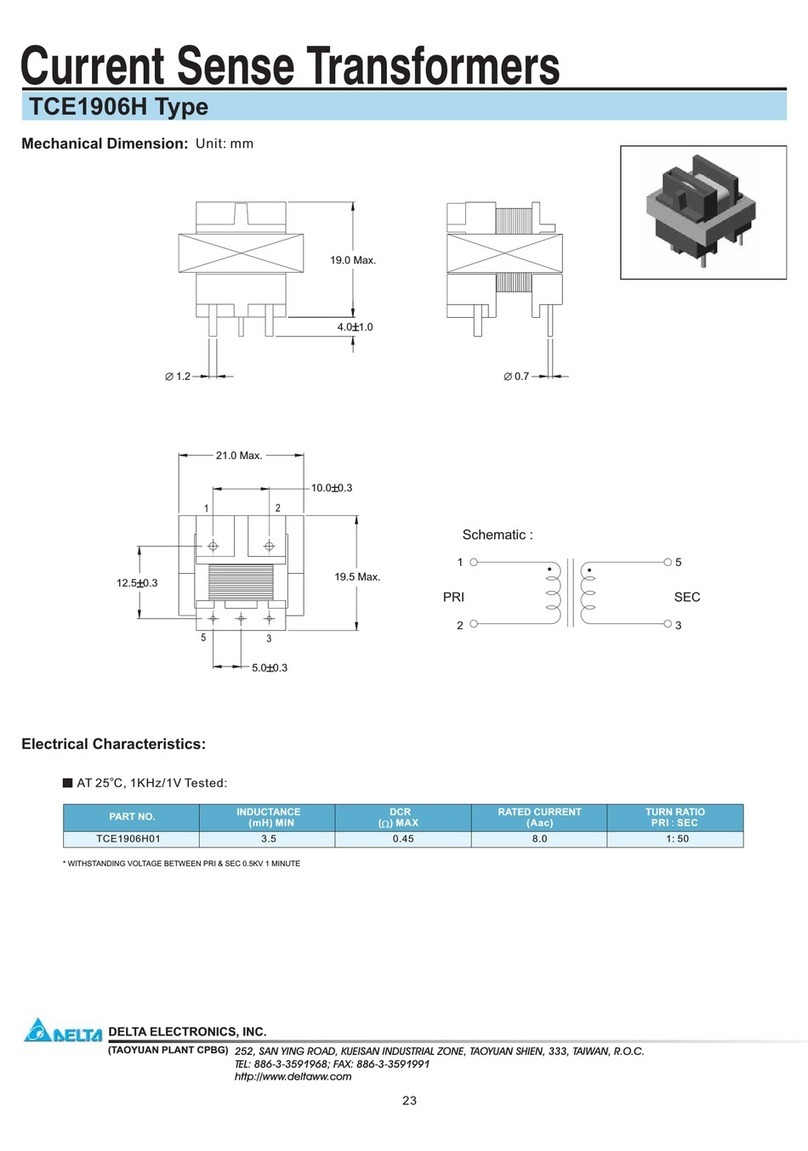
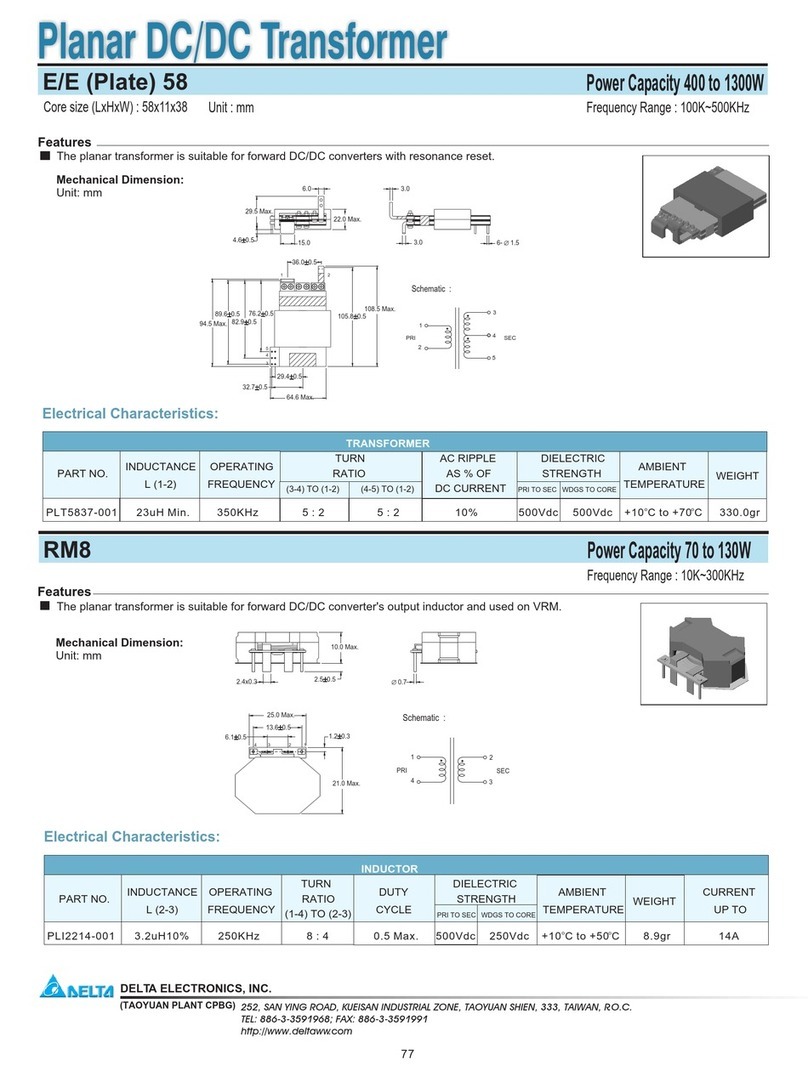
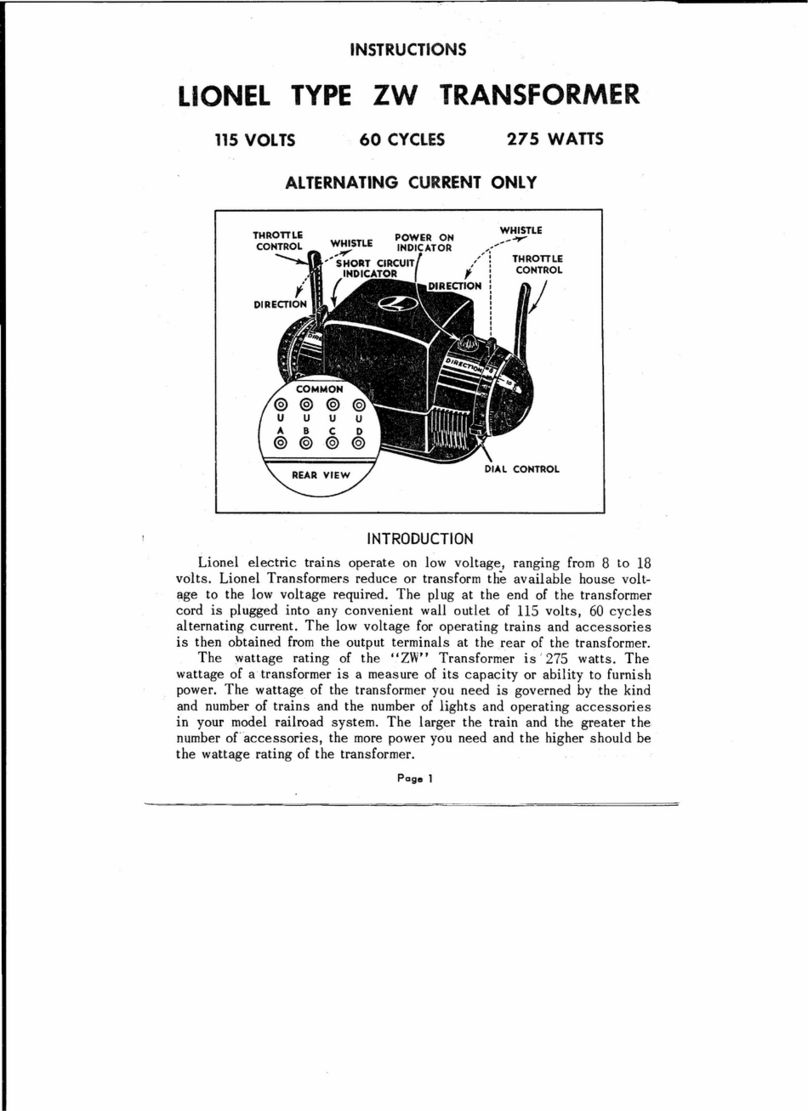
Introduction
Eaton provides installation and maintenance instructions
for its Cooper Power™ series transformers in Service
Information MN202001EN. These transformers are designed
for installation on three-phase underground systems. All
units are constructed for weather-exposed mounting on a
concrete pad with high- and low-voltage cable entering the
operating compartments through an opening in the pad.
