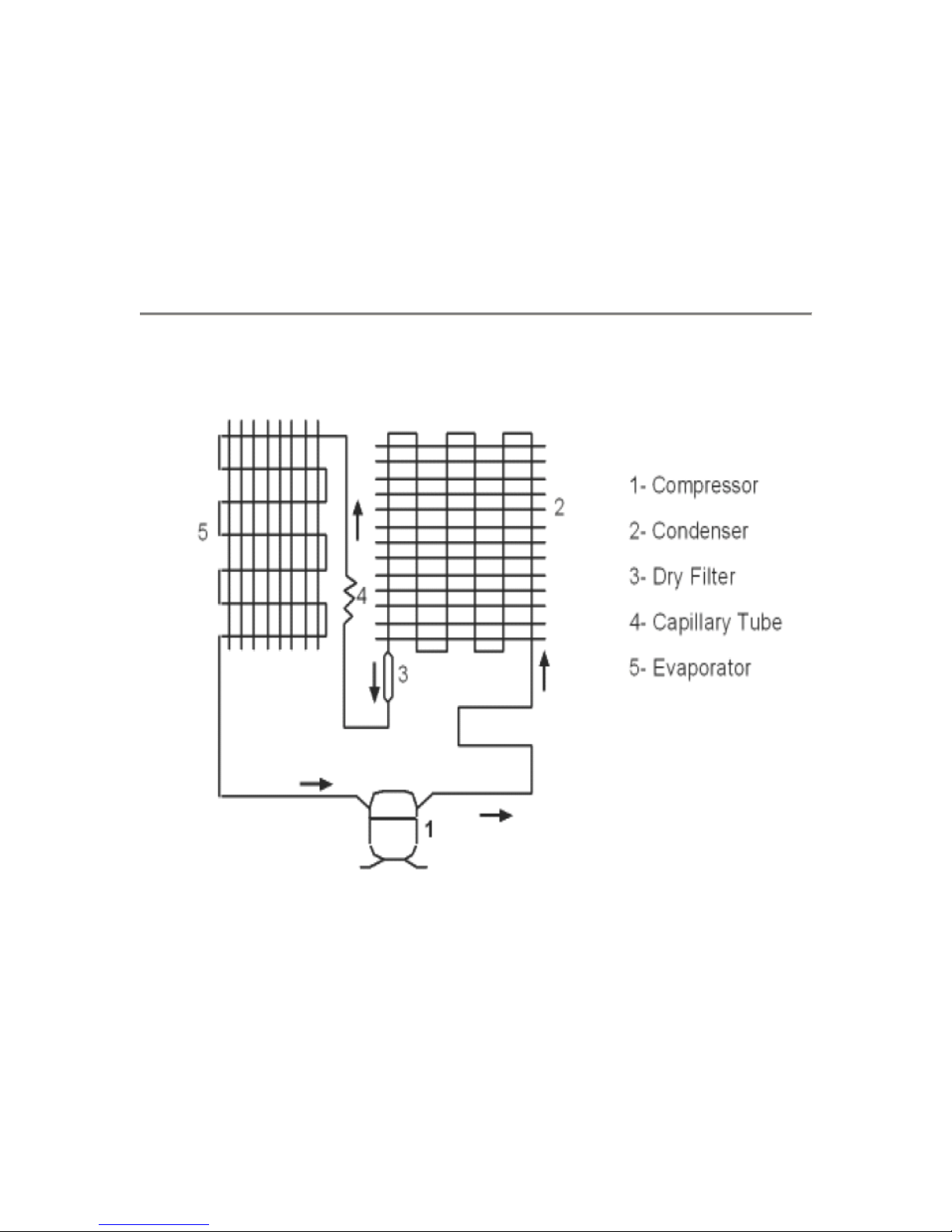
2. Listen
a. Listen to the noises made while the compressor is running. During the normal
operation of compressor, a slight and uniform humming sound due to undulation of
electric currents will be heard. The sounds listed below indicate a malfunction.
• Humming sounds from a fully enclosed aggregate unit indicate that the
motor was not started properly.
• Clattering sounds from the start relay indicate that the start contacts cannot
be released normally.
• Whistling sounds indicate the release of high-pressure gas from a crack in
the pressure tube inside the compressor.
• Clucking sounds indicate that the suspended spring inside the compressor
has broken
• Knocking sounds from inside the compressor indicates that a large
quantity of moist refrigerant vapor or refrigerating oil has leaked into the
compressor cylinder.
• Striking sounds from metal parts inside the compressor indicate that
moving parts are loose.
b. Listen to the gas flowing in the evaporator by opening the refrigerator door while the
compressor is in operation. Normally, refrigerant circulating in the evaporator produces a
gentle whistling accompanied by a sound similar to water flowing. If only the whistling
can be heard and there is no sound similar to water flowing, then the refrigerant has
already percolated. If neither sound can be heard, the filter or capillary is clogged.
3. Touch and Feel
a. Feel the compressor while it is running. Its temperature should be less than 90ºF. Its
temperature may exceed 90ºF if it has been running for an extended period of time.
b. After the compressor has operated for 5~10 minutes, feel the condenser. The
temperature of its upper part should be higher than that of its lower part (or its right part
is hotter than its left part, depending on the type of condenser coil). This indicates that the
refrigerant is circulating properly. If the condenser is not hot, then the refrigerant is
leaking. If the condenser is hot for only a few minutes and then cools down, the filter and
capillary are clogged. If hot air is blown out of the forced air-cooling condenser, the
system is out of order.
c. Feel the filter’s temperature. Normally, the temperature on the filter’s surface should
be a little higher than the ambient temperature. If the filter is lower than the ambient
temperature, then the meshes of its screen are clogged. This obstructs the flow of
refrigerant and causing a drop in temperature due to throttling.
d. Feel the temperature of exhaust gas from the refrigerating system. The exhaust gas
should be very hot as the normal working state. If the refrigerator has an enclosed
compressor refrigerating system, there should be no frost or condensation on the gas
suction tube, otherwise, there is some problem with the system (frosting may show when
starting machine, this is normal condition).