Optical wavelength 850 nm infrared
Operating temperature range -10°C ... +70°C [+14°F ... +158°F]
Interference immunity EN 61000-6-2
Radiated interference EN 55011 Class B1
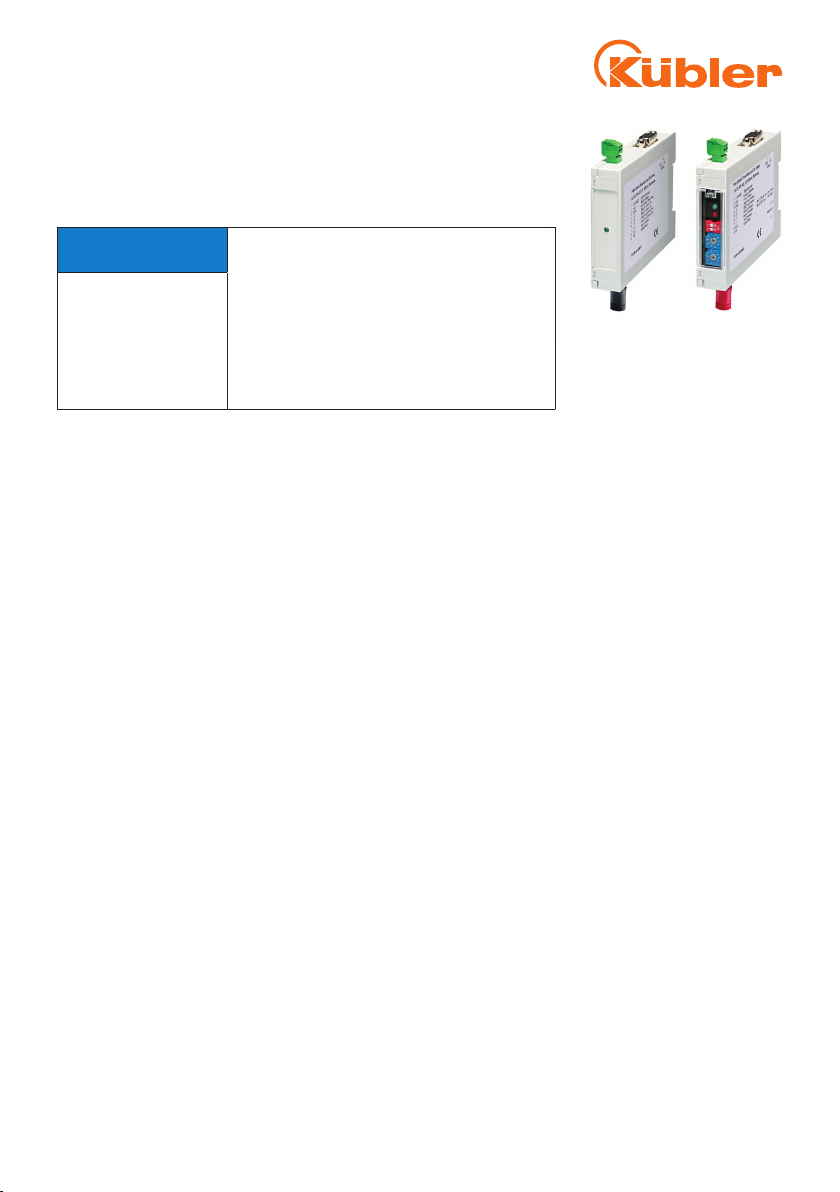
4. Areas of application for the optical fibre modules are mainly when signals should be transferred in
an environment with strong interferences present, or when, due to high ground potential differences
between signal source and evaluating equipment, a separation of the potentials is necessary.
High ground potential differences generally also appear in case of large distances between the
rotation encoder and the PLC, or other processing electronics.
The optical fibre cable is fail-safe, i.e. there is no danger in case of damage. Since the light-emitting
component used is not a laser, but a light-emitting diode, the transmission line is totally safe, even
when looking directly into the opened connector or into the broken glass fibre.
The optical fibre cable can be routed through explosion-hazard areas.
If a level conversion should be simultaneously linked with the potential separation, this is possible
without any problem. Since all devices use the same signal transmission protocol on the optical fibre
cable, any transmitter can be combined with any receiver.
A specific feature of the transfer mode used is the fact that the SSI signal is transmitted without the
disturbing round-trip delays between the clock and the data. This also allows a quick reading of the
encoder even when using cable lengths exceeding 2000 m.
5.1 Connection of the modules
The clock pulse and data lines are to be routed in pairs, i.e. the two cores of a signal are to be routed
in paired cables. A utilization of bundle cables (so-called control cables) is not permissible, since in
this case neither the correct signal transmission nor the EMC characteristic values can be ensured.
The cable screening is to be connected on both sides, i.e. to the rotation encoder and to the optical
fibre transmitter or optical fibre receiver, and to the evaluator unit. For this, the connections are
provided with GND/screening.
The RS422-outputs on the control signal receiver require a differential input with an input impedance
of 100 - 120 Ω.
The outputs of the modules are short-circuit-proof to a limited extent only, so that it is
absolutely necessary to avoid a short circuit with each other or to ground.
Any exceeding of the power supply for the modules with 5 V power supply beyond a value of
approx. 6 V leads to the melting of the fuse located inside the unit and therefore must be avoided.
For the modules with a power supply of 10 - 30 V, this value is 33 V.
The fuse is to be replaced by the manufacturer. Any attempt to repair the device voids the guarantee.
For the connection of the modules to each other, 50/125 µm or µ 62.5/125 m multimode optical fibre
cables can be used. Single mode optic fibres are not usable.
Keep the dust protection caps of the optical transmitters and receivers and use them for closure
again if no optical fibre guide is connected to the modules, in order to prevent any dirt accumulation
through dust or other materials.
ENG - P. 3