EverMore GM-X205 User manual

EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
1
GM-X205
GPS Receiver Module
User’s Guide
EverMore Technology Inc.

EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
2
MANUAL REVISION HISTORY
Revision Date Update Summary
Issue A April 2000 Initial release
Issue B Dec 2001 Updated NMEA output message format
© EverMore Technology Inc. All rights reserved.
Not to be reproduced in whole or part for any purpose without written permission of EverMore Technology
Inc. Information provided by EverMore Technology Inc. is believed to be accurate and reliable. However,
no responsibility is assumed by EverMore Technology Inc. for its use. EverMore Technology Inc. reserves
the right to change specification at any time without notice.

EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
3
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION
Table of Contents ---------------------------------------------------------3
1 Introduction -------------------------------------------------------5
1.1 Overview ---------------------------------------------------------5
1.2 Features ---------------------------------------------------------5
2 Receiver Operation -------------------------------------------------6
2.1 Receiver Specification -------------------------------------------7
3Hardware Interface -------------------------------------------------8
3.1 Mechanical Dimensions -------------------------------------------8
3.2 RF Module Hardware Interface ------------------------------------9
3.3 Baseband Hardware Interface -------------------------------------10
3.4 One-Pulse-Per-Second Output --------------------------------------11
4Software Interface -------------------------------------------------12
4.1 NMEA Output Message Specification -------------------------------12
4.1.1 NMEA Checksum Calculation -------------------------------------12
4.1.2 GGA - Global Positioning System Fix Data ----------------------13
4.1.3 GLL - Geographic Position - Latitude / Longitude --------------14
4.1.4 GSA - GNSS DOP and Active Satellites --------------------------15
4.1.5 GSV - GNSS Satellites in View ---------------------------------16
4.1.6 RMC - Recommended Minimum Specific GNSS Data ------------------17
4.1.7 VTG - Course Over Ground and Ground Speed ---------------------18
4.2 EverMore Binary Message Specification ----------------------------19
4.2.1 EverMore Binary Message 0x80: Initialization ------------------20
4.2.2 EverMore Binary Message 0x81: Data Logging -------------------- 21
4.2.3 EverMore Binary Message 0x86: Elevation Mask Input ------------21
4.2.4 EverMore Binary Message 0x87: DOP Mask Input ------------------21
4.2.5 EverMore Binary Message 0x89: Set Operating Mode --------------22
4.2.6 EverMore Binary Message 0x02: Navigation Data Output ----------23
4.2.7 EverMore Binary Message 0x04: DOP Data Output -----------------24
4.2.8 EverMore Binary Message 0x06: Channel Status Output -----------25
4.2.9 EverMore Binary Message 0x08: Measurement Data Output ---------26
4.3 Data Logging -----------------------------------------------------27
4.3.1 Data Logging Input Messages -----------------------------------28
4.3.1.1 LogConfig Set -----------------------------------------------28

EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
4
4.3.1.2 LogData Dump ------------------------------------------------29
4.3.1.3 LogData Erase -----------------------------------------------29
4.3.1.4 LogConfig Read ----------------------------------------------29
4.3.2 Data Logging Output Messages ----------------------------------30
4.3.2.1 LogData -----------------------------------------------------30
4.3.2.2 LogConfig Info ----------------------------------------------30
4.3.3 Data Logging Programming Description --------------------------31
4.3.3.1 Configuring for Data Logging --------------------------------31
4.3.3.2 Retrieving Logged Data --------------------------------------31
Appendix A Supported Datum List -----------------------------------------32
Appendix B Default Values -----------------------------------------------39

EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
5
SECTION 1
INTRODUCTION
1.1 OVERVIEW
The GM-X205 GPS Receiver is intended for use in a wide range of applications. The receiver
simultaneously tracks up to twelve satellites, provides accurate satellite positioning data with
fast time-to-first-fix (TTFF) and low power consumption. It is designed for high performance
and maximum flexibility in a wide range of applications including mobile asset tracking,
in-vehicle automotive guidance, location sensing, telematics and so on. The highly integrated
receiver achieves high performance, minimizes board size and power consumption
requirements. The GM-X205 is designed to withstand harsh operating environments; however,
it should be used inside an enclosure as a part of the application product designed by the
system integrator.
1.2 FEATURES
The GM-X205 GPS receiver offers following features:
lTwelve parallel tracking channels
lFast TTFF and low power consumption
lCompact design suitable for applications requiring small space
lOn-board rechargeable battery sustained real-time clock and memory for fast satellite
acquisition during power-up
lHigh accuracy one-pulse-per-second output
lSupports NMEA-0183 protocol
lFull navigation accuracy achievable with Standard Positioning Service
lOptimized for navigation in urban-canyon environments
lAutomatic cold start with no user initialization required

EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
6
SECTION 2
RECEIVER OPERATION
Upon power up, after initial self-test has completed, the GM-X205 will begin satellite
acquisition and tracking process. Under normal open-sky condition, position-fix can be
achieved within approximately 45 seconds (within 15 seconds if valid ephemeris data is
already collected from recent use). After receiver position has been calculated, valid position,
velocity and time information are transmitted through the on board serial interface.
The receiver uses the latest stored position, satellite data, and current RTC time to achieve
rapid GPS signal acquisition and fast TTFF. If the receiver is transported over a large distance
across the globe, cold-start automatic-locate sequence is invoked. The first position fix may
take up to five minutes searching the sky for the GPS signal. The acquisition performance can
be improved significantly if the host initializes the receiver with a rough estimate of time and
user position.
As soon as GPS signal is acquired and tracked, the GM-X205 will transmit valid navigation
information through its serial interface. The navigation data contains following information:
lReceiver position in latitude, longitude, and altitude
lReceiver velocity
lTime
lDOP error-magnification factor
lGPS signal tracking status
The GM-X205 will perform 3D navigation when four or more satellites are tracked. When three
or fewer satellites are tracked, altitude-hold is enabled using the last computed altitude and 2D
navigation mode is entered.
With signal blockage or rising and setting of the satellites, where a change in satellite
constellation used for position fix occurred, large position error may result. The GM-X205
incorporates a proprietary algorithm to compensate the effect of satellite constellation change,
and maintains an accurate smooth estimate of the receiver’s position, velocity, and heading.

EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
7
2.1 RECEIVER SPECIFICATION
FEATURES DESCRIPTION
General L1 frequency, C/A code, 12-channel
Sensitivity -165 dBW minimum
Update Rate 1Hz
Accuracy Position: 25m CEP without S/A
Velocity : 0.1/sec without S/A
Acquisition Cold start: < 150sec (typical)
Warm start: < 45sec (typical)
Hot start: < 15sec
Reacquisition <100msec
Dynamics Altitude: -1000m to 18000m
Velocity: 500m/sec
Acceleration: ±4g
Operation Temperature -20oC to +75oC
Storage Temperature -55oC to +90oC
Operating Humidity 5% to 95%
Primary Power +3.8V ~ 8V DC
Current Consumption 125mA @ 3.3V
Serial Interface RS-232
Protocol EverMore Private @ 4800/9600 baud, 8-None-1
NMEA-0183 v2.20 @ 4800/9600 baud, 8-None-1
Datum 219 standard datum, default WGS-84
Antenna On-Board Patch Antenna
NMEA Message GGA, GLL, GSA, GSV, RMC, and VTG
Dimension 45.5mm x 31mm x 15mm
EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
8
SECTION 3
HARDWARE INTERFACE
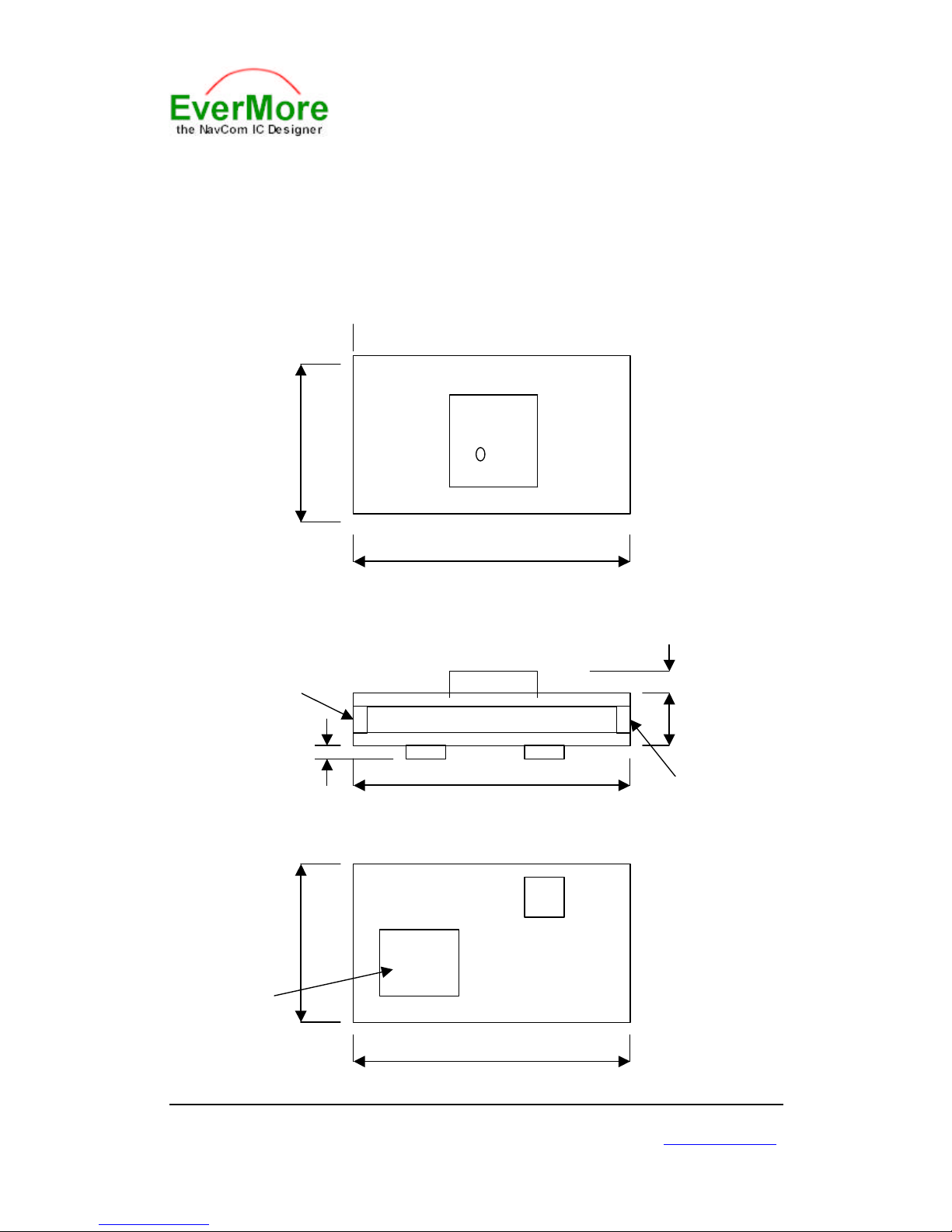
3.1 MECHANICAL DIMENSIONS
Unit:mm
Top View
Lateral View
Bottom View
45.5± 0.2
31.0± 0.2
45.5± 0.1
4.0 9.0± 0.1
2.0
I/O Pin
I/O Pin
45.5± 0.2
31.0
CPU

EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
9
3.2 RF MODULE HARDWARE INTERFACE
Pin Description
1NC
2NC
3Vcc Input : 3.3V
4CTRL : Input signal for RF module power-saving control
5GND : Power and signal ground
6REF Out : 16.367MHz reference output
7GND : Power and signal ground
8IF Out : 4.092MHz IF signal output
9NC
10 NC
RFIC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10

EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
10
3.3 BASEBAND HARDWARE INTERFACE
The 10 pin-connector is the same as the RF connector.
A1 : GND, Ground
A2 : 1PPS Valid Signal (1:Valid, 0:Invalid)
A3 : 1PPS
B1 : TX,Serial port output (GPS navigation output)
B2 : RX, Serial port input
B3 : Vcc, Power supply input, 3.8V ~ 8.0V DC unregulated
The following is a functional description of the pins on the 6-pin interface connector.
Pin 1. TX, Serial port output (GPS navigation output)
Pin 2. RX, Serial port input
Pin 3: Vcc, Power supply input, 3.8V ~ 8.0V DC unregulated
Pin 4: GND, Ground
Pin 5: 1PPS Valid Signal (1:Valid, 0:Invalid)
Pin 6: 1PPS
BBP1202
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
A3
A1
B3
B1
1
6

EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
11
3.4ONE-PULSE-PER-SECOND (1PPS) OUTPUT
The one-pulse-per-second output is provided for applications requiring precise timing
measurements. The output pulse is 1usec in duration.Rising edge of the output pulse is
accurate to +/-1usec with respect to the start of each GPS second. Accuracy of the
one-pulse-per-second output is maintained only when the GPS receiver hasvalid position fix.
The 1PPS output is always generated when the GPS receiver is powered-on. Proper
adjustment of the 1PPS output to align with the GPS second requires calculation of the
receiver clock offset and clock drift-rate as part of the position-velocity-time (PVT) solution.
When enough satellite signals are received to generate valid position fixes, the 1PPS output is
adjusted to align with the GPS second in several seconds. When the 1PPS output is brought in
sync with the GPS second, the 1PPS Valid Signal on the I/O pin becomes active (HIGH); when
the 1PPS output is not yet in sync with the GPS second, the 1PPS Valid Signal remains
inactive (LOW).
As long as enough satellite signals are received to generate valid position fixes, the 1PPS
output remains synchronized to the GPS second, and the 1PPS Valid Signal remains active. If
signal blockage prevents the receiver from generating valid position fix, the 1PPS output will
drift away from the GPS second and the 1PPS Valid Signal will become inactive. Upon
re-acquiring enough satellites to generate consecutive valid position fixes, the 1PPS Valid
Signal will become active again, signaling that the 1PPS output is again synchronized with the
GPS second.
For best stable operation of the 1PPS signal, it is to be operated in static environment having
clear view of the sky.

EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
12
SECTION 4
SOFTWARE INTERFACE
This section describes the details of the serial port commands through which the GM-X205 is
controlled and monitored. The serial port commands allow users to set the receiver
parameters, configure output message type, and retrieve status information. The baud rate
and protocol of the host COM port must match the baud rate and protocol of the GPS receiver
serial port for commands and data to be successfully transmitted and received. The default
receiver protocol is 4800baud, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, and none parity.
4.1 NMEA OUTPUT MESSAGE SPECIFICATION
The GM-X205 supports NMEA-0183 output format as defined by the National Marine
Electronics Association (http://www.nmea.org). The currently supported NMEA messages for
GPS applications are:
GGA Global Positioning System Fix Data
GLL Geographic Position –Latitude / Longitude
GSA GNSS DOP and Active Satellites
GSV GNSS Satellites in View
RMC Recommended Minimum Specific GNSS Data
VTG Course Over Ground and Ground Speed
4.1.1 NMEA Checksum Calculation
The optional NMEA checksum can be enabled or disabled when setting up the NMEA protocol.
The checksum consists of a “*” and two hexidecimal digits derived by exclusive-OR of all the
characters between, but not inlcuding, the “$” and “*” characters.

EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
13
4.1.2 GGA –Global Positioning System Fix Data
Purpose
Output time, position and position-fix related data.
Format
$GPGGA,hhmmss.sss,ddmm.mmmm,a,dddmm.mmmm,a,x,xx,xx.x,xxxxx.x,M,,M,xxx,xxxx*CS
Example
$GPGGA,153639.385,2446.5243,N,12100.1494,E,1,08,00.9,00163.8,M,,M,,*74
Field Name Example Unit Description
1Message ID $GPGGA GGA protocol header
2UTC Time 153639.385 hhmmss.sss
hour, minute, sec & decimal sec
000000.000 ~ 235959.999
Leading zeros transmitted
3Latitude 2446.5243 ddmm.mmmm
degree, minute & decimal minute
Leading zeros transmitted
4N/S Hemisphere Indicator Na, N=north or S=south
5Longitude 12100.1494 dddmm.mmmm
degree, minute & decimal minute
Leading zeros transmitted
6E/W Hemisphere Indicator Ea, E=east or W=west
7GPS Position Fix Indicator 1x
0 = no position fix or invalid
1 = valid fix, SPS mode
2 = valid fix, DGPS, SPS mode
8# of Satellites Used 08 xx, 00 ~ 12,
Leading zeros transmitted
9HDOP 00.9 xx.x, Leading zeros transmitted
10 MSL Altitude 00163.8 Meter xxxxx.x
MSL altitude = WGS-84 ellipsoid
height minus geoidal separation.
Currently this field is WGS-84
ellipsoid height
Leading zeros transmitted
11 Unit of Altitude MMeter
12 Geoid Separation Not supported
13 Unit of Geoid Separation MMeter
14 Age of Differential GPS Data
second
xxx
Time in seconds since last RTCM
SC-104 Type-1 or Type-9 update.
Null when DGPS is not used
15 Differential Reference
Station ID xxxx, 0000 ~ 1023
Leading zeros transmitted
Null when DGPS is not used
16 Checksum *74

EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
14
4.1.3 GLL –Geographic Position –Latitude / Longitude
Purpose
Output latitude and longitude of current position, time, and status.
Format
$GPGLL,ddmm.mmmm,a,dddmm.mmmm,a,hhmmss.sss,x*CS
Example
$GPGLL,2446.5311,N,12100.1377,E,110519.259,A*35
Field Name Example Unit Description
1Message ID $GPGLL GLL protocol header
2Latitude 2446.5311 ddmm.mmmm
degree, minute & decimal minute
Leading zeros transmitted
3N/S Hemisphere Indicator Na
N=north or S=south
4Longitude 12100.1377 dddmm.mmmm
degree, minute & decimal minute
Leading zeros transmitted
5E/W Hemisphere Indicator
Ea
E=east or W=west
6UTC Time 110519.259 hhmmss.sss
hour, minute, sec & decimal sec
000000.000 ~ 235959.999
Leading zeros transmitted
7Status AA=data valid
V=data invalid
8Checksum *35
EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
15
4.1.4 GSA –GNSS DOP and Active Satellites
Purpose
Output operating mode, satellites used for navigation, and DOP values.
Format
$GPGSA,x,x,xx,xx,xx,xx,xx,xx,xx,xx,xx,xx,xx,xx,xx.x,xx.x,xx.x*CS
Example
$GPGSA,A,3,27,31,08,20,13,28,03,01,02,11,22,,01.3,00.8,01.0*0C
Field Name Example Unit Description
1Message ID $GPGSA GSA protocol header
2
Manual or
Automatic Mode Ax
A=automatic, allowed to switch 2D/3D automatically
M=manual, forced to operate in 2D or 3D mode
3Navigation
Solution Mode 3x
1=fix unavailable
2=2D
3=3D
4
ID Numbers of the
Satellites Used In
Solution
27,31,08,20,
13,28,03,01,
02,11,22
xx
SV ID of the satellites used for navigation
Null for unused channels.
Leading zeros transmitted
5PDOP 01.3 xx.x
Leading zeros transmitted
6HDOP 00.8 xx.x
Leading zeros transmitted
7VDOP 01.0 xx.x
Leading zeros transmitted
8Checksum *0C

EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
16
4.1.5 GSV –GNSS Satellites in View
Purpose
Output number of SVs in view, PRN numbers, elevation, azimuth and SNR values. Four
satellites maximum per transmission, additional satellite data sent in the second or the third
sentence.
Format
$GPGSV,x,x,xx,xx,xx,xxx,xx … xx,xx,xxx,xx*CS
Example
$GPGSV,3,1,11,27,59,276,44,31,50,046,44,08,38,309,44,20,07,165,39*70
$GPGSV,3,2,11,13,10,223,41,28,13,304,38,03,14,054,41,01,13,186,40*73
$GPGSV,3,3,11,02,06,303,43,11,73,165,43,22,06,113,35,,,,*48
Field Name Example Unit Description
1Message ID $GPGSV GSV protocol header
2Total Messages 3x, 1 ~ 3
3Message Number 1x, 1 ~ 3
4Total Number of Satellites In View 11 xx, 0 ~ 12
Leading zeros transmitted
5Satellite Number #1 27 xx, SV1 ID number, 01 ~ 32
Leading zeros transmitted
6Elevation Angle #1 59 degree xx, 00 ~ 90
Leading zeros transmitted
7Azimuth Angle #1 276 degree xxx, 000 ~ 359
Leading zeros transmitted
8C/No #1 44 dB/Hz xx, C/No 00 ~ 99
Leading zeros transmitted
9Satellite Number #2 31 SV2 ID number, 01 ~ 32
10 Elevation Angle #2 50 degree 00 ~ 90
11 Azimuth Angle #2 046 degree 000 ~ 359
12 C/No #2 44 dB/Hz C/No 00 ~ 99
13 Satellite Number #3 08 SV3 ID number , 01 ~ 32
14 Elevation Angle #3 38 degree 00 ~ 90
15 Azimuth Angle #3 309 degree 000 ~ 359
16 C/No #3 44 dB/Hz C/No 00 ~ 99
17 Satellite Number #4 20 SV3 ID number, 01 ~ 32
18 Elevation Angle #4 07 degree 00 ~ 90
19 Azimuth Angle #4 165 degree 000 ~ 359
20 C/No #4 39 dB/Hz C/No 00 ~ 99
21 Checksum *70

EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
17
4.1.6 RMC –Recommended Minimum Specific GNSS Data
Purpose
Output time, date, position, course and speed data.
Format
$GPRMC,hhmmss.sss,x,ddmm.mmmm,a,dddmm.mmmm,a,xxx.x,xxx.x,ddmmyy,,*CS
Example
$GPRMC,153638.741,A,2446.5243,N,12100.1494,E,000.0,000.0,061101,,*02
Field Name Example Unit Description
1Message ID $GPRMC RMC protocol header
2UTC time 153638.741 hhmmss.sss
hour, minute, sec & decimal sec
000000.000 ~ 235959.999
Leading zeros transmitted
3Status Ax
A=Data valid
V=Navigation receiver warning
4Latitude 2446.5243 ddmm.mmmm
degree, minute & decimal minute
Leading zeros transmitted
5N/S hemisphere indicator Na
N=north or S=south
6Longitude 12100.1494 dddmm.mmmm
degree, minute & decimal minute
Leading zeros transmitted
7E/W hemisphere indicator
Ea
E=east or W=west
8Speed Over Ground 000.0 knot xxx.x
Leading zeros transmitted
9Course Over Ground 000.0 degree xxx.x
Leading zeros transmitted
10 Date 061101 ddmmyy
day, month, year (2 digit)
Leading zeros transmitted
11 Magnetic variation Not implemented
12 Magnetic variation
reference Not implemented
13 Checksum *02

EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
18
4.1.7 VTG –Course Over Ground and Ground Speed
Purpose
Outputs actual track made good and speed relative to the ground.
Format
$GPVTG,xxx.x,T,,M,xxx.x,N,xxxx.x,K*CS
Example
$GPVTG,051.6,T,,M,056.5,N,0104.7,K*56
Field Name Example Unit Description
1Message ID $GPVTG VTG protocol header
2Heading 051.6degree xxx.x
Heading of the receiver when moving
Leading zeros transmitted
3True TIndicates true heading
4Heading degree Degrees magnetic
Not supported
5MMIndicates magnetic heading
6Speed 056.5knots xxx.x
Speed in knots
Leading zeros transmitted
7NNIndicates speed in knots
8Speed 0104.7Km/hr xxxx.x
Speed in km/hr
Leading zeros transmitted
9KKIndicates speed in km/hr
10 Checksum *56

EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
19
4.2 EVERMORE BINARY MESSAGE SPECIFICATION
The EverMore binary message protocol consists of 3 parts:message header, message body,
and message footer.
Message Header Message Body Message Footer
Start Sequence
Length of Message Body Message Checksum End Sequence
0x10 0x02 1 or 2 bytes Up to 253 bytes 1 or 2 bytes 0x10 0x03
Message Header
The Message Header consists of 3 or 4 bytes:
Byte #1 -DLE = 0x10
Byte #2 -STX = 0x02
Byte #3 -Length of Message Body + 2
Byte #4 -when Byte #3 equals DLE (0x10), DLE (0x10) is sent out as the 4th byte of the
message header; otherwise it is not sent.
Message Body
When DLE (0x10) is encountered in the message body, it is repeated. The EverMore Binary
Message supports following message types for receiver configuration and status monitoring:
Message Type 0x80: Initialization Command Input
Message Type 0x02: Navigation Data Output
Message Type 0x04: DOP Data Output
Message Type 0x06: Channel Status Output
Message Type 0x08: Measurement Data Output
Message Footer:
The Message Footer consists of 3 or 4 bytes:
Byte #1 -checksum of the Message Body (it is calculated by summing all bytes in the
Message Body and taking the sum modulo 256)
Byte #2 -when Byte #1 equals DLE (0x10), DLE (0x10) is sent out as the 2nd byte of the
message footer; otherwise it is not sent.
Byte #3 -DLE (0x10). If checksum is not 0x10, this DLE character becomes Byte #2
Byte #4 -ETX (0x03). If checksum is not 0x10, this ETX character becomes Byte #3

EverMore Technology Inc.
2F, No.7, R&D Road 1, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 310, R.O.C. http://www.emt.com.tw
20
4.2.1 EverMore Binary Input Message 0x80: Initialization
Purpose
Used to :
1. Set the initial time and position of the GPS receiver.
2. Select datumn other than the default WGS-84.
3. Select the type of NMEA messages to output.
4. Enable or disable EverMore binary message output.
5. Change the baud rate configuration.
Format
Byte # Contents Range Size Scale Unit
1Message ID = 0x80 Unsigned byte
2 ~ 3 GPS week 0 ~ 65535 Unsigned 16bit integer week
4 ~ 7 GPS tow 0 ~ 60479900 Unsigned 32bit integer 1/100 sec
8 ~ 9 Latitude +/-900 Signed 16bit integer 1/10 degree
10 ~ 11
Longitude +/-1800 Signed 16bit integer 1/10 degree
12 ~ 13
Altitude -1000 ~ 18000 Signed 16bit integer meter
14 ~ 15
Datumn ID 0 ~ 65535 Unsigned 16bit integer
16 Restart Mode (decimal)
1 = hot start
2 = warm start
3 = cold start
4 = test start
10 = datumn input
Unsigned byte
17 NMEA Message Control Switch (1:ON, 0:OFF)
bit0 : GGA message on/off
bit1 : GLL message on/off
bit2 : GSA message on/off
bit3 : GSV message on/off
bit4 : RMC message on/off
bit5 : VTG message on/off
bit6 : Checksum on/off
EverMore Message Control Switch
bit7 : EverMore binary message on/off
18 Baud Rate Control
0 = 4800bps
1 = 9600bps
2 = 19200bps
3 = 38400bps
See Appendix-A for Datum ID to use.
When changing the Datum ID, Reset Mode field has to be set to 0x0A.
Table of contents
Other EverMore GPS manuals

EverMore
EverMore SA-320 User manual

EverMore
EverMore SA-320 User manual

EverMore
EverMore GeoTagger GT-800 User manual

EverMore
EverMore GM-R900 User manual

EverMore
EverMore Switch & PoE Splitter User manual

EverMore
EverMore ST-K700 User manual

EverMore
EverMore GM-307 User manual

EverMore
EverMore BT-R900 User manual

EverMore
EverMore SA-320 User manual

EverMore
EverMore GeoTagger GT-800 User manual