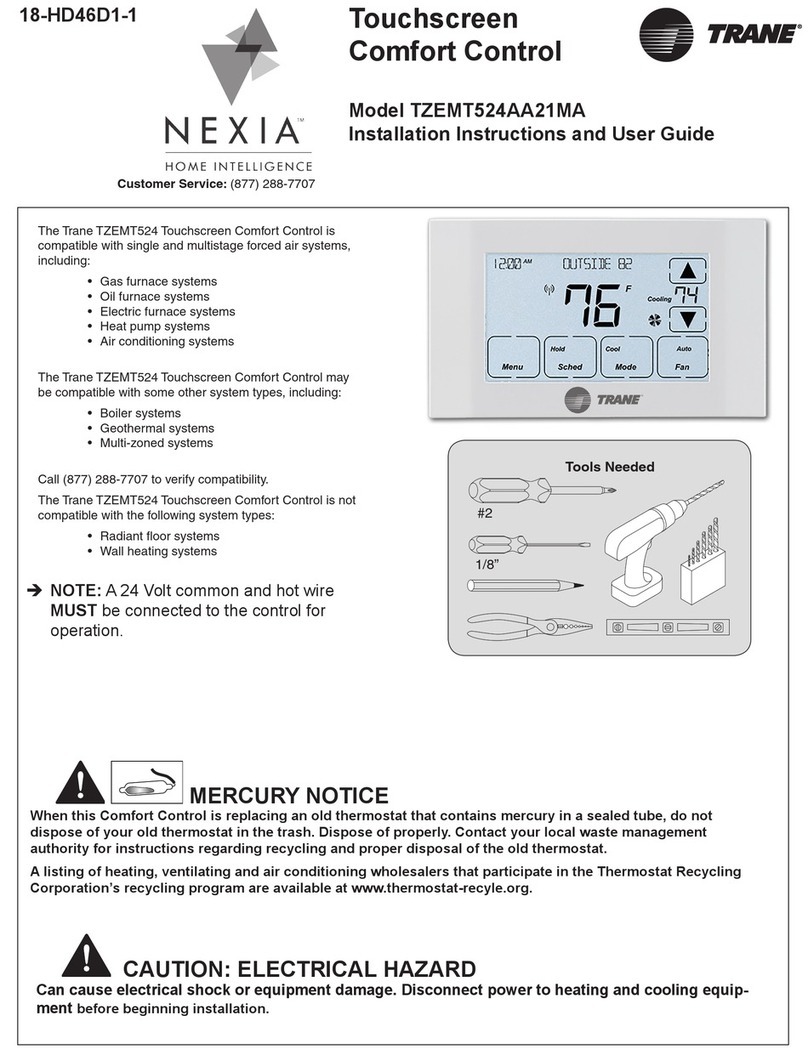
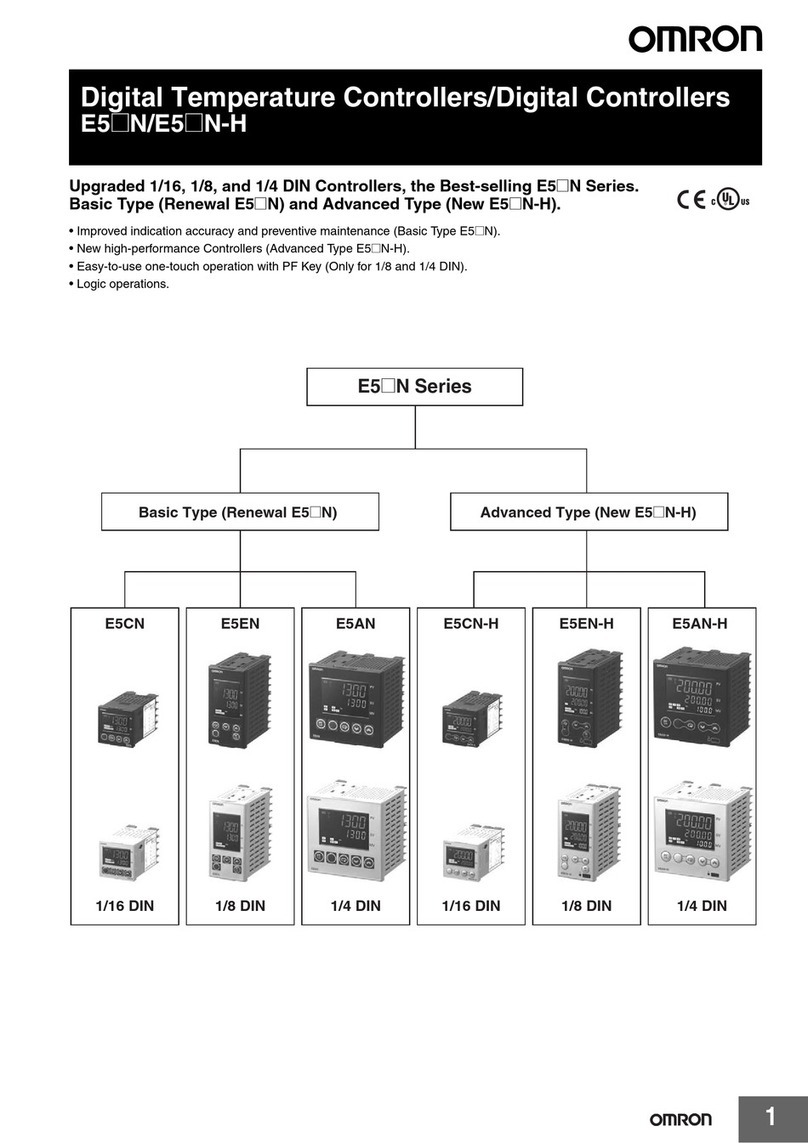
FineTek PT-8320 Series User manual

