ELTEC IPIN-300 User manual

elektronik mainz
IPIN-300
Serial IPIN Module
Hardware Manual
Revision 3 A

© 1992 ELTEC Elektronik AG, Mainz
The information in this document has been carefully checked and is believed to be entirely reliable. However, no responsibility
is assumed for inaccuracies. ELTEC reserves the right to make changes to any products to improve reliability, function or
design. ELTEC does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit described in this
manual; neither does it convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of others. ELTEC products are not authorized
for use as components in life support devices or systems intended for surgical implant into the body or intended to support or
sustain life. Buyer agrees to notify ELTEC of any such intended end use whereupon ELTEC shall detemine availability and
suitability of its product or products for the use intended.
This document contains copyrighted information. All rights including those of translation, reprint, broadcasting,
photomechanical or similar reproduction and storage or processing in computer systems, in whole or in part, are reserved.
EUROCOM is a trademark of ELTEC Elektronik AG. Other brands and their products are trademarks of their respective
holders and should be noted as such.
This document is edited and printed by:
Rev. Changes Date
Revision History IPIN-300
Editorial Team:
ELTEC Elektronik AG
Galileo-Galilei-Str. 11 Postfach 42 13 63
D-55129 Mainz D-55071 Mainz
Telephone +49(61 31) 9 18-0
Telefax +49(61 31) 9 18-1 99
0 A Preliminary 13.07.87, H.R.
1 A First Edition 26.08.87, H.R.
2 A Second Edition with IPIN-302/3 15.05.90, H.R.
3 A Third Edition,
improved device reliability,
valid for Hardware Revision 3.A 08.07.92, H.R.
H.K., U.I., J.G.

Table of Contents
Page
IPIN-300 Table of Contents
Hardware Manual III
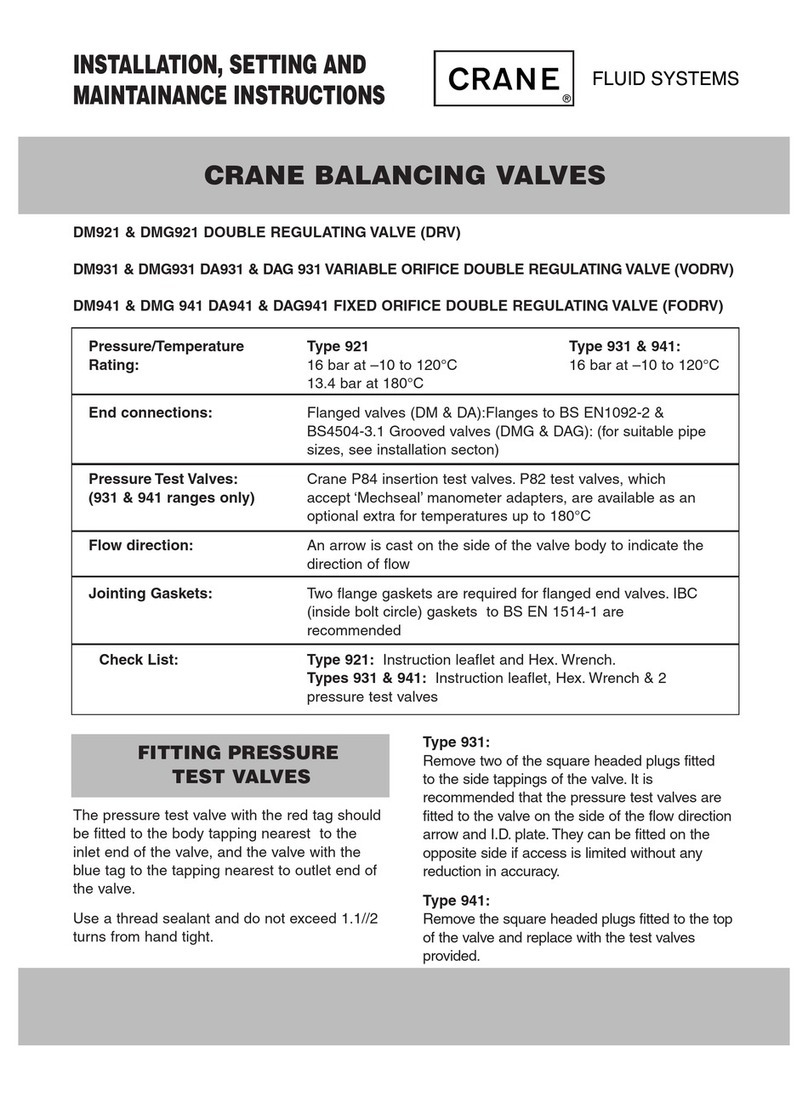
1General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
2LEB Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
3Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3.1 Installation of the Serial IPINs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3.2 Connecting to the I/O Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
4Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4.1 The Configuration Array of IPIN-300. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
4.2 The Configuration Array of IPIN-302. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4.3 The Configuration Array of IPIN-303. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5Address Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
6Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
7Serial I/O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
7.1 Baud Rate Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
7.2 I/O Connectors of IPIN-300 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
7.3 I/O Connector of IPIN-302 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7.4 I/O Connectors of IPIN-303 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
8Differences between IPIN-300 and IPIN-302/3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Appendix. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Technical Action Request Form Sheet
Reader Comments Form Sheet

