT VALUES.......................................................................................................................27
7. APPENDIX A: MODBUS PROTOCOL ............................................................................... 29
MODBUS COMMUNICATION PROTOCOL.........................................................................................29
8. APPENDIX B: CALCULATIONS AND EQUATIONS.........................................................49
CALCULATIONS ..........................................................................................................................49

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 3 of 51
1. About this document
General purpose
This document is the Installation Instructions for the Multi-configurable AC Transducer, the MTR-
3. The general purpose of the document is to help the user with the first steps of installing and
using the unit. It contains instructions for installations and use of the MTR-3.
Contents/overall structure
This document is divided into chapters, and in order to make the structure simple and easy to
use, each chapter will begin from the top of a new page.
Please make sure that you read this document before starting to work with the
MTR-3. Failure to do this could result in human injury or damage to the
equipment.

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 4 of 51
2. Warnings and legal information
This chapter includes important information about general legal issues relevant in the handling of
DEIF products. Furthermore, some overall safety precautions will be introduced and
recommended. Finally, the highlighted notes and warnings, which will be used throughout this
document, are presented.
Legal information and responsibility
DEIF takes no responsibility for installation or operation of the MTR-3. If there is any doubt
regarding installation and use of the system in which the instrument is used for measuring or
supervision, please contact the person or company responsible for the installation of such system.
Electrostatic discharge awareness
Sufficient care must be taken to protect the terminals against static discharges during the
installation. Once the unit is installed and connected, these precautions are no longer necessary.
Safety issues
Installing the unit implies work with dangerous currents and voltages. Therefore, the installation
of the unit should only be carried out by authorised personnel who understand the risks involved
in the working with live electrical equipment.
Definitions
Throughout this document, a number of notes with helpful user information will be presented. To
ensure that these are noticed, they will be highlighted in order to separate them from the general
text.
Note symbol
Warnings
Be aware of the hazardous live currents and voltages. Do not touch any AC
measurement inputs as this could lead to injury or death.
The notes provide general information which will be helpful for the reader to bear
in mind.
The warnings indicate a potentially dangerous situation which could result in
death, personal injury or damaged equipment if certain guidelines are not
followed.
The units are not to be opened by unauthorised personnel. If opened anyway, the
warranty will be lost.

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 5 of 51
Safety warnings and instructions for use
Check the following before switching on the device:
•Nominal voltage
•Proper connection of auxiliary supply
•Nominal frequency
•Voltage ratio and phase sequence
•Current transformer ratio and terminals’ integrity
•Protection fuse – recommended maximal external fuse size is 6 A
•Proper connection of I/O modules
Waste
It is forbidden to deposit electrical and electronic equipment as municipal waste. The
manufacturer or provider shall take waste electrical and electronic equipment free of charge. The
complete procedure after lifetime should comply with the Directive EZ 2002/96/EG about
restriction on the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment or a
corresponding Url 118/04.
The secondary output of the current transformer should be short-circuited before
connecting the transducer.

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 6 of 51
3. Basic description and operation of the MTR-3
Introduction
What is in the delivery?
The consignment includes:
•Multi transducer MTR-3
•Label for I/O functionality description
•Quick Start Guide
Description of symbols
In different chapters or tables, different symbols may appear in the installation instructions.
According to the position of symbols, they have different meanings.
Double insulation in compliance with the SIST EN 61010-1 standard.
Functional ground potential.
Note: this symbol is also used for marking a terminal for protective ground
potential if it is used as a part of connection terminal or auxiliary supply
terminals.
Compliance of the product with directive 2002/96/EC, as first priority, the
prevention of waste electrical and electronic equipment
(WEEE), and in
addition, the reuse, recycling and other forms of recovery of such wastes so as
to reduce the disposal of waste. It also seeks to improve the environmental
performance of all operators involved in the life cycle of electrical and electronic
equipment.
Compliance of the product with European CE directives.
Subchapter
Symbols next to the subchapters indicate accessibility of functions described.
Accessibility of functions is indicated with the following symbols:
Function accessible via communication (M-Set software)
Tables
Supported functions and measurements are listed in tables. Symbols in tables
indicate support of enabled functions. Additionally, a legend is placed the below
table of used symbols. The meaning of symbols is:
●Function is supported
× Function is not supported
○Symbol meaning varies and is described in the legend below the table