PT-8320
User Manual
1

DIMENSION / PANEL CUTOUT
2

PANEL DESCRIPTION:
EXPLANATION FOR TERMINAL WIRING:
3

STANDARD SPECIFICATIONS
Power Supply 85~265V AC 50/60 Hz
Power Consumption 7VA Maximum
Display
Upper:Red 4 digit of 7 segment display
Bottom:Green 4 digit of 7 segment display
10 segment bar-graph display
Input Signal
Thermocouple:J, K, B, N, R, S, T, E
RTD:PT100, JPT100
Direct Voltage:0~230mV
Relay Output SPST-NO,5A/250V AC
Pulse Output(Drive SSR) 12VDC(NPN),20mA (MAX.)
Control
Output Analog 4~20mA ,0~10V DC (MAX.600Ω)
Alarm Output SPST-NO,5A/250VAC
Alarm Delay Time 0 ~ 99 second
Alarm Output HysteresisAdjustment 0 ~ 9999 degree C
Communication Interface RS485(MODBUS)
Working Temperature 0 ~ 50℃(20~85% RH)
Cycle Time of Output Control 0 ~ 50.0 seconds
Digital 0 ~ 3 digital
Digital Filter 1 ~ 100 times
Control Method ON/OFF or PID+Fuzzy(Auto Tuning)
Input Compensation -1999 ~ 9999
Fraction Value 0.0 ~ 999.9
Setting Range -1999 ~ 9999
Accuracy 0.3%FS ± 1digit
Sampling Interval 400ms
Memory Retention EEPROM
OTHER FUNCTIONS
Sensor Error Detection Error code displayed on PV, with sensor error alarm
output ability.
Detect the loop break and Heater Break Alarm
HBA(Heater Break Alarm), Current error of heater can
be detected via CT transformer.
Or using LBA(Loop BreakAlarm) to detect system failure
via software.
Remote Set Point (RSP) Remote Setting Voltage、Current signal in order to
change SV value
EVENT function Remote control for executing specific command
Re-transmission Re-transmit the voltage、current after the exchange of
PV、SV
4