Page
Table of Contents IPIN-300
IV Hardware Manual
Tables:
Table1: I/O Functions of IPIN-300. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Table2: Jumpers J401 to J406: TD/RD - Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Table3: Address Range of IPIN-300/2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table4: SCC Time Constants for x16 Clock Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Table5: I/O Connectors (X2, X3, X4) of IPIN-300 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Table6: Connection of IPIN-300 to Various Standards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Table7: Pin Assignment of 9-pin Sub-D Connectors (IPIN-300). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table8: Connection of 9-pin to 25-pin Sub-D Connectors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table9: I/O Connector of IPIN-302 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table10: Pin Assignment of 6-pin Modular Jacks (IPIN-303). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table11: Differences between IPIN-300 and IPIN-302/3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Figures:
Figure1: Block Diagram IPIN-300. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Figure2: Block Diagram IPIN-302/3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Figure3: Jumper Location Diagram (Bottom View) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure4: Jumper Location of IPIN-302 (Bottom View) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11

Scope of Delivery
Description: Order No.:
IPIN-300 Scope of Delivery
Hardware Manual V
NOTE: The last letter of the order numbers refers to the hardware revision and is subject to
changes. Please contact ELTEC for information about valid order numbers.
IPIN-A300 V-IPIN-A300
Serial IPIN with 3 x cable (0.3m) 18-pin DIL to 2x9-pin Sub-D
and front panel
IPIN-A302 V-IPIN-A302
Opto-isolated serial IPIN
IPIN-A303 V-IPIN-A303
I/O for 2 x IPIN-A302
with 2x26-pin connection cable to IPIN-A302 (0.25m)

Options
Description: Order No.:
Options IPIN-300
VI Hardware Manual
NOTE: The last letter of the order numbers refers to the hardware revision and is subject to
changes. Please contact ELTEC for information about valid order numbers.
Related Products
Description: Order No.:
3 x Cable (1.5 m) 18-pin DIL to 2x9-pin Sub-D V-IPIN-Z300
and Front Panel
Documentation:
Hardware Manual IPIN-300 V-IPIN-C993
Hardware:
Connection Cable 9-pin to 25-pin Sub-D, 2 m V-CABL-A119
RxD TxD =
Connection Cable 9-pin Sub-D , 2 m V-CABL-A120
RxD TxD X
Connection Cable 6-pin to 25-pin Sub-D , 3 m V-CABL-A143
Connection Cable 6-pin to 9-pin Sub-D , 3 m V-CABL-A144
RS232 to RS422/485 Converter V-CONV-A100
Data Sheets:
Data sheet Zilog SCC Z8530 V-DTBT-A906

