KMS Fuel/FA23 manual
Version 3.01 2
Contents page.
1KMS (Kronenburg Management Systems)............................................................... 3
2Software installation....................................................................................... 4
3KMS software................................................................................................. 5
3.1 The injection characteristic diagram ............................................................. 5
3.2 The function bar....................................................................................... 6
3.2.1 Function key F1 ..................................................................................... 6
3.2.2 Function key F2 ..................................................................................... 6
3.2.3 Function key F3 ..................................................................................... 6
3.2.4 Function key F4 ..................................................................................... 6
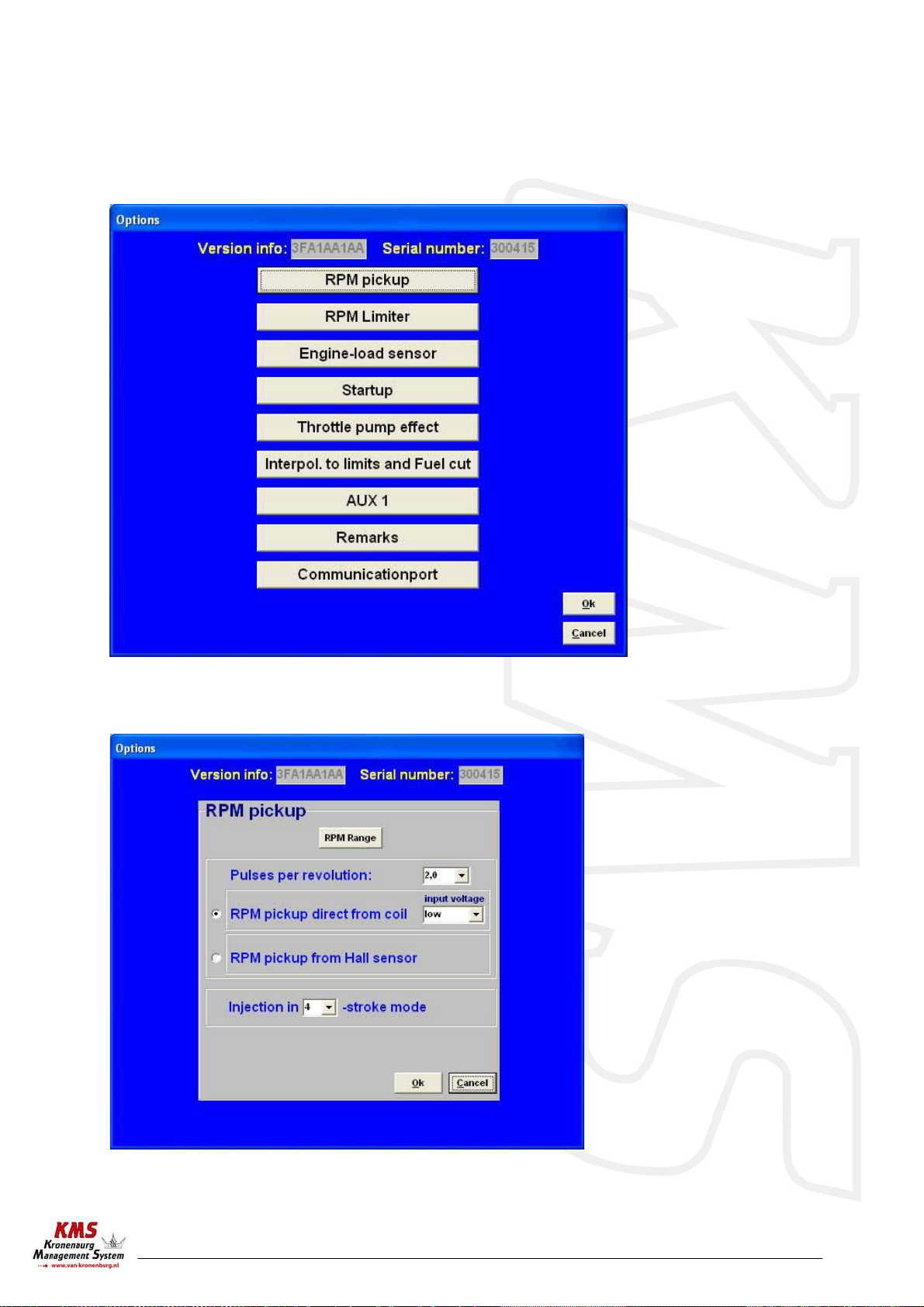
3.2.4.1 Options......................................................................................... 7
3.2.4.1.1 RPM pickup................................................................................ 7
