EPE Conseil ESI 23 User manual

Contact: E.P.E. Conseil, Vincent Joly, Le Vieux Serrant, 49170 Savennières, France.
[email protected], N° SIRET : 53093796000017
Electro-Smog (EMF) Detector ―Radio Frequencies detection
with enhanced sensitivity ―50 MHz to 6 GHz frequency range ― excellent
Wi-Fi detection
What is Electro-Smog?
We refer to Electro-Smog as Electro-Magnetic Fields (EMF) produced by technology. EMF are
“generated in the radiofrequency bands (RF/EMF) by popular wireless devices like cell phones,
cordless phones, baby monitors, tablets, Wi-Fi enabled computer equipment, cell phone towers/antenna arrays,
radio/television broadcast facilities, and wireless smart meters, among others. EMFs are also emitted in the
extremely low frequency band (ELF/EMF) by electrical appliances, electrical wiring, and power lines”. (source:
https://emfscientist.org)
Operate your detector: the battery
Insert / changing: when putting the battery in place, please make sure that the battery cable is not sited
underneath the battery, but is placed instead at the side of the battery, between the battery and the
compartment wall. Failure to comply with instructions can cause damage to cable and / or cause battery
compartment lid to not close properly.
Battery check: upon start up, one of the two upper LEDs will light up briefly, either the green one (battery power
between 25% and 100%) or the red one (battery power below 25%). If the red LED is steadily flashing, power is too
low and the battery needs to be replaced.
Battery saving: the device will switch off automatically after 10 minutes in order to save battery.
Detect ambient electro-smog (i.e. electric fields from electric cables and appliances (such as computers, fuse boards,
lamps and power supplies), magnetic fields from high voltage lines, transformers and inverters, or Hyper Frequencies resulting from cell
towers, WiFi/WiMax networks or cordless landline phones, etc.)
1. Press once the “on-off” button to switch on the device in standard mode.
2. Hold the device at arm length away from your body.
3. Move slowly around to detect ambient electro-smog (the device performs a new detection every two
seconds).
NB: to switch the sound on or off, press and hold the “on-off” button.
Detect ambient Radio Frequencies (RF) smog with enhanced sensitivity (detecting peak
values) (i.e. Radio Frequencies resulting from cell towers, WiFi/WiMax networks or cordless landline phones, radio and TV
broadcasting, etc.)
1. Press once the “on-off” button to switch on the device in standard mode.
2. Press the “select” button once to enter high-resolution RF mode. LED 1 and 2 will stay lit.
3. Hold the device at arm length away from your body.
4. Move slowly around to detect ambient radiation (the device performs a new detection every two seconds).
NB: In this mode, all 15 LEDs show RF radiation. LED 1 and 2 (bottom left) show the lowest radiation level while LED
18 (top right) shows the highest radiation level.
To switch the sound on or off, press and hold the “on-off” button.
Check electrical appliances for avoidable electric fields (originating from appliances such as lamps)
A switched off electrical appliance lacking a grounding cable will often generate an electric field, if the socket is
plugged the wrong way around. Your device allows to check for plug direction.
1. Press the “on-off” button to switch on the device in standard mode.
2. Press the “select” button twice to enter plug checking mode. The upper green LED (next to the plug
symbol) will light up.
3. Hold the device at arm length away from your body, and near the switched off appliance you want to test
(e.g. lamp). The upper red LED (next to the plug symbol) will light up if an electric field is present.