Warning !
This equipment generates and can radiate radio frequencies. If not installed in accordance
with the instruction manual, it may cause interference to radio communications. The
equipment has not been tested for compliance with the limits for class A computing devices,
pursuant to subpart J of part 15 of FCC rules, which are designed to provide reasonable
protection against such interference, but temporary usage is permitted as per regulations.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interference, in which case
the user, at his own expense will be required to take whatever measures may be required to
shield the interference.
Unpacking Instructions
Carefully remove the board from the shipping carton.
Save the original shipping container and packing material for storing or reshipping the board.
Avoid touching integrated circuits except in an electrostatic free environment.
Electrostatic discharge can damage these circuits.
Inspect the board for any shipping damage. If undamaged, the module can be prepared for
system installation.
CAUTION
IPIN-300 Unpacking and Warning
Hardware Manual VII

Conventions
If not otherwise specified, addresses are written in hexadecimal notation and identified by a
leading dollar sign ("$").
Signal names preceded by a slash ("/"), indicate that this signal is either active low or that this
signal becomes active with the trailing edge.
Used abbreviations:
bbit
Bbyte
Kkilo, means the factor 400 in hex (1024decimal)
Mmega, the multiplication with 100 000 in hex (1 048576 decimal)
MHz 1 000 000 Hertz
Conventions IPIN-300
VIII Hardware Manual

IPIN-300 1 General Description
Hardware Manual 1
1 General Description
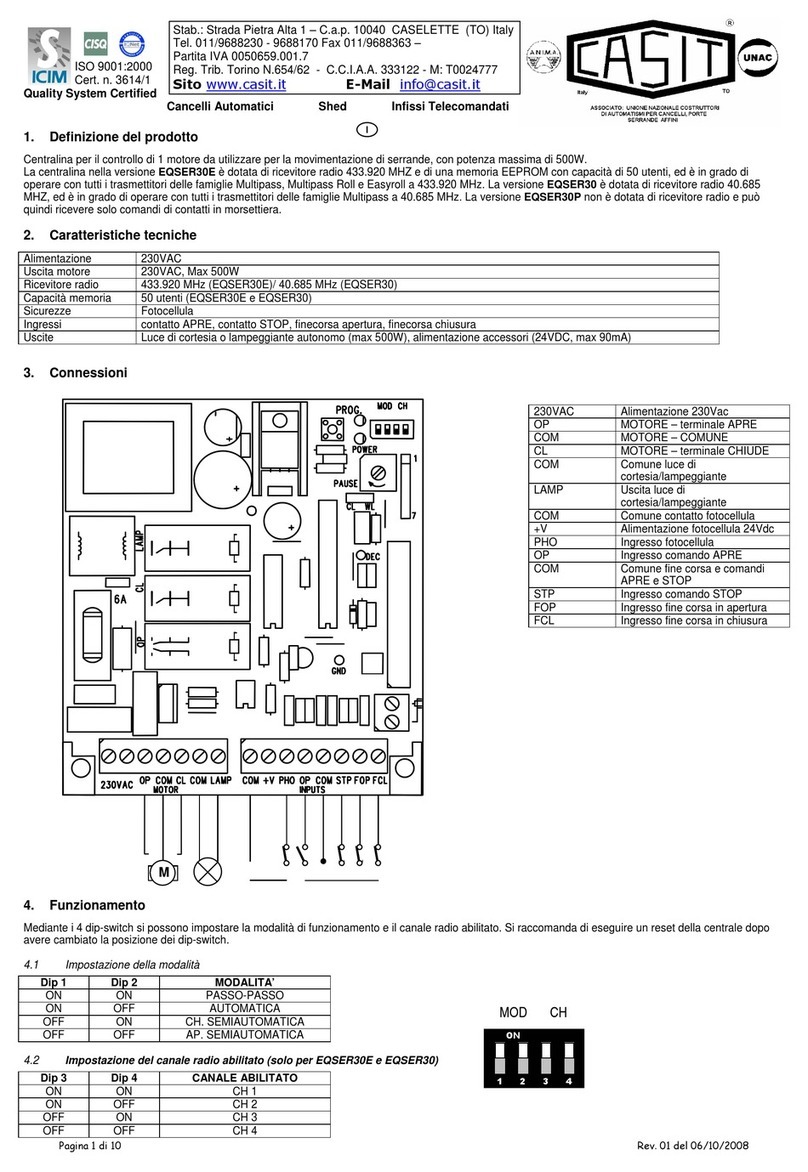
The IPIN-300 and IPIN-302 are single Intelligent Peripheral INterface (IPIN) modules for use
in connection with an ELTEC Local Extension Bus (LEB) base module.
The most important features of these IPINs are:
•Three Zilog Z8530 8MHz serial communications controllers (SCCs) for six high-speed,
multi-mode, multi-protocol channels with program control.
•In asynchronous mode, each channel is programmable for five to eight bits per word with
one, one and one-half, or two stop bits. The user can also select odd, even, or no parity.
•Programmable baud rate generators and digital phase-locked loops for clock recovery for
50bps up to 115 200bps in asynchronous x16 mode.
•In synchronous mode, you can select external or internal character synchronization on one
or two characters, CRC generation and checking with CRC-16 or CRC-CCITT, present to
either 1s or 0s.
•Each SCC has also an SDLC/HDLC mode with comprehensive frame-level control,
automatic zero insertion and deletion, I-field residue handling, abort generation and
detection, CRC generation and checking and SDLC loop mode operation.
•Multi-protocol operation under program control; programmable for NRZ, NRZI, or FM data
encoding.
•Vectored interrupt support with three different vectors per channel for transmit, receive, and
status interrupt sources.
•Software driver for OS-9 and UNIX, for other operating systems sample drivers available.
•In connection with an IBAM board, the user has up to 18 multi-mode high-speed serial I/O
channels in a single VME slot.
Special features of the IPIN-300:
•0 to 2Mbps in synchronous mode.
•RS232 / V 24 (X.21 bis) full modem control with a 9-pin IBM compatible Sub-D connector.
•RS422,485 / V 11 (X.21) converter available.
•500mV pico fuse to protect 12V supplied chips.
Special features of the IPIN-302:
•On-board level converter for RS232 or RS422.
•Opto-isolated channel, 500VDC isolation voltage against system, not between channels.
•Only RxD and TxD supported.
•Front panel with 12 x 6-pin modular jack for two IPIN-302s available (IPIN-A303).