A. ANUE DESCRIPTION
Main parameters selection
Main Parameters Name of Parameter Description of Parameter
PV value
SV value
Present value
Setting value
LV-0 Status information
LV-1 PID setting
LV-2 Advance setting for control
Prog Ramp & Soak setting
ALM Alarm setting
StUP Hardware construction setting
EXPA Expansion function setting
CoMM Communication setting
LoCK Lock function
SCAL Analog auxiliary input setting
rSP Remote Set Point auxiliary input setting
Ct Current transformer input setting
Under operating mode, please press MOD button in order to exchange above
Main menu selection
5

B. Parameters block description
Parameters Display Name of Parameters Description of Parameters Display Range Default
Pattern Display the present executing
pattern
~
0
Step Display the present executing
step
~
/
0
Link Display the present link
setting
~
0
Program Ramp & Soak control On/Off
/
/
rSt
Advance Skip to next step
/
OFF
Standby time Display waiting time for start
(minute)
~
0
Elapse time Display schedule of executing
time (minute)
~
0
Repeat time Display style executed time
~
0
Heater MV Display heater output
.
~
.
0
Cooler MV Display cooler output
.
~
.
0
section shows controller status, mainly for Ramp/Soak information.
To go to LV-0, please press MOD once under SV/PV, the details are listed as below:
¾
: Indication of the on-going pattern
0:Not in the Ramp/Soak control mode, which means oPEr = onoF or Pid
¾
:Indication of the on-going step
0:Ramp/Soak control not starts yet.
SV:Maintain the last SV (EXPA->Pend=SV) after patterns are completed.
1、3、5、7、9、11、13、15:Ramp step
2、4、6、8、10、12、14、16:Soak step
¾
:Next pattern。(0: there is no next pattern)
¾
:Program control:Change is effective while LV2->oPEr not be onoF or Pid.
rSt:Reset ramp/soak status, and control/alarm output stop action.
rUn:Ramp/soak control begins or continues.
Hold:Hold ramp/soak timing
¾
:Skip to next step.
Ramp=>Soak:SV becomes the setting of the next soak step.
Soak=>Ramp:
EXPA=>PVSt=PV, PV reaches soak value after ramp time from the current PV.
EXPA=>PVSt=SV, PV reaches soak value after ramp time from the current SV setting.
¾
:Remaining time before controller actuates (min).
¾
:Time performed of the on-going step (min)
¾
:Remaining repeat times.
¾
:Percentage of manipulate value for the heater.
¾
:Percentage of manipulate value for the cooler.
6

C. Parameters block description
Parameters display Name of Parameters Description of Parameters Display range Default
Tun Auto Tuning
/
OFF
Proportional Proportional parameter
~
.
2.0
Integral Time Integral parameter (second)
~
100
Derivative Derivative parameter
~
10
Tau Fuzzy parameter
.
~
.
0.060
Cooling Coefficient Cooling parameter
.
~
.
1.00
MARE Manual reset
.
~
.
0
Auto Tune Offset SV Offset duringAuto-tuning
~
0
Heater Hysteresis Control output hysteresis for
heater
~
0
Cooler Hysteresis Control output hysteresis for
cooler
~
0
Heater period Cycle time of control heater
output (second)
.
~
.
5.0
Cooler period Cycle time of control cooler
output (second)
.
~
.
5.0
Dead band Dead band control
/
OFF
Heater dead band Dead band of heater
~
0
Cooler dead band Dead band of cooler
~
0
CT current monitor Display CT -1.
Heater burnout Heater break setting
~
.
0
section of parameters are used for basic control,P、I、D、tAU、CoEF parameters affect PID+Fuzzy control
algorithm performance,theses parameter can be auto calculated by auto-tune function, without the need of complex
PID tuning. Fuzzy compensation control makes system response faster and more reliable.
To go to LV-1, press MOD twice under SV/PV, and its sub options are listed below:
¾:Auto tuning
on:Auto tuning on oFF:Auto tuning off.
When auto tuning is on, controller will start heating and cooling around the setting SV. After two cycles, PID
parameters can be calculated. With these PID parameters, the controller can stabilize the system to a desire
process value. You can also adopt the oFSt function (especially used during the auto tuning process), to prevent
system over-heat during the auto tuning process.
7

