iii
Wiring
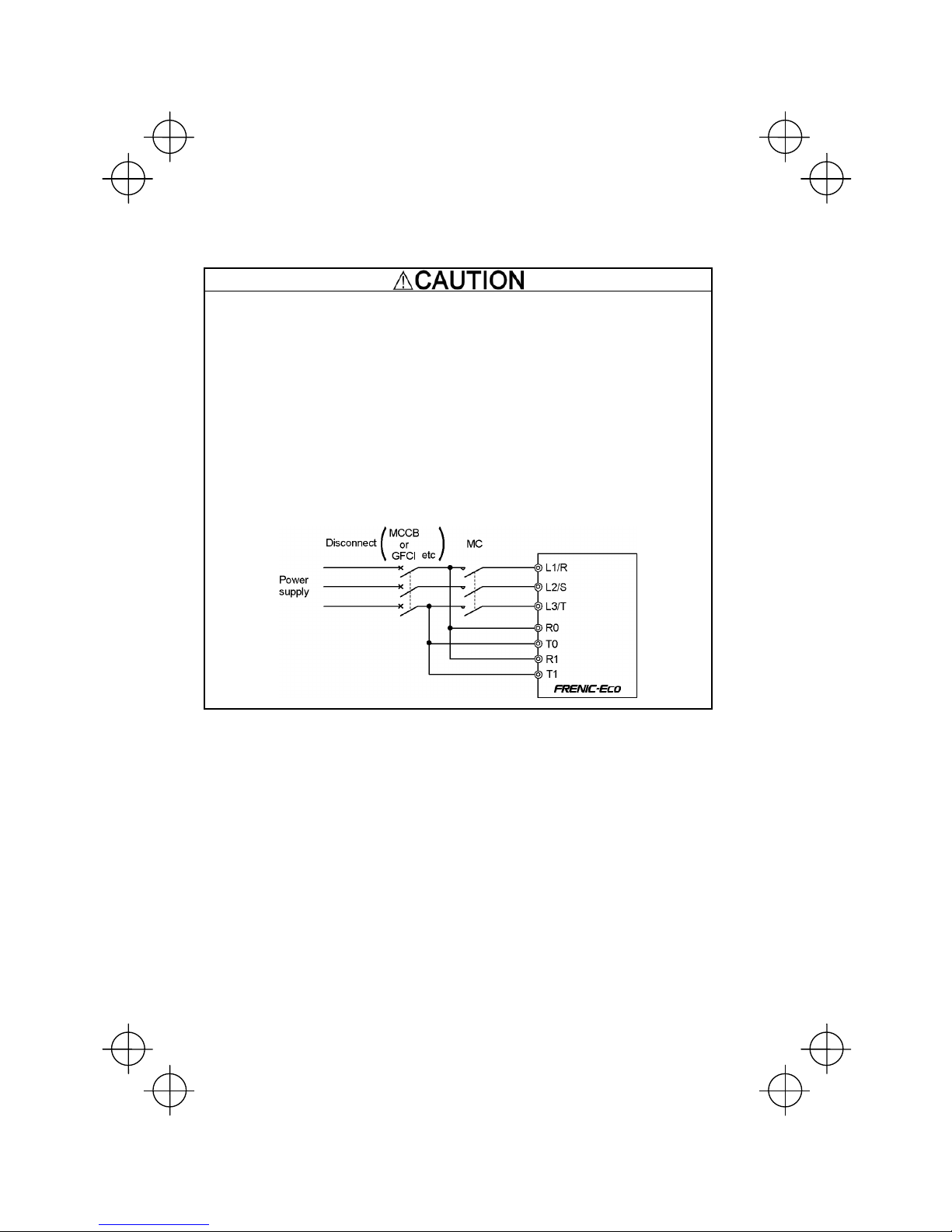
• When wiring the inverter to the power source, insert a recommended molded case circuit breaker
(MCCB) or residual-current-operated protective device (RCD)/a ground fault circuit
interrupter(GFCI)(with overcurrent protection) in the path of power lines. Use the devices within the
recommended current range.
• Use wires in the specified size.
Otherwise, fire could occur.
• Do not use one multicore cable in order to connect several inverters with motors.
• Do not connect a surge suppressor to the inverter's output (secondary) circuit.
Doing so could cause fire.
• Ground the inverter in compliance with the national or local electric code.
Otherwise, electric shock could occur.
• Qualified electricians should carry out wiring.
• Be sure to perform wiring after turning the power OFF.
Otherwise, electric shock could occur.
• Be sure to perform wiring after installing the inverter body.
Otherwise, electric shock or injuries could occur.
• Ensure that the number of input phases and the rated voltage of the product match the number of
phases and the voltage of the AC power supply to which the product is to be connected.
Otherwise fire or an accident could occur.
• Do not connect the power source wires to output terminals (U, V, and W).
Doing so could cause fire or an accident.
• Generally, control signal wires are not enforced- insulated. If they accidentally touch any of live parts in
the main circuit, their insulation coat may break for any reasons. In such a case, an extremely high
voltage may be applied to the signal lines. Make a complete remedy to protect the signal line from
contacting any hot high voltage lines.
Otherwise, an accident or electric shock could occur.
• Wire the three-phase motor to terminals U, V, and W of the inverter, aligning phases each other.
Otherwise injuries could occur.
• The inverter, motor and wiring generate electric noise. Take care of malfunction of the nearby sensors
and devices. To prevent the motor from malfunctioning, implement noise control measures.
Otherwise an accident could occur.