INTRODUCTION
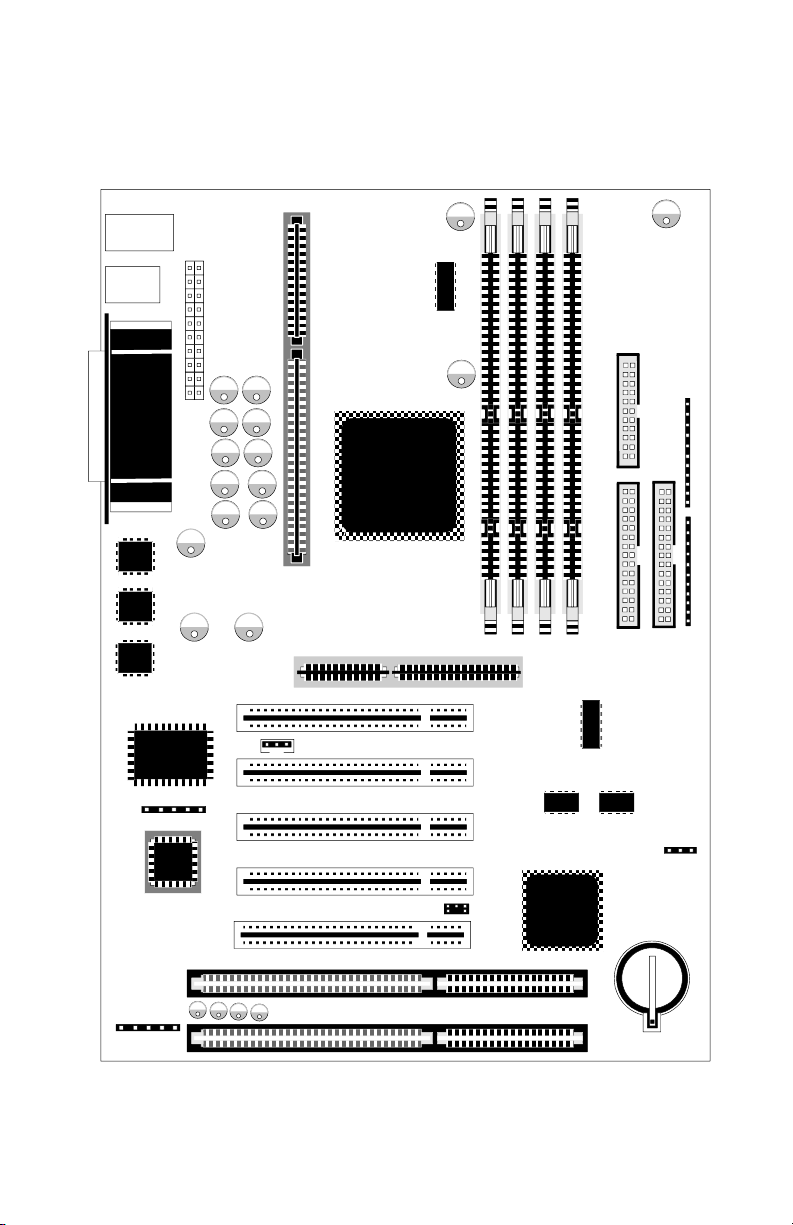
This mainboardisdesignedforthe newgenerationCPU.It supportsthe Intel
CPU SLOT1 (Pentium®II), up to 512MBof memory,superI/O, and Green
PC functions.The mainboardprovideshighperformance forthe server
system and meetsthe requirementsof thedesktopsystem for multimedia in
the future.