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 7 of 51
User information
For unknown technical terms, please refer to the below glossary.
Glossary
Term Explanation
RMS
Root Mean Square value
Modbus
Industrial protocol for data transmission
M-Set
Software for MTR-3
AC
Alternating voltage and current
PA total
Angle calculated from total active and apparent power
PA1, PA2, PA3
Angle between fundamental phase voltage and phase current
PF
Power factor
THD
Total Harmonic Distortion
MD
Measurement of average values in time interval
Hand-over place
Connection spot of consumer installation in public network
M
v
− Sample factor
Defines a number of periods for measuring calculation on the basis of
measured frequency
M
p
− Average
interval
Defines frequency of refreshing displayed measurements on the basis
of a sample factor
Hysteresis
expressed as
percentage [%]
Percentage specifies increase or decrease of a measurement from a
certain limit after exceeding it.
Description of the product
The measuring transducer is intended for measuring, analysing and monitoring single-phase or
three-phase electrical power network. It measures RMS value by means of fast sampling of
voltage and current signals, which makes the instrument suitable for acquisition of transient
events. A built-in micro controller calculates measurements (voltage, current, frequency, energy,
power, power factor, THD phase angles, etc.) from the measured signals.
Appearance
The measuring transducer can differ from yours depending on the type and functionality.
1 Communication ports
2 Outputs
3 Auxiliary supply
4 Voltage inputs
5 Current inputs
6 Power ON LED
Communication ports and LED indicators
Serial communication can be connected by using screw-in connector (RS485). A USB can be
connected through a USB-mini type connector at the bottom of the transducer.
LED indicator is intended for POWER ON signalling (red LED).
The USB communication port is NOT galvanically insulated and can be used
ONLY UN-connected to aux. supply and power inputs!

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 8 of 51
Universal auxiliary supply
Auxiliary supply is connected by two screw-in connectors. For safety purposes, it is important that
all wires are firmly fastened. Auxiliary supply is wide range (24V DC-300V DC; 40V AC-276V AC).
Voltage inputs
Each voltage input is connected to a measuring circuit through an input resistor chain (3.3 MΩ
per phase). Maximum value of input voltage is 600 VL-N (1000 VL-L).
Current inputs
Each current input is connected to a measuring circuit through a current transformer (0.01 Ωper
phase). Maximum allowed thermal value of input current is 15 A (cont.).
Purpose and use of measuring transducer
The instrument is used for monitoring and measuring electric quantities of three-phase electrical
power distribution system. The meter is provided with 32 programme-adjustable alarms and
communication. With the RS485 and USB communication, the transducer can be configured and
by RS485 also measurements can be read. The transducer also functions as an energy counter
(up to four energy counters).

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 9 of 51
Supported measurements
Basic measurements
Phase
Voltage U1, U2, U3and U~
Current I1, I2, I3, In, Itand Ia
Active power P1, P2, P3, and Pt
Reactive power Q1, Q2, Q3, and Qt
Apparent power S1, S2, S3, and St
Power factor PF1, PF2, PF3and PF~
Power angle φ1, φ2, φ3and φ~
THD of phase voltage Uf1, Uf2 and Uf3
THD of power angle I1, I2and I3
Phase-to-
phase
Phase-to-phase voltage U12, U23, U31
Average phase-to-phase voltage Uff
Phase-to-phase angle φ12, φ23, φ31
THD of phase−to−phase voltage
Energy
Counter 1
Counter 2
Counter 3
Counter 4
Active tariff
Other measurements
MD values
Phase current I1, I2, I3
Active power P (Positive)
Active power P (Negative)
Reactive power Q − L
Reactive power Q − C
Apparent power S
Other measurements
Measurements
Frequency
Internal temperature