ESI 23 –QUICK START GUIDE

Baubiologie MAES-SBM. (2015). Valeurs indicatives en Baubiologie pour les zones de repos. In Complément au standard de la technique de mesure en baubiologie SBM-2015. Retrieved December
2, 2015, from http://baubiologie.fr/IMG/pdf/valeurs_sbm-2015_fr.pdf. (recommendation)
BioInitiative. (2012). BioInitiative Report 2012. In A Rationale for Biologically-based Exposure Standards for Low-Intensity Electromagnetic Radiation. Retrieved November 16, 2015, from
http://www.bioinitiative.org/table-of-contents/. (recommendation)
Council of Europe. (2011). Resolution 1815 (2011) Final version. In The potential dangers of electromagnetic fields and their effect on the environment. Retrieved November 16, 2015, from
http://assembly.coe.int/nw/xml/XRef/Xref-XML2HTML-en.asp?fileid=17994&. (recommendation)
NCRP, (1995) “Biological Effects and Exposure Criteria for Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields”, NCRP Report No.86, Bethesda, Maryland, USA. (norm)
TCO Development. (2012). TCO-Certified-Displays-6.0. In TCO Development. Retrieved November 16, 2015, from http://tcodevelopment.com/files/2013/04/TCO-Certified-Displays-6.0.pdf#page=28.
(norm)
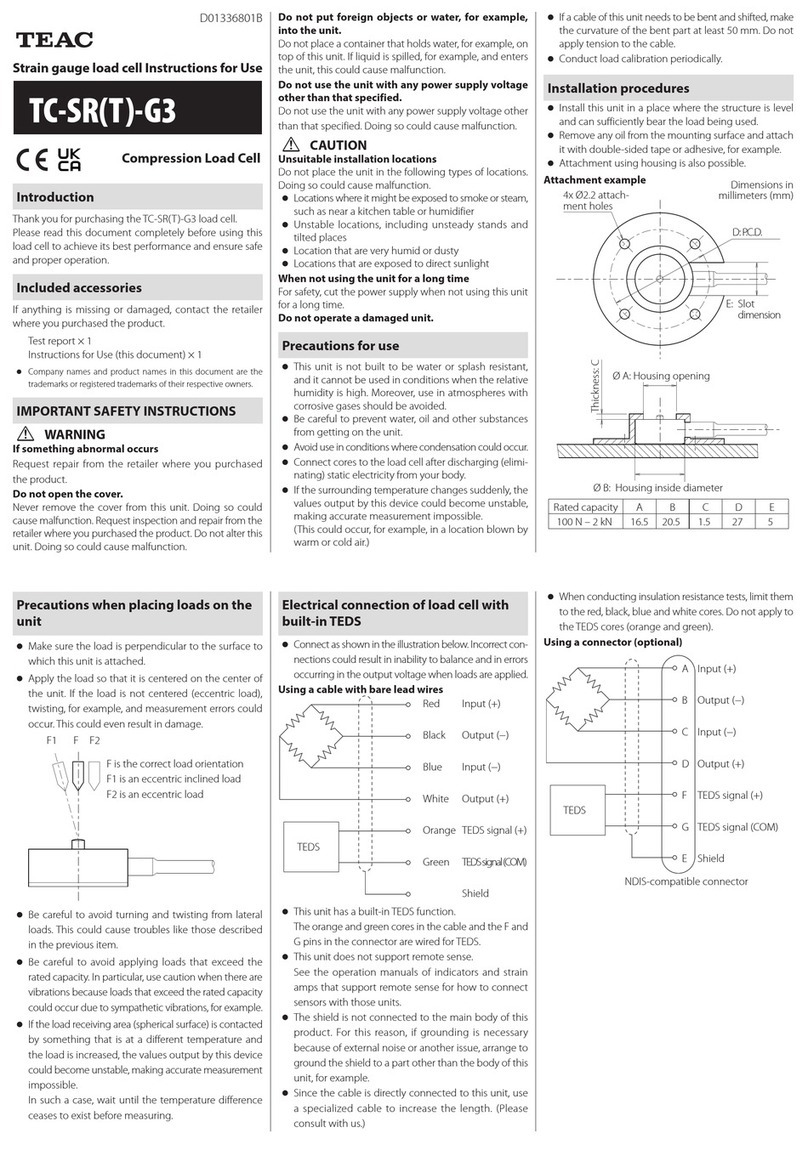
Standard mode table (indicative field strength is shown by means of each row of 5 LEDs)
Low-frequency magnetic and electric field (detection range: 16 Hz - 3 kHz; detection on all three dimensions (3D)) and
RF field (radio waves) (detection range: 50 MHz - 6 GHz)
Values*for
the ESI 23 Detector
Green
Green
/
Amber 1
Amber 1
Amber 1
/
Amber 2
Amber 2
Amber 2
/
Red 1
Red 1
Red 1
/
Red 2
Red 2
Alternating magnetic
field* in nT (Nanotesla)
< 20
20 to
80
80 to
120
120 to
160
160 to
200
200 to
300
300 to
400
400 to
1000
> 1000
Alternating electric
field* in V/m (Volt per
meter)
< 6
6 to 15
15 to
20
20 to
25
25 to
30
30 to
35
35 to
40
40 to
50
> 50
Radio Frequency field*
around 2,5 GHz
in V/m (Volt per meter)
< 0,08
0,08 to
0,12
0,12 to
0,19
0,19 to
0,27
0,27 to
0,34
0,34 to
0,43
0,43 to
0,53
0,53
to
0,61
> 0,61
Radio Frequency field*
around 2,5 GHz
in µW/m² (Microwatt per
square meter)
< 15
15 to
40
40 to
100
100 to
200
200 to
300
300 to
500
500 to
750
750
to
1000
> 1000