¾
:Proportional Gain parameter。Can be calculated by auto tuning or adjusted manually. This
parameter is responsible to the system deviation. When offset occurs, proportional regulator
responds to reduce the offset.
¾
:Integral parameter。Can be calculated by auto tuning or adjusted manually. When steady offset
exist in a consistent temperature, Integral regulator will start compensating until offset is fixed.
¾
:Derivative parameter。Can be calculated by auto tuning or adjusted manually. Derivative regulator
can predict the system trend by rate of change; derivative regulator will fix the offset in advance,
before offset happens.
¾
:Fuzzy factor parameter. Can be calculated by auto tuning or adjusted manually.
Fuzzy control compensates the insufficiency of PID controller and helps to reach the target based
on the deviation and rate of change.
Bigger Tau, more Fuzzy compensation!
¾
:Cooling coefficient. Can be calculated by auto tuning or adjusted manually.
Cooler proportional gain = P / Coef
This function is used in cooling control, to tell the performance of cooler.
¾
:Manual reset.
When Integral i=0, and PV>SV, then MV=MArE.
¾
:SV offset setting during Auto tuning
When this function is set up, auto tuning will make the system to oscillate around SV + oFSt . For
example, SV=200°C;OFST= -10°C. Auto tuning will calculate as SV+OFST=200+(-10)=190°C,
to avoid over-heating.
¾
:Hysteresis for heater on/off control.
¾
:Hysteresis for cooler on/off control.
During ON/OFF control, control output should be turned off when PV>SV, and turned on when
PV<SV. To avoid frequent ON and OFF control, hysteresis can be set. When HYS is set,
PV>SV+HYS to turn off the control output, and turned on when PV<SV-HYS.
¾
:Heater control cycle time(sec)
¾
:Cooler control cycle time(sec)
For any control output that is not in linear analog signal such as relay and 12V pulse output, signal
output status will be ON/OFF only. For better PID result, Time Proportional is used. For example,
period is set to be 5 seconds and PID is 30%. (ON)= 30%. 5*0.3=1.5 sec. (OFF)= 70%
5*0.7=3.5 sec.
Control output reacts quicker as cycle time gets shorter. When mechanical contact output is used,
please consider issue of mechanical life.
8

¾
:Enable/disable dead band control.
¾
:Dead band for heater.
¾
:Dead band for cooler.
Heating and cooling range can be controlled via dead band setting
Heater dead band control:If PV>SV+DB-H, heater is not active.
Cooler dead band control:If PV<SV+DB-C, cooler is not active.
DB-H>0;DB-C>0 DB-H>0;DB-C<0
Over SV+DB-H deactivates heater Over SV+DB-H deactivates heater
Under SV+DB-C deactivates cooler Under SV+DB-C 以deactivates cooler
Deactivatesheater
Deactivates cooler Deactivates cooler Deactivates heater
SV SV+(DB-H)SV+(DB-C) SV+(DB-C) SV SV+(DB-H)
DB-H<0;DB-C<0 DB-H<0;DB-C>0
Over SV+DB-H deactivates heater Over SV+DB-H deactivates heater
Under SV+DB-C deactivates cooler Under SV+DB-C deactivates cooler
Deactivates heater
Deactivates cooler Deactivates heater Deactivates cooler
SV+(DB-C) SV+(DB-H) SV SV+(DB-H) SVSV+(DB-C)
¾
:Display CT (current transformer)input current
Install CT input expansion module, it will display relative current value
¾
:Heater break alarm setup: when CT transformer current is lower than SV during heating, it will be
considered heater break. Thus, alarm will send out.
9