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 10 of 51
4. Connection
Introduction
This chapter deals with the instructions for connection of the measuring transducer. Both the use
and connection of the device includes handling with dangerous currents and voltages. Only
qualified persons should therefore perform connection. DEIF does not take any responsibility
regarding the use and connection. If any doubt occurs regarding connection and use in the
system, please contact the person or company responsible for such installations.
Before use: check voltages and phase rotation, supply voltage and nominal frequency.
Check protective fuse rating (the recommended maximum rating of the external protective fuse
for this equipment is 6 A - Red Spot type or equivalent).
Mounting
The MTR-3 is designed for DIN rail mounting. It should be mounted on a 35 mm DIN rail by means
of three plastic fasteners. Before installation, fasteners should be in open position (pulled). When
the device is in place, lock (push) the fasteners to closed position.
Electric connection
Voltage inputs of the measuring transducer can be connected directly to a low-voltage network or
via an appropriate voltage measuring transformer to a medium or high voltage network.
Current inputs of the measuring transducer can be connected directly to a low-voltage network or
via a corresponding current transformer.
Choose the corresponding connection from the following figures and connect the corresponding
voltages and currents. Information on electrical characteristics is given in the data sheet.
Wrong or incomplete connection of supply, measurement or other terminals
may cause malfunction or damage the device.
After connection, settings are performed via communication (connection mode,
current and voltage transformers ratio...).

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 11 of 51
System/connection Terminal assignment
Connection 1b (1W)
Single-phase connection
Connection 3b (1W3)
Three-phase – three-wire connection with
balanced load
Connection 3u (2W3u)
Three-phase – three-wire connection with
unbalanced load
Direct connection 3u (2W3u)
Three-phase, three-wire direct connection
Connection 4b (1W4)
Three-phase – four-wire connection with
balanced load

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 12 of 51
Connection 4u (3W4)
Three-phase – four-wire connection with
unbalanced load
Connection of input/output modules
Connect the module contacts as specified on the label. Examples of labels are given below and
describe modules built in the device.
Analogue output module with analogue
output, proportional to measured qua
ntities. The outputs may be either short- or
open-circuited. They are electrically insulated
from each other and from all other circuits.
(Example of analogue output 1).
Fast analogue output module with analogue
output, proportional to measured quantities.
The outputs may be either short- or open-
circuited. They are electrically insulated from
each other and from all other circuits.
(Example of analogue output 1).
Communication connection
The MTR-3 is equipped with one standard serial (RS485) communication port and one service
communication port (USB).
Connect the communication line by means of the corresponding terminals. Connection
information is stated on the instrument label. Connector terminals are marked on the label on the
upper side of the instrument.
The USB connector is positioned on the bottom side of the instrument under removable plastic
cover. For driver installation, the below note. The instrument will establish USB connection with
the PC approx. 5 seconds after physical connection to the USB port.
More detailed information about communication specifications is available in the data sheet.
The USB communication port is NOT galvanically insulated and can be used
ONLY UN-connected to aux. supply and power inputs!
Check the module features that are specified on the label, before connecting
module contacts. Wrong connection may cause damage or destruction of
module and/or device.

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 13 of 51
Serial communication port (RS485)
SERVICE communication port (USB)
RS485
RS485 communication is intended for connection of devices to network where several
instruments with RS485 communication are connected to a common communication interface.
It is necessary to provide the corresponding connection of individual terminals of the screw
terminal connector (see the table below).
USB
USB communication serves as a fast peer-to-terminal data link. The instrument is detected by
host as a USB 2.0 compatible device. The USB connection is provided through a USB standard
type mini B connector.
When the MTR-3 is connected to a PC through USB communication for the first
time, a user is prompted to install a driver. The driver is provided when
downloading M-Set. The M-Set software can be downloaded at www.deif.com.
When the driver is installed, the USB is redirected to a serial port, which should
be selected when using M-Set software.

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 14 of 51
Survey of communication connections
Connector
Terminals
Position
RS485
SCREW
TERMINAL
11 A
12 C
13 B
11
A
12
NC
13
B
USB-mini B
Standard USB 2.0 compatible cable recommended
(type mini B plug)
Connection of auxiliary power supply
The MTR-3 multi transducer has universal (AC/DC) auxiliary power supply. Information on electric
consumption is given in the data sheet. Auxiliary supply is connected through a screw terminal
connector.
Connection of universal power supply to terminals 1 and 2.
For safety purposes, it is important that both wires (Line and Neutral) are firmly
connected.