1 General Description IPIN-300
2Hardware Manual
Figure1: Block Diagram IPIN-300

IPIN-300 1 General Description
Hardware Manual 3
Figure2: Block Diagram IPIN-302/3

1 General Description IPIN-300
4Hardware Manual

IPIN-300 2 LEB Parameters
Hardware Manual 5
2 LEB Parameters
• Slave Data Transfer Options:
-D8 odd
• Interrupter Options:
-vectored IRQs
• Clock Speed:
-max. 25MHz
• Environmental Options:
-Operating temperature: 0°C to 70°C
-Storage temperature: -40°C to 85°C
-Maximum operating humidity: 85%
• Power Options:
-1.0A at +5V±5%
-0.2A at +12V±20% only IPIN-300
-0.2A at -12V±20% only IPIN-300

2 LEB Parameters IPIN-300
6Hardware Manual

IPIN-300 3 Installation
Hardware Manual 7
3 Installation
3.1 Installation of the Serial IPINs
To install the IPIN-300 or IPIN-302 on a LEB base module, plug the IPIN into the LEB
connector and fix it with three screws.
The serial IPINs have only a 80-pin LEB connector. If you use a base module with a 100-pin
LEB connector, row E is not used.
The front panel may be attached just aside the base board or at the back side of the card cage.
This panel has the same size as a front panel of a single width, double high VME board, i.e.
4TE, 6HE.
The connection cable is appropriately 0.3m. For special usage, a cable with a length of 1.5m
is available.
For the address of the LEB, please refer to the documentation of the base module. I.e. the
EUROCOM-5 uses the address space $FE40.0000 to $FE7F.FFFF for the LEB.
If you use the IBAM, the base address of the IPIN module connected to X4 is $50.0000 and
X3 and X2 have the base addresses $50.8000 and $51.0000. For more information, refer to
the hardware manual of the LEB base module.
3.2 Connecting to the I/O Panel
IPIN-300:
The serial input/output connectors (X2, X3 and X4) should be connected with a double 9-pin
Sub-D cable. Six 9-pin Sub-D connectors (all channels of an IPIN-300) can be fixed at the
front panel.
As shipped, the IPIN-300 has a configuration as a RS232 interface. For other usage, the IPIN
can be arranged (see Chapter 4 ‘Configuration’) in different ways.
IPIN-302:
The IPIN-302 uses a 26-pin connector for all isolated I/O lines. It should be connected to the
IPIN-303 via a 26-pin flat cable.
The IPIN-303 mounting panel can be used as I/O for up to two IPIN-302 (12 I/O channels).