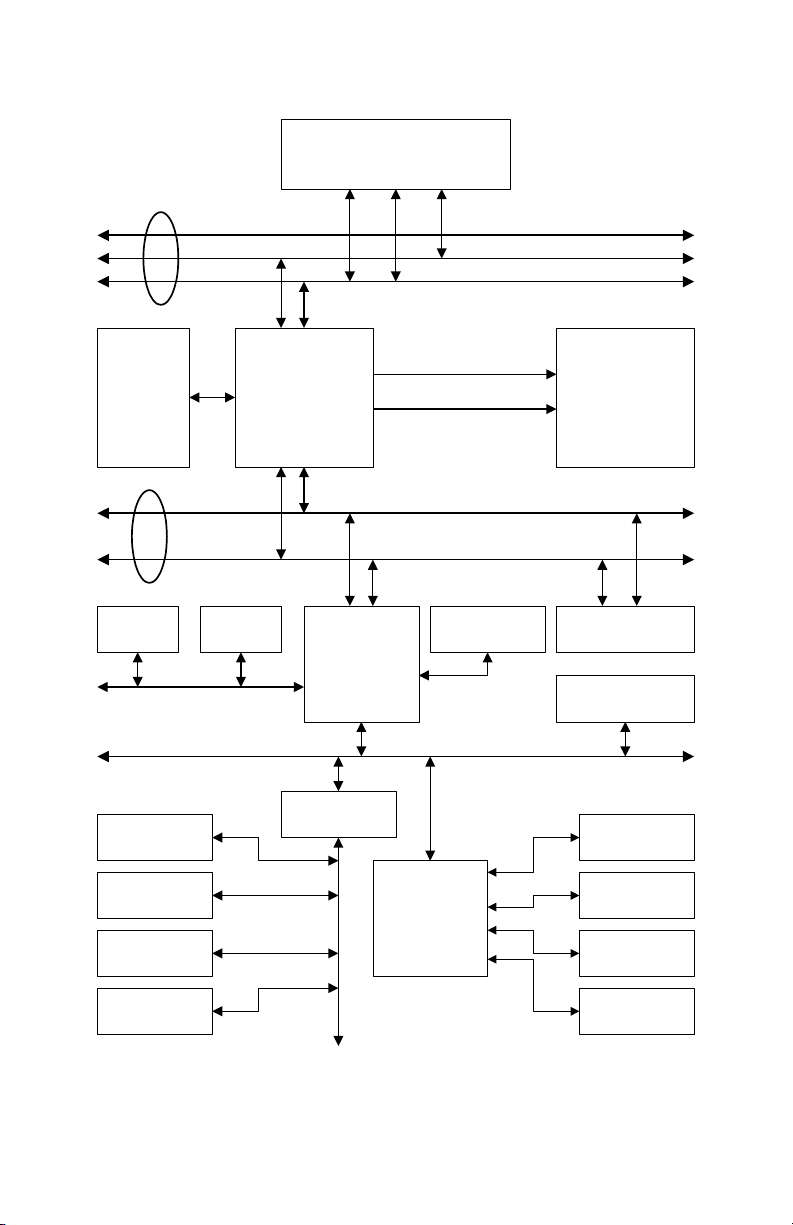
This mainboardbased onthe new 440BX chipsetwhich revolutionizesthe
way Pentium®IIPCs use memorybyemployinganOpen PageArchitecture,
a new memoryarchitecture thatlets the CPUaccess main memoryfaster.
Essentially,this meanstheCPU can leave a virtual fingerin up to 32 different
pagesof its memory,makingiteasyforyou to flip back to any of them at any
time.Currently, like a dogged A-to-Z readerof the encyclopedia,a Pentium II
can onlykeepits memoryopento onepageat a time.The CPU usespages
of memoryin a similarmannertopeople leafing through reference works.It
wants to flip backand forthbetweena particularset of pagesat a time.
Flippingrightto them instead of taking that extra microsecond tofindthem
makesthe wholePCruns faster.
Anotherimprovementinthe chipsethelpsthe CPU whenit findsa single-bit
error while reading error-correctingmemory(thatis, onebit in a byte of
information isincorrect).With the 440BX, the errorcan be correctedon the
fly, withthe correctionwritten back into memory.Current Pentium® IIs can’t
write the correction back.
However,this mainboardoffersmoreobviousimprovements.Most
importantly,supportforthe faster system bus willhave a profound effecton
performance.
But other performance benefitsaccrue formainstreamdesktopsaswell.The
mostobviousof these is support for2x AGP. This meanstheAGP bus is
clocked twice as fastand Sidebandchannel(aslowersidechannelforcontrol
information)isalso used. CurrentAGP implementations onlyuse a single-
speed main channel andmixcontrolinformation withthe data.
1998 Jaton Corporation, USA