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 15 of 51
5. Settings
Introduction
Instrument settings can be remotely modified with communication (RS485 or USB) and M-Set
software when connected to a PC.
M-Set software
M-Set is a software tool for complete monitoring of measuring instruments, connected to a PC via
serial or USB communication. A user-friendly interface consists of four segments: device
management, instrument settings, real-time measurements and software upgrading.
Device management
Select the instrument in a favourite’s line. Use the network explorer to set and explore the device’s
network. Communication parameters of all devices and their addresses in the network can be
easily set.
Instrument settings
Multi register edit technology assures a simple modification of settings that are organised in a tree
structure. Besides transferring settings into the instrument, storing and reading from the setting
files are also available.
Real-time measurements
All supported measurements can be captured in real time in a table form. For further processing
of the results of measurements, copying via a clipboard into standard Windows formats is
supported.
Software upgrading
Always use the latest version of software, both M-Set and software in the instrument. The
programme automatically informs you on available upgrades that can be transferred from the
website and used for upgrading.
More information about the M-Set software can be found in the M-Set help
system.

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 16 of 51
M-Set user interface
Setting procedure
In order to modify instrument settings with M-Set, current parameters must be loaded first.
Instrument settings can be acquired via a communication link (serial or USB) or can be loaded
off-line from a file on a local disk. Settings are displayed in the M-Set setting window - the left part
displays a hierarchical tree structure of settings, the right part displays parameter values of the
chosen setting group.
General settings
General settings are essential for the transducer. They are divided into four additional sublevels
(Connection, Communication, Display and Security).
Description and location
Two parameters that are intended for easier recognition of a certain unit. They are especially used
for identification of the device or location on which measurements are performed.
Average interval
The averaging interval defines the refresh rate of measurements on communication and remote
display.
Temperature unit
Choose a unit for temperature display.
Maximum demand calculation (MD mode)
The instrument provides maximum demand values using thermal function. A thermal function
assures exponent thermal characteristic based on simulation of bimetal meters. Maximum values
and time of their occurrence are stored in the device. A time constant (t. c.) can be set from 1 to
255 minutes and is 6 times the thermal time constant (t. c. = 6 * thermal time constant).
You can download freeware M-Set from www.deif.com.

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 17 of 51
Example:
Mode: thermal function
Time constant: 8 min.
Current MD and maximal MD: reset at 0 min.
Starting current for PF and PA (mA)
At all measuring inputs, noise is usually present. It is constant, and its influence on the accuracy
is increased by decreasing measuring signals. It is present also when measuring signals are not
connected, and it occurs at all further calculations as very sporadic measurements. By setting a
common starting current, a limit of input signal is defined where measurements and all other
calculations are still performed.
Starting current for all powers (mA)
Noise is limited with a starting current also at measurements and calculations of powers.
Minimum synchronisation voltage
If all phase voltages are smaller than this (noise limit) setting, the instrument uses current inputs
for synchronisation. If also all phase currents are smaller than Starting current for PF and PA
setting, synchronisation is not possible and frequency displayed is 0.
Reactive power and energy calculation
Two different principles of reactive power and energy calculation are used:
Standard method:
With this method, a reactive power and energy is calculated, based on the assumption that all
power (energy), which is not active, is reactive.
Q2= S2– P2
This also means that all higher harmonics will be measured as reactive power (energy).
Delayed current method:
With this method, reactive power (energy) is calculated by multiplication of voltage samples and
delayed current samples (see chapter 8, “Appendix B: Calculations and equations” on page 36):
Q = U × I|+90°
With this method, reactive power (energy) only represents the true reactive component of
apparent power (energy).
Thermal function
0 1 2 3 45678910 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
Time [min.]
Measured value
Present MD MD peak Input