3.2.4.1.2 RPM limiter (not available at older Fuel systems).................................. 8
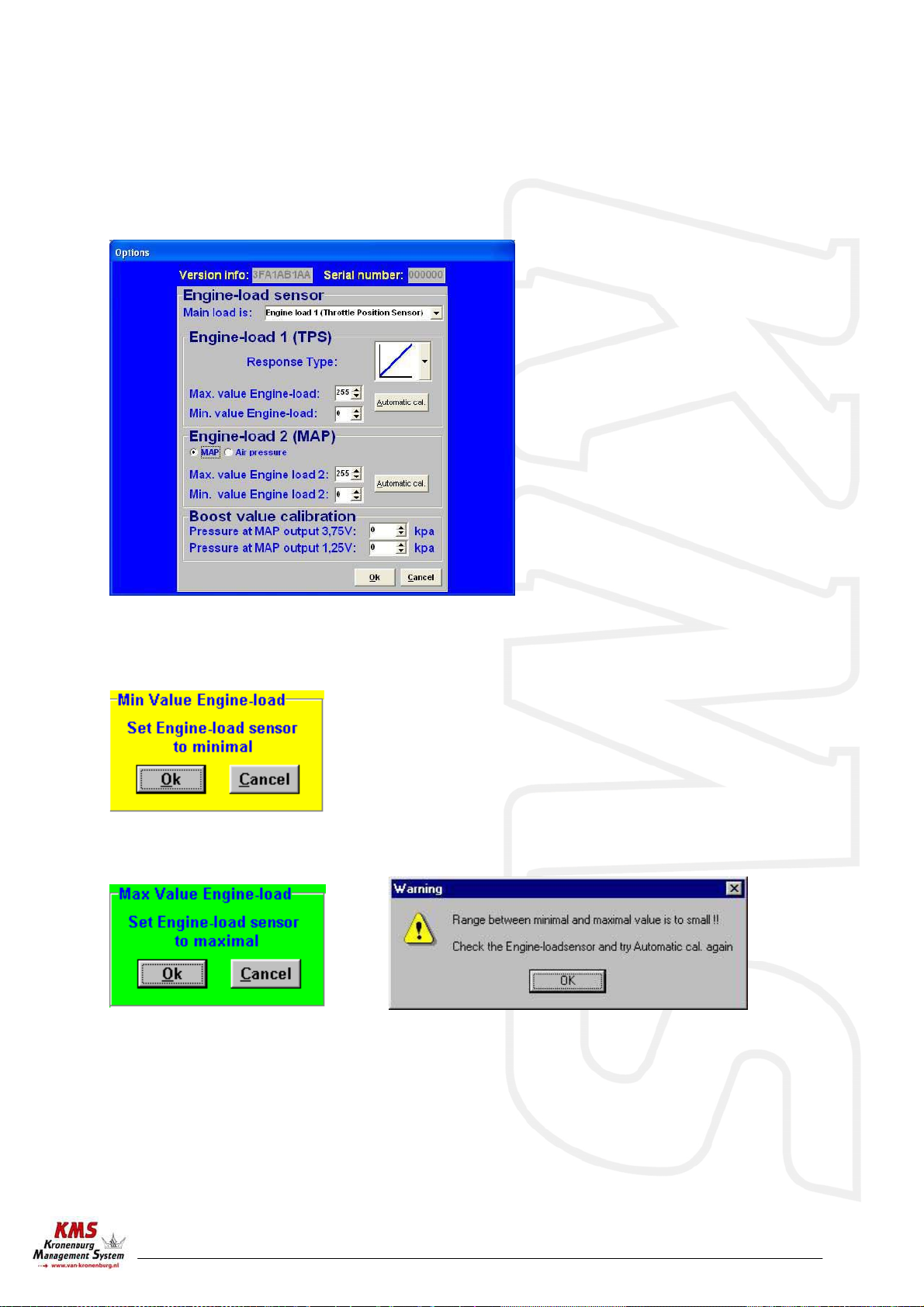
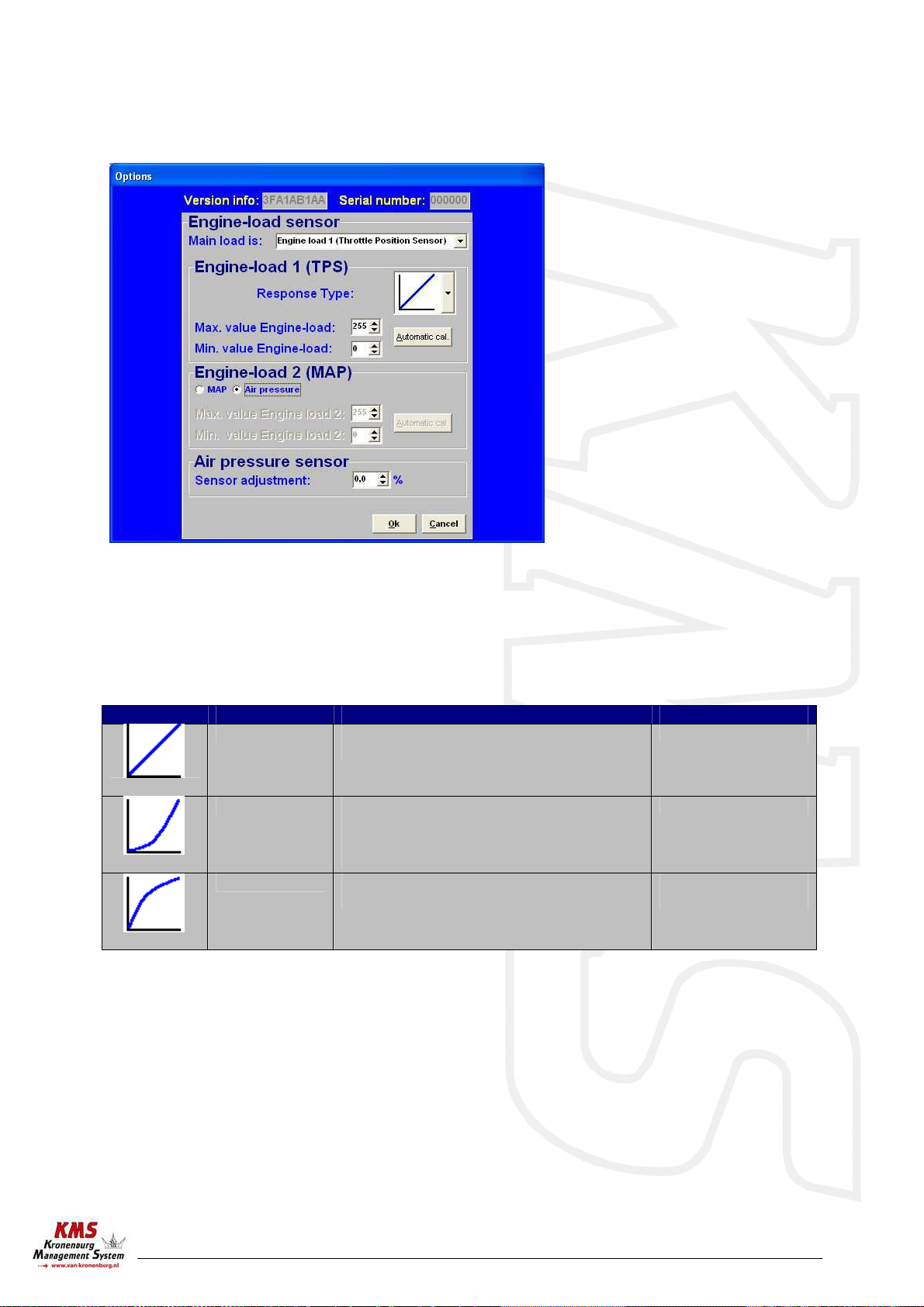
3.2.4.1.3 Engine load sensor....................................................................... 9
3.2.4.1.4 Start-up...................................................................................11
3.2.4.1.5 Throttle pump effect...................................................................12
3.2.4.1.6 Interpolations to limit and fuel cut..................................................12
3.2.4.1.7 AUX 1 (Second stage on older Fuel system) ........................................13
3.2.4.1.8 Correction-table (only for older Fuel systems) ....................................14
3.2.4.1.9 Remarks .................................................................................14
3.2.4.1.10 Communication port .................................................................15
3.2.5 Function key F5 ....................................................................................15
3.2.6 Function key F7 ....................................................................................17
3.2.7 Function key F10...................................................................................18
3.3 The communication bar............................................................................ 19
4Programming ............................................................................................... 21
4.1 Manual changing..................................................................................... 21
4.2 Bar charts ............................................................................................. 21
5Hardware installation.................................................................................... 22
5.1 Fitting the ECU....................................................................................... 22
5.2 Connecting the communication cable........................................................... 22
6Fault tracing................................................................................................ 23
7Specifications .............................................................................................. 24
8Wiring diagram FA23 ..................................................................................... 25
9Wiring examples KMS