Read this manual first
Read and understand the contents of this manual and follow
all locally approved procedures and safety practices before
installing or operating this equipment.
Additional information
These instructions are not intended to cover all details
or variations in the equipment, procedures, or process
described, nor to provide directions for meeting every possible
contingency during installation, operation, or maintenance. For
additional information, contact your Eaton representative.
Acceptance and initial inspection
Receiving Inspection
It is important that a thorough inspection of the transformer
be made before it is unloaded from the carrier.
1. Ensure that all parts listed on the bill of lading are present.
2. Before unloading the transformer, inspect for signs of
damage or mishandling. Locate accessory parts that
may have been shipped separately.
3. If damage is detected or shortages are noticed, write
a brief description on the freight bill. Normally, the
transformer is shipped FOB point of manufacture,
and it is the customer’s responsibility to file a claim
against the carrier. If the transformer was shipped FOB
destination, notify your Eaton representative. He or she
will, with the inspector’s report, take the necessary
steps to file a claim against the carrier.
Handling
Special procedures must be followed when handling
transformer in ambient temperatures below -20 °C. Contact
your Eaton representative for further instructions. Failure to
follow special handling procedures may cause premature
failure of transformer and its components.
Transformer weight
The transformer weight is shown on the transformer
nameplate. Most of the weight in a pad-mounted
transformer assembly is in the main tank that holds the core
and coil assembly and the insulating liquid.
Moving transformers shipped on pallets
Transformers shipped on pallets may be lifted or moved by
forklift trucks of proper capacity. When using a forklift, lift
with the transformer tank closest to the mast of the forklift
since most of the transformer weight is in the tank. Pallet-
mounted equipment may also be moved by crane or hoist.
Lifting transformers by crane or hoist
Check the weight of the transformer and the capacity and
condition of all hoisting or lifting equipment. Do not use
worn, frayed or damaged cables or slings. Do not use
hoisting machinery with load capacity less than the weight
of the transformer. Improper use of hoist or jack could
seriously damage the transformer or its attachments or
cause serious personal injury.
For unloading, lifting lugs are provided near the top of the
transformer tank. Lifting chain or cable angles should not be
over 30° from vertical. Otherwise, spreaders should be used
to hold the lifting cables apart to avoid any bending of the
structure or lifting lugs.
Do not attempt to lift the transformer by placing a
continuous loop of chain or cable around the unit or lifting
lugs. This can damage the transformer and can cause
accidents resulting in serious personal injury.
If the transformer cannot be lifted by crane, it may be
skidded or moved by rollers.
Using jacks
Place jacks under the tank base on the open ends of the
transformer tank. Jacking pads are provided for transformers
with bases greater than 6”. Do not place jacks under
radiators or terminal compartment frames.
When jacking a transformer for insertion of rollers
underneath it, ensure that four jacks are used and that two
adjacent corners are raised simultaneously and evenly to
avoid warping the base. When using rollers, use as many as
necessary to distribute the weight uniformly.
Do not attach pulling lines to moldings or other sheet metal
parts of the transformer.
IMPORTANT
Do not Exceed Transformer Ratings. Transformers
should be operated only at the ratings specified on the
transformer nameplate. Prolonged overload operation
will measurably shorten the projected service life of a
mineral oil-filled transformer. Eaton’s Cooper Power™
series PEAK™ transformers may help to extend
insulation life and can be operated at higher capacities
than traditional units while still exceeding ANSI®
standard insulation life.
WARNING
Heavy Equipment. Improper handling can cause severe
injury, death, or damage to transformer. Before moving
the transformer, read the handling instructions provided
in this manual.
1Three-phase pad-mounted compartmental type installation and maintenance instructions MN202001EN August 2015