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 18 of 51
Connection
Connection
When connection is selected, load connection and the supported measurements are defined (see
chapter 6, “Measurements” regarding connection mode, on page 23).
Setting of current and voltage ratios
Before setting current and voltage ratios, it is necessary to be familiar with the conditions in which
the device is to be used. All other measurements and calculations depend on these settings. Up
to five decimal places can be set.
Settings range
VT primary
VT secondary
CT primary
CT secondary
Maximum value
1638.3 kV
13383 V
1638.3 kA
13383 A
Minimum value
0.1 V
1 mV
0.1 A
1 mA
Used voltage and current range
Setting of the range is connected with all settings of alarms, analogue outputs and a display
(calculation) of energy and measurements recording, where 100% represents 500 V 5 A. In case
of subsequent change of the range, alarms settings must be correspondingly changed, as well.
Nominal frequency
A valid frequency measurement is within the range of nominal frequency ±32 Hz. This setting is
used for alarms.
Energy flow direction
This setting allows manual change of energy flow direction (IMPORT to EXPORT or vice versa)
in the readings tab. It has no influence on readings sent by communication.
CT connection
If this setting is set to REVERSED, it has the same influence as if CTs would be reversely
connected. All power readings will also change their sign.
Communication
Serial Communication
Define parameters that are important for the operation in the RS485 network. Factory settings of
communication are #33\115200,n,8,2 (address 1 to 247\baud rate 2400 to 115200 b/s, parity,
data bits, stop bit).
Modbus table: with this setting, a Modbus table for measurements and settings is defined. Modbus
addresses for measurements and settings can be compatible with the previous family of
transducers (MTR-2). For a more detailed description, see chapter 7, “Appendix A: Modbus
protocol”, on page 28.
USB Communication
For description of all settings see Serial Communication, appendix A. For driver installation,
see the note on page 13. The instrument will establish a USB connection with the PC approx. 5
seconds after physical connection to the USB port.
Settings of connections must reflect actual state, otherwise measurements are
not valid.

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 19 of 51
Security
Parameter settings are divided into three groups regarding security level:
1. At the first level (PL1), settings of a real time clock can be changed, and energy meters
and MD can be reset.
2. At the second level (PL2), the access to all data that are protected with the first level
(PL1) and setting of all other parameters in the »SETTINGS« menu is available.
3. A backup password (BP) is used if passwords at levels 1 (PL1) and 2 (PL2) have been
forgotten, and it is different for each device (depending on a serial number of the meter).
The BP password is available in the support department at DEIF, and is entered instead
of the password PL1 or/and PL2. Do not forget to state the meter serial number when
contacting the personnel at DEIF.
User information
Password setting
A password consists of four letters taken from the British alphabet from A to Z. When setting a
password, only the letter being set is visible while the others are covered with *.
Two passwords (PL1, PL2) and the time of automatic activation could be set.
Password modification
A password can be modified; however, only that password can be modified to which the access
is unlocked at the moment.
Password disabling
A password is disabled by setting the "AAAA" password.
Energy
Active tariff
When active tariff is set, one of the tariffs (up to four) is defined as active.
Common energy exponent
Common energy exponent defines minimal energy that can be displayed on the energy counter.
On the basis of this and a counter divider, a basic calculation prefix for energy is defined (−3 is
10−3Wh = mWh, 4 is 104Wh = 10 kWh). A common energy exponent also influences in setting a
number of impulses for energy of pulse output or alarm output functioning as an energy meter.
Define the common energy exponent as recommended in the table below, where counter divider
is value 10 as default. Values of primary voltage and current determine a proper common energy
exponent.
A serial number of device is stated on the label and also accessible with the M-
Set software.
A factory-set password is “AAAA” at both access levels (L1 and L2). This
password does not limit access.
After modification of energy parameters, the energy meters must be reset.
Otherwise, all further energy measurements could be incorrect.

MTR-3 Installation Instructions
DEIF A/S Page 20 of 51
Current
Voltage
1 A
5 A
50 A
100 A
1000 A
110 V
-1
0
1
1
2
230 V
0
0
1
2
3
1000 V
0
1
2
3
4
30 kV
2
2
3
4
4*
* Counter divider should be at least 100
Counter divider
Additionally, the counter divider defines precision of a certain counter, according to settings of a
common energy exponent. This is done to prevent the counter from having an early energy
overflow.
An example for 23.331 kWh of consumed active energy:
Divider
Exponent
Resolution
Displayed
1
0
1 x 10^0 = 1 W
23.331 kW
10
0
10 x 10^0 = 10 W
23.33 kW
100
0
100 x 10^0 = 100 W
0.0233 MW
1000
0
1000 x 10^0 = 1 kW
0.023 MW
1
1
1 x 10^1 = 10 W
23.33 kW
1
2
1 x 10^2 = 100 W
0.0233 MW
1
3
1 x 10^3 = 1 kW
0.023 MW
1
4
1 x 10^4 = 10 kW
0.02 MW
10
2
10 x 10^2 = 1 kW
0.023 MW
Analogue outputs
Number of analogue outputs depends on the version of MTR-3.
Analogue outputs
Each of up to four analogue outputs is fully programmable and can be set to any of 6 full-scale
ranges. Within each of those 6 ranges, other required output ranges can be set. For example,
4…20 mA range can be set when ±20 mA full-scale range is selected:
Output parameter
Sets the measured parameter to be transformed onto the analogue output.
Table of contents
Other Deif Transducer manuals
Popular Transducer manuals by other brands