D. Parameters block description
Parameter display Name of Parameters Description of Parameters Display Range Default
Input Input signal selection
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
/
K type
Operation Control mode selection //
/
OnoF
Remote/Local SV Remote/unit intput / off
Set Value Temperature setting
~
0.0
Dot Decimal point setting
~
dot1
Unit Temperature unit display
/
℃
Multiplier PV Multiplier
.
~
.
1.000
Bias PV compensation input
~
0.0
Mode Control mode setting
/
H-C
Filter Digital filter
~
5
Standby timer Waiting time for control
starting (second) ~
0
LbA detection Time Detection time of heater
break (second) ~
0
LbA detection Width Detection of temperature
differentiation of heater
break
~
1.0
LED Status Bar Bar-graph display HEAT/CooL/Prog HEAT
Transfer SV Hi Re-transmit SV high value
~
100.0
Transfer SV Lo Re-transmit SV low value
~
0
section is for advanced control parameters, ON/OFF or PID control mode can be configured to achieve the
requirement.
Under SV/PV mode press 3 times of MOD button, it is for main menu of LV-2, the sub-selection as following:
¾
:Input signal
:K Type thermocouple input
Input range:-200~1370°C 0.3%±1Digit。
:J Type thermocouple input
Input range:-210~1200°C 0.3%±1Digit。
:T Type thermocouple input
Input range:-200~400°C ±2°C±1Digit。
:E Type thermocouple input
Input range:-200~1000°C 0.3%±1Digit。
:R Type thermocouple input
Input range:-50~1760°C 0.3%±1Digit。
:S Type thermocouple input
Input range:-50~1760°C 0.3%±1Digit。
:B Type thermocouple input
Input range:250~1820°C ±8°C±1Digit。
:N Type thermocouple input
Input range:-200~1300°C 0.3%±1Digit。
:PT Type thermocouple input
Input range:-200~850°C 0.3%±1Digit。
:JPT Type thermocouple input
Input range:-200~850°C 0.3%±1Digit。
:DC Type voltage input
Input range:0~230mV 0.3%±1Digit。
¾
:
:ON-OFF;
:PID
:Program;
:Program-ONOFF
10

On/Off mode
On/Off mode control is a very common and simple control mode. When the control output is programmed as
the heating output and the temperature lower than setting value, control output start to activate; if the
temperature is higher than setting value, control output deactivate in order to control the temperature. It also
can adjust hysteresis band to reduce the overshooting on the system to achieve the best control and stability.
PID mode
MV
SV
PV
PID control is corresponding to three constants which are proportional, integral, derivative. P is to handle the
immediate error, I is to learn from the past and D is to handle the future. When control output is the heating
output, the PT-series will apply PID+ Fuzzy algorithm to calculate a MV value (manipulate value) to be used in
determining whether the control output should be strong or weak in order to constantly calculating the
deviation of stability and prediction. The built-in Fuzzy control is to enhance the system in stability for
achieving the best control and efficient.
Program /Program ONOFF Mode
Program mode offers 8 patterns temperature control. Every pattern includes temperature setup, time of ramp,
time of soak. Measurement unit is minute. The 8 patterns temperature control allows the system to reach the set
temperature within the set time of ramp(increase/decrease), and to maintain the set temperature within the set time
of soak. It can also utilize Wait Width(EXPA->WAit) to let the system stay close to the setup even if the system is
unable to follow the setup perfectly. There are 8 sub-patterns for set up in one pattern. Via Link function, 64
sub-patterns temperature control can be given with ON/OFF and PID control as optional.
11