3 Installation IPIN-300
8Hardware Manual

IPIN-300 4 Configuration
Hardware Manual 9
4 Configuration
4.1 The Configuration Array of IPIN-300
The IPIN-300 can be configurated for synchronous or asynchronous serial data transfer.
The next figure shows the position of all jumpers. On the soldering side, pin1 is marked by a
bevelled corner.
Figure3: Jumper Location Diagram (Bottom View)
Normally the pins6 and 18 of the serial I/O connectors SIOC (X2, X3, and X4) are used for
the DSR signals of each channel. For a synchronous data transfer, these pins may be used as
clock input or output signals. Pin18 is used for channelA and pin6 is used for channelB of
each SCC.

4 Configuration IPIN-300
10 Hardware Manual
DSR can only be used in asynchronous mode as input. In synchronous mode, SCC allows this
pin only as SYNCH output, so the signal DCD of channelB is used as DSR input of
channelA.
The following table shows the connection between the function of each SCC and the
configuration of his jumper field.
x to be replaced by the attached SCC number.
Table1: I/O Functions of IPIN-300
Jumper Configuration
Channel A Channel B Function
Jx1
Jx2
Jx3
1-2
open
open
Jx5
Jx6
Jx7
Jx4
1-2
open
open
2-3
Clock as output,
no DSR,
two independent channels per SCC
Jx1
Jx2
Jx3
2-3
1-2
open
Jx5
Jx6
Jx7
Jx4
2-3
1-2
open
2-3
Clock as input,
no DSR,
two independent channels per SCC
Jx1
Jx2
Jx3
2-3
open
2-3
Jx5
Jx6
Jx7
Jx4
2-3
open
1-2
2-3
No clock,
DSR in asynchronous mode only,
two independent channels per SCC
(Default setting)
Jx1
Jx2
Jx3
Jx4
2-3
open
1-2
1-2
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
---
No clock,
DSR in synchronous mode only for channel A,
DCD for channel B not available,
but independent usage of all the other functions
of channel B possible.
Jx8 Common for channelA and B to supply +5V at
pin9 of the connector.

IPIN-300 4 Configuration
Hardware Manual 11
4.2 The Configuration Array of IPIN-302
The IPIN-302 can be configurated for different opto-coupler and data transfer options. The
next figure shows the jumper location of the IPIN-302.
Figure4: Jumper Location of IPIN-302 (Bottom View)
• Jumpers J301 and J302: Opto-Coupler Configuration
These jumpers are used to connect pin8 of the opto-coupler to Vcc or GND (Vaa or AGND).
They have to be configurated as shipped. Do not change these jumpers!

4 Configuration IPIN-300
12 Hardware Manual
• Jumper J401 to J406: TD/RD - Selection
For differential data transfer (RS422) the pins3 and 4 of the 6-pin modular jacks of the
IPIN-303 are used for the inverted receive and transmit signals. For asymmetric data
transfer (RS232) these pins must be connected to signal ground.
4.3 The Configuration Array of IPIN-303
The IPIN-303 can be used as I/O connector board for up to two IPIN-302 modules.
Each modular jack has a jumper to connect pin1 and pin6 (RDYin - RDYout) and a resistor
to terminate the receive data lines (RD+ and RD-) for RS422 applications. As shipped, the
jumpers are open and the resistors are not inserted.
Table2: Jumpers J401 to J406: TD/RD - Selection
Channel Jumper Mode
RS422 RS232
1J 401 open 1-2, 3-4
2J 402 open 1-2, 3-4
3J 403 open 1-2, 3-4
4J 404 open 1-2, 3-4
5J 405 open 1-2, 3-4
6J 406 open 1-2, 3-4
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents
Other ELTEC Control Unit manuals