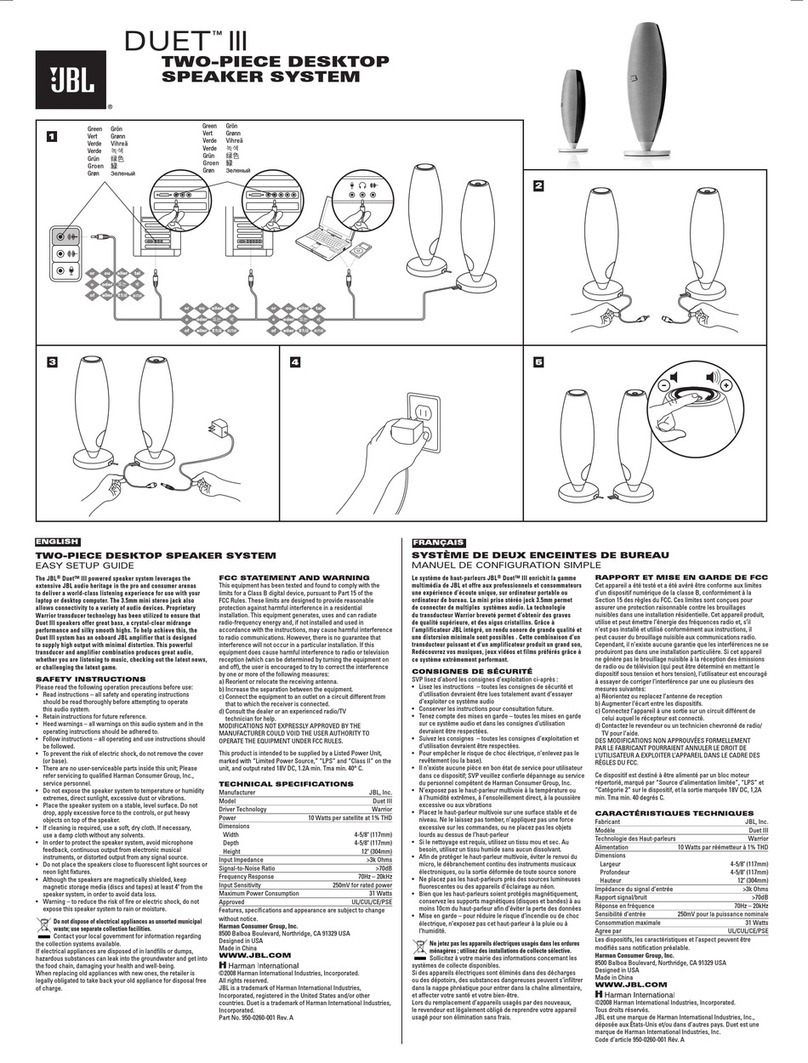
-4-
Suspending Loudspeaker Arrays
IMPORTANT SAFETY WARNING!
The information in this section has been assembled from recognized engineering data and is intended for
informational purposes only. None of the information in this section should be used without first obtaining
competent advice with respect to applicability to a given circumstance. None of the information presented
herein is intended as a representation or warranty on the part of JBL. Anyone making use of this
information assumes all liability arising from such use.
All information presented herein is based upon materials and practices common to North America and
may not directly apply to other countries because of differing material dimensions, specifications, and/or
local regulations. Users in other countries should consult with appropriate engineering and regulatory
authorities for specific guidelines.
Correct use of all rigging hardware is required for secure system suspension. Careful calculations should
always be performed to ensure that all components are used within their working load limits before the
array is suspended. Never exceed the maximum recommended load ratings.
Before suspending any speaker system always inspect all components (enclosure, rigging frames, pins,
eyebolts, track fittings, etc.) for cracks, deformations, corrosion, missing, loose or damaged parts that
could reduce strength and safety of the array. Do not suspend the speaker until the proper corrective
action has been taken. Use only load-rated hardware when suspending Application Engineered™ Series
and Precision Directivity™ Series loudspeakers.
Are You New to Rigging?
If you are new to rigging, you should do the following:
•Read and study JBL Technical Note Volume 1, Number 14: Basic Principles for Suspending
Loudspeaker Systems (available at http://www.jblpro.com/pub/technote/tn_v1n14.pdf).
•Know the rules for safe rigging.
•Attend a safe rigging seminar, such as that presented by professionals like Rigging Seminars™
(www.riggingseminars.com) or by Chain Motor Hoist manufacturers like Columbus McKinnon
Corp. (manufacturers of the C/M Lodestar).
•Meet and establish a relationship with a licensed mechanical or structural engineer. Get in the
habit of asking them questions instead of guessing about their answers. Learn from what they tell
you.
•Meet and discuss this aspect of your business with your Insurance Agent.
•Research and understand the codes, practices, and requirements in the venues where you intend
to install and operate sound systems.
General Hardware Information
Any hardware used in an overhead suspension application must be load rated for the intended use.
Generally, this type of hardware is available from rigging supply houses, industrial supply catalogs and
specialized rigging distributors. Local hardware stores do not usually stock these products. Hardware that
is intended for overhead suspension will comply with ASME B30.20 and will be manufactured under
product traceability controls. Compliant hardware will be referenced with a working load limit (WLL) and a
traceability code.
Attachment to Structures
A licensed Professional Engineer must approve the placement and method of attachment to the structure
prior to the installation of any overhead object. The following performance standards should be provided