¾
:Remote(RSP) or local SV
:Remote mode (RSP);
:Local mode。
¾
:Temperature set value;Set value between。
¾
:Decimal point set value。
:decimal point 0
:decimal point 1
:decimal point 2
:decimal point 3
¾
:Measurement Unit setup。/℃℉
¾
:PV magnification adjustment。
¾
:PV Offset input。When PV’s current value and expected value does not match, PV offset input
function can be utilized for adjustment.PV = PV*MUL + biAS
¾
:Control setup。
:for system heating and cooling。
:for system cooling。
¾
:Digital filter;Decrease static signal。1~100 filter time can be set。Digital filter can only affect PV
value time update, not speed update。
¾
:Wait Width:System can be set to control when the system can be actuated.When Wait Width is set
to be 0, there will be no Wait function.
¾
:LBA heater burnout time:Set LBA burnout cycle time(second)
,when LbAt is set to be 0,there is no LBA function。
¾
:LBA heater burnout temperature difference:Set LBAburnout temperature difference. When
system is being heated and temperature increase is less than the temperature difference within
LBA time, controller will assume heater is broken then LBA alarm signal will be sent out.
¾
:Bargraphic Indicator
:Heating control value,one light represents 10% value.
:Cooling control value,one light represents 10% value.
:8 modes are active.
First light blinks:First mode of temperature increasing/decreasing is active.
First light on constantly:First mode of temperature holding is active.
Second light blinks:Second mode of temperature increasing/decreasing is active.
Second light on constantly:Second mode of temperature holding is active.
¾
:Set to re-transfer greatest SV value:
¾
:Set to re-transfer smallest SV value:
When output is the SV re-transfer analog output, SV can be transferred into the corresponding
voltage and current output.
Example:TR-H =100.0 TR-L=0.0 Liner output 0~10VDC
SV 0.0 ~ 100.0 corresponds to 0~10V analog output
12

E. Parameter Table
Parameters display Name of Parameters Description of Parameters Display range Value
Pattern NO. Pattern selection
~
1
Number of steps Steps needed to be performed
~
8
~
Set Value Temperature setup
~
0
~
Ramp time Time increase/decrease(min) ~
0
~
Soak time Time of temperature holding(min) ~
0
Repeat time Repeat time ~
0
Link pattern Link pattern ~8 0
Time signal step Output signal step 1
~
r1
Signal 1 ON time Signal 1 ON time (min) ~
0
Signal 1 OFF time Signal 1 OFF time (min) ~
0
Time signal2 step Output signal step 2
~
r1
Signal2 ON time Signal 2 ON time (min) ~
0
Signal2 OFF time Signal 2 OFF time (min) ~
0
Parameter is a multi-pattern control function. Every pattern can perform 8 steps of temperature control.
Via link pattern, 64 steps of temperature control can be performed.
Press MOD 4 times under SV/PV mode,sub-menu can be selected under the main menu as below:
¾
:8 pattern selection:Total of 8 patterns for selection. It is also the first action pattern among
the 8 patterns.
¾
:Step selection:Step 1~8. Temperature increase/decrease, temperature hold can be set in each
step.
¾
~
:Temperature setup:Set target temperature in each step.
Ex.:SV=50 PV=30 SV1=50 tr1=1 ts1=2
PV starts to increase to reach SV(increase speed is in inverse ratio to ramp time). After 1
minute, SV reaches 50 and temperature begins holding for 2 minutes.
¾
~
:Time of increase/decrease(Ramp):Set time needed(minute) in order to reach the set
temperature.
¾
~
:Time of holding(Soak):Time of hold(minute) after ramp time.
13

¾
:Repeat time:Repeat time for each step
Default setting=0,Repeat time= 0,Total action= 1
Default setting=1,Repeat time= 1,Total action= 2, and so on.
¾
:Pattern Link:Pattern selection followed by completion of each pattern.
Ex.:Set Link=2 followed by Pattern 1.
Link=1 followed by Pattern 2.
¾
/
:Signal output procedure:signal output setup
r1:Temperature increase 1
s1:Temperature holding 1
r2:Temperature increase 2
s2:Temperature holding 2
¾
/
:Signal on wait time:Signal output turns on at set wait time
¾
/
:Signal off wait time: Signal output turns off at set wait time.
Signal will be turned off followed by time signal 1~2. Signal will be turned on in specified step.
14

