5 - 2
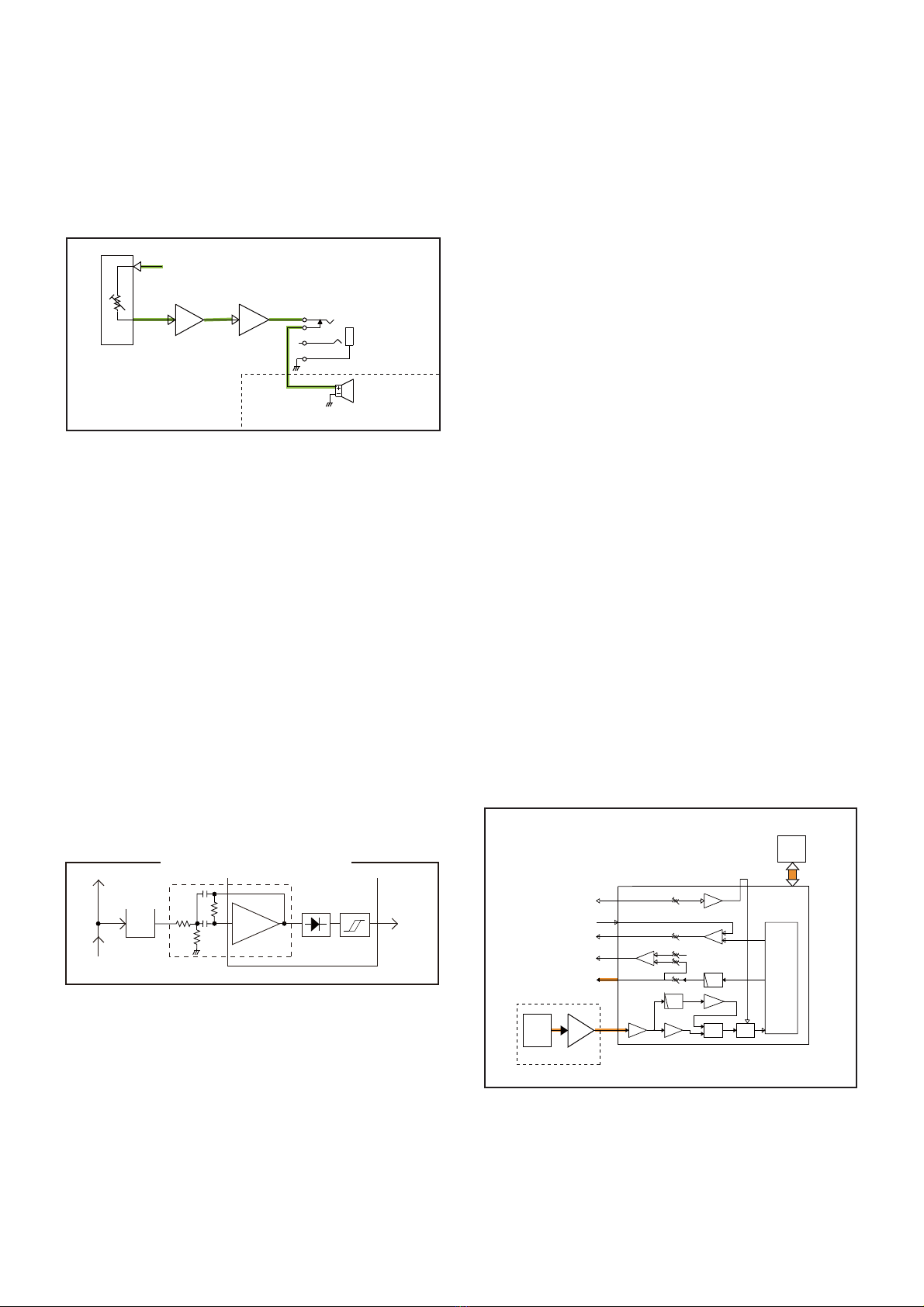
RX AF CIRCUITS
The detected audio signals adjusted by the linear codec’s
electoronic volume (inside the AF CUSTOM IC (IC1010)).