*All values are peak values. Actual values can slightly vary from the values specified in this table as a result of differences in individual
electronic components. Exposure limits depend on individual sensitivities. The measured values are purely indicative and do not create
liability of EPE Conseil.
High-resolution RF mode table (enhanced sensitivity) (indicative field strength is shown
by means of all 15 LEDs) Detection range: 50 MHz - 6 GHz, values in V/m (Volt per meter) and µW/m² (Microwatt per
square meter), values for frequencies around 2.5 GHz
LED
1+2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
V/m*
0,02
0,03
0,05
0,06
0,08
0,14
0,17
0,19
0,31
0,43
0,61
0,69
0,75
0,81
0,87
µW/m²*
1
2,5
5
10
20
50
75
100
250
500
1000
1250
1500
1750
2000
*All values are peak values. Actual values can slightly vary from the values specified in this table as a result of differences in individual electronic components.
Exposure limits depend on individual sensitivities. The measured values are purely indicative and do not create liability of EPE Conseil.
Standard mode graph with thresholds (indicative field strength is shown by means of each row of 5 LEDs)
RF:0V/m
0,08 V/m
0,12 V/m
0,19 V/m
0,27 V/m
0,34 V/m
0,43 V/m
0,53 V/m
0,61 V/m
∞
RF:0µW/m²
15 µW/m²
40 µW/m²
100 µW/m²
200 µW/m²
300 µW/m²
500 µW/m²
750 µW/m²
1000 µW/m²
EF:0V/m
6 V/m
15 V/m
20 V/m
25 V/m
30 V/m
35 V/m
40 V/m
50 V/m
MF:0nT
20 nT
80 nT
120 nT
160 nT
200 nT
300 nT
400 nT
1000 nT
Indicative field strengths for Radio Frequencies (RF) in Volt per meter (V/m) and Microwatt per square meter (µW/m²), Electric Fields (EF) in Volt per meter (V/m) and Magnetic Fields
(MF) in Nanotesla (nT), depending on the colour of the LEDs that light up. The thresholds mentioned above are recommendations and norms from the corresponding sources (see
hereunder).
MF: Baubiologie, SBM (2015)
RF: Bio-Initiative (2012) and Council of Europe (Resolution 1815, short term (2011))
MF: TCO 99 norm (1999) and NCRP (USA-1995)
EF: TCO 99 norm (1999) and NCRP (USA-1995)
RF: Council of Europe (Resolution 1815, medium term (2011))
EF: Baubiologie, SBM (2015)
RF: Baubiologie, SBM (2015)
Very strong
Very weak
Table of contents
Other EPE Conseil Measuring Instrument manuals