F. Parameter Table
Parameters display Name of Parameters Description of Parameters Display range Reset Value
Soft Start Alarm soft start
/
OFF
Position 1 Alarm position 1
~
0.0
Hysteresis 1 Hysteresis 1
~
0.0
Delay Time 1 Delay time 1(sec)
~
0
Style 1 Style 1
~
,
Sty1
Position 2 Alarm position 2
~
0.0
Hysteresis 2 Hysteresis 2(sec)
~
0.0
Delay Time 2 Delay Time 2
~
0
Style 2 Style 2
~
,
Sty1
Position 3 Alarm position 3
~
0.0
Hysteresis 3 Hysteresis 3(sec)
~
0.0
Delay Time 3 Delay Time 3
~
0
Style 3 Style 3
~
,
Sty1
Position 4 Alarm position 4
~
0.0
Hysteresis 4 Hysteresis 4(sec)
~
0.0
Delay Time 4 Delay Time 4
~
0
Style 4 Style 4
~
,
Sty1
There are 4 sets of alarm parameter setting designed to fit different application condition. In addition, there is
Error Alarm function(ALM->StyLE->SErr) for additional protection for your system. Press MOD 5 times under SV/PV
mode to go to ALM main menu. Sub-menu:
¾
:Alarm soft start on/off
Alarm will go off when system is within the alarm range twice.
¾
:Position 1 setup.
¾
:Hysteresis 1 setup.
¾
:Delay time 1 setup(sec).
¾
:Style 1 selection(Please refer to StyL alarm style description).
¾
:Position 2 setup.
¾
:Hysteresis 2 setup.
¾
:Delay time 2 setup(sec).
¾
:Style 2 selection(Please refer to StyL alarm style description).
15

¾
:Position 3 setup.
¾
:Hysteresis 3 setup.
¾
:Delay time 3 setup(sec).
¾
:Style 3 selection(Please refer to StyL alarm style description).
¾
:Position 4 setup.
¾
:Hysteresis 4 setup.
¾
:Delay time 4 setup(sec).
¾
:Style 4 selection(Please refer to StyL alarm style description).
16

6.1
OffsetHighAlarm
Alarm Style
Alarm output on
When PV>=SV+POS1, DY1 starts timing.
When DY1 finishes timing, alarm sends out
signal output.
Alarm output off
When PV<SV+POS1-HYS1, alarm output stops.
Ex.:
PV= present value
SV= set value
POS1= Alarm set point
DY1= Alarm delay time
SV=60;POS1=10;
HYS1=5;DY1=5;
When PV>=70, DY1 starts timing.
When DY1 finishes timing, alarm
sends out signal output.
When PV<65, alarm output stops.
17

6.2
Offset High Alarm
Alarm output on
When PV>=SV-POS1, DY1 starts timing.
When DY1 finishes timing, alarm sends out
signal output.
Alarm output off
When PV<=SV-POS1-HYS1, alarm output stops.
Ex.:
PV= present value
SV= set value
POS1= Alarm set point
DY1= Alarm delay time
SV=60;POS1=10;
HYS1=5;DY1=5;
When PV>=50, DY1 starts timing.
When DY1 finishes timing, alarm
sends out signal output.
When PV<45, alarm output stops.
18

6.3
Offset Low Alarm
Alarm output on
When PV<=SV-POS1, DY1 starts timing.
When DY1 finishes timing, alarm sends out
signal output.
Alarm output off
When PV>=SV-POS1+HYS1, alarm output stops.
Ex.:
PV= present value
SV= set value
POS1= Alarm set point
DY1= Alarm delay time
SV=60;POS1=10;
HYS1=5;DY1=5;
When PV<=50, DY1 starts timing.
When DY1 finishes timing, alarm
sends out signal output.
When PV>=55, alarm output stops.
19

6.4
Offset Low Alarm
Alarm output on
When PV<=SV+POS1, DY1 starts timing.
When DY1 finishes timing, alarm sends out
signal output.
Alarm output off
When PV>=SV+POS1+HYS1, alarm output stops.
Ex.:
PV= present value
SV= set value
POS1= Alarm set point
DY1= Alarm delay time
SV=60;POS1=10;
HYS1=5;DY1=5;
When PV<=70, DY1 starts timing.
When DY1 finishes timing, alarm
sends out signal output.
When PV>=75, alarm output stops.
20
Other manuals for PT-8320 Series
1
Table of contents
Other FineTek Temperature Controllers manuals