DIVERSIFIED METAL FABRICATORS, INC. RW-1016
1-2 © 2017 DMF, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
1.1 GENERAL DESCRIPTION, WEIGHTS & CAPACITIES
1.1.1 Features and Description
DMF’s RW-1016 Railgear is designed for Class 2 & 3 single rear wheel heavy duty pickup trucks.
The front and rear Railgear assemblies are visually similar and share many common
components. Railgear assemblies attach to the truck frame with bracketry specific to the
vehicle make and model. All structural members and brackets are constructed of carbon steel.
Select components are hot dip galvanized or zinc plated for additional corrosion resistance.
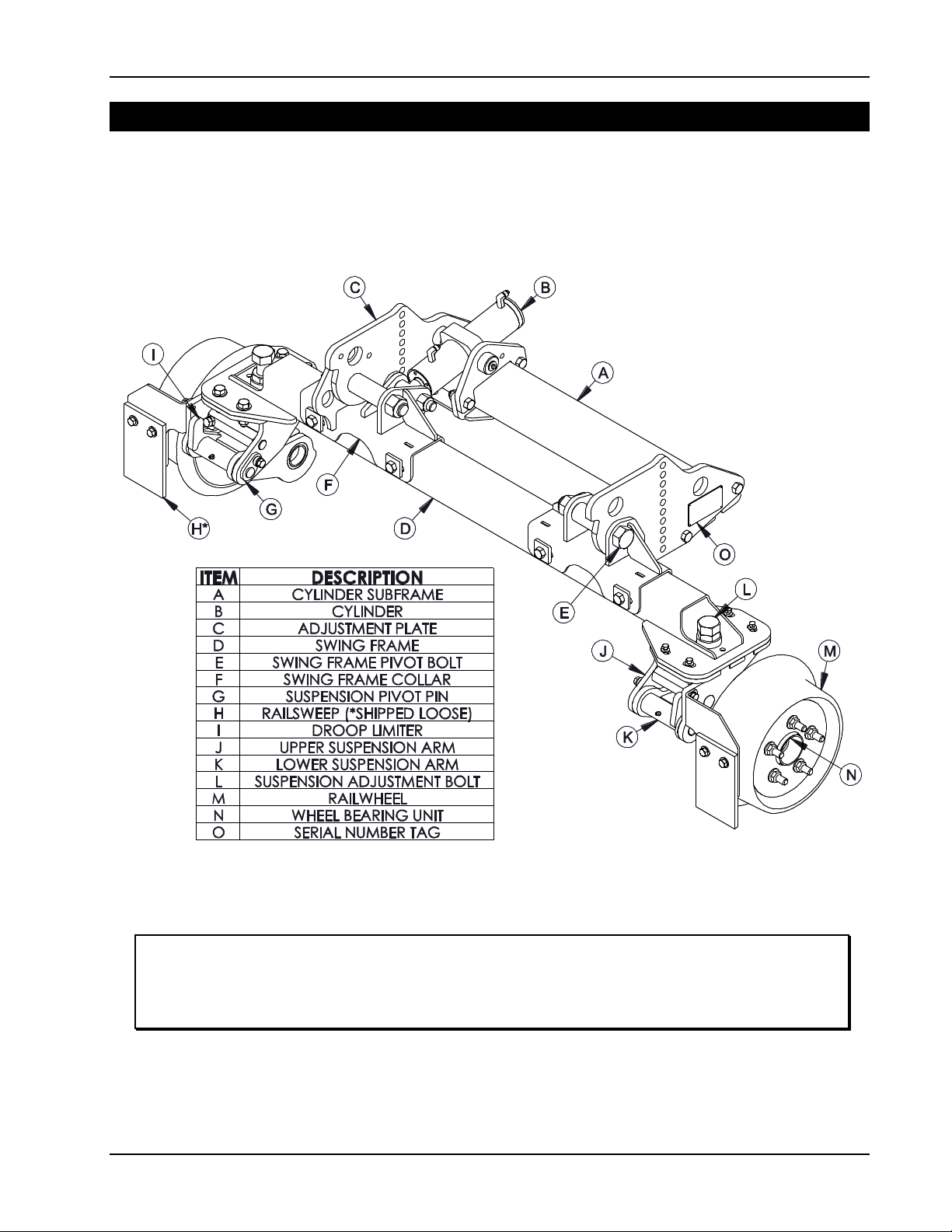
Each Railgear assembly is actuated is by a single hydraulic cylinder. In the rail position, the
Railgear is “over-center”, which prevents a hydraulic failure from allowing the gear to collapse.
In the highway position, hydraulic locking valves prevent the Railgear from falling due to a
system leak. An emergency hand pump allows the gear to be lifted into the highway position in
the event of hydraulic system failure while on rail.
RW-1016 Railgear features an independent suspension system at each railwheel. Rubber
springs provide a smooth and quiet ride over uneven rail surfaces. The load on each railwheel
can be adjusted individually. The 10” guide wheels are machined from cast steel, and mounted
to automotive-style unitized hub bearings that maximize service life and minimize maintenance
Unlike most of our larger models, RW-1016 does not lift the steer axle off the rail. All vehicle
tires remain in contact with the rail. RW-1016 does not provide braking or drive power, and
relies on the vehicle tires for those functions.
Most vehicles require installation of alternate wheels and tires to properly align the vehicle’s
track width to the rails. DMF offers Wheel Modification Kits for many popular chassis models for
use on standard gage rail. These kits include the necessary rims, wheel adapters, TPMS
sensors, steering stops, and steering wheel locks.
RW-1016 was engineered to meet a wide range of customer requirements in its standard
configuration. DMF also offers many options for RW-1016 to meet your specialized needs.
Contact DMF for additional information on standard and optional features.
RW-1016 Standard Features
56.5” rail gauge
Steel tread railwheels
Wireless Railgear controls
4-corner rail wheel insulation
Hydraulic locking valves, highway & rail position (front & rear)
Low-profile 12VDC hydraulic power unit and emergency hand pump
Front and rear rail sweeps and de-rail skids
RW-1016 Optional Features
Truck wheel and tire modification kits
In-cab switchable rail shunting
Heavy duty cable pinoff system (front & rear)
Rubber tread railwheels
Additional wireless handheld transmitter for backup/emergency use
Hardwired Railgear controls @ bumpers and/or in cab
Railgear position sensing for GPS/Telematics integration
Custom rail gauges & wheel profiles