The level-adjusted AF signal is then amplified by the pre-
AMP (IC1004) and AF power AMP (IC1009).
The power amplified AF signal is passed through the exter-
nal speaker jack (J1002), and then applied to the internal
speaker.
• RX AF CIRCUIT
SQUELCH CIRCUIT (Analog mode only)
The squelch circuit cuts off the AF output signals when no
RF signals are received. Detecting noise components in the
demodulated AF signals, the squelch circuit stops audio sig-
nals being heard.
A portion of the demodulated AF signal from the IF IC (IC4)
is passed through the AF CUSTOM IC (IC1010) for level
(=threshold) adjustment. The level-adjusted AF signals are
passed through the noise filter (IC4, pins 7, 8 and Q9, R42,
R44–R45, C68–C70) to filter only the noise components (ap-
proximately 30 kHz signals). The noise components are rec-
tified, resulting in a DC voltage corresponding to the noise
level.
If the noise level is higher than the preset one, the internal
comparator set the “NOISE” signal to the CPU to “High,” then
the CPU turns the “AFON” signal, which controls the AF
mute SW, (Q1008, Q1012, D1007) to “Low,” to stop the AF
output.
• SQUELCH CIRCUIT
AF
AMP
AF
AMP
IC1009 J4
SP1
Int.speaker
Ext.speaker
From the IF IC
IC1004
AFO
AFVO
Electronic
volume
FRONT UNIT
IC1010
DAC Noise
AMP
Noise filter
From IF IC
(IC4, Pin16)
To RX AF circuits
Noise
detector
Com-
parator
NOISE SQUELCH DIAGRAM
“NOIS”
IC1006
IC4
14
8
7
13
15
J1
FRONT UNIT
[MIC
JACK] AMP
IC7
DSP
IC2007
AMP
HPF
ALC
AMP
BUFF
LPF
BUFF
LIMIT
AMP
BUFF
MOD
LINE
CTRL
DAFO
SW
IC1010
VCON REF
TX/RX
AFVO
BEEP
SQIN
MOD DMO
BAL
MICI
CODEC
LINEAR
5-2 TRANSMITTER CIRCUIT
TX AF CIRCUIT
The audio signal from the microphone (MIC signal) is passed
through the MIC AMP (IC7), and then applied to the AF CUS-
TOM IC (IC1010).
• WHILE OPERATING IN THE ANALOG MODE
The amplified MIC signal is passed through the HPF (inside
the AF CUSTOM IC (IC1010, pin 3)), which attenuates fre-
quencies 300 Hz and below, and then applied to the limiter
AMP
(inside the AF CUSTOM IC (IC1010
, pin 4)).
The am-
plitude-limited MIC signal is applied to the AF CUSTOM IC
(inside the IC1010).
The MIC signal is converted into a digital audio signal by
the linear codec (inside the AF CUSTOM IC (IC1010)), pro-
cessed by the DSP (IC2007), and then converted into an
analog baseband signal (modulation signal).
• WHILE OPERATING IN THE DIGITAL MODE
The amplified MIC signal is applied to the ALC (inside the AF
CUSTOM IC (IC1010, pin10)) which keeps the signal level
fixed.
The level-adjusted MIC signal is
applied to the linear codec
(
inside the AF CUSTOM IC (IC1010)) through the MIC line
SW (inside the AF CUSTOM IC (IC1010)).
The MIC signal is converted into a digital audio signal by
the linear codec (inside the AF CUSTOM IC (IC1010)), pro-
cessed by the DSP (IC2007), and then converted into the
digital baseband signal (modulation signal).
The signal from the linear codec (inside the AF CUSTOM IC
(IC1010)) is passed through the LPF (inside the AF CUS-
TOM IC (IC1010)), and then applied to the D/A converter
(inside the AF CUSTOM IC (IC1010))
which adjusts its level
(=deviation)
.
The level-adjusted modulation signal is applied to the modu-
lation circuit.
• TX AF CIRCUIT