Mianyang Weibo Electronic
Mianyang Weibo Electronic WBP114S91 user manual

Simrad
Simrad 38-200 COMBI C - REV D installation manual

KYOWA
KYOWA PHF-S-SA4 instruction manual

Desoutter
Desoutter DRT5 Sq 5000 User instructions

Balluff
Balluff MICROPULSE BTL7-A/E1 0-M Series Condensed guide

BDI
BDI ST350 Operation manual

HBM
HBM U2B Mounting instructions

Setra Systems
Setra Systems Multi-Sense 231RS operating instructions

Bitronics
Bitronics M651 user manual

Setra Systems
Setra Systems 355X Series Operating & installation instructions
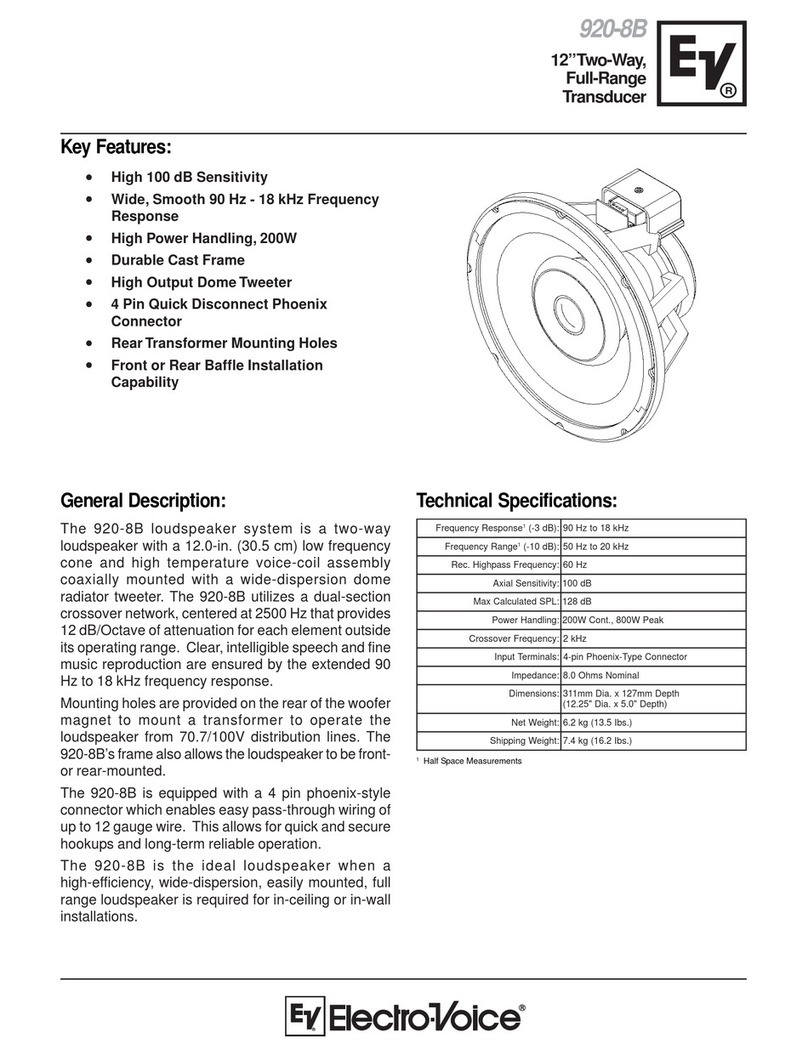
Electro-Voice
Electro-Voice 920-8B Technical specifications

Setra Systems
Setra Systems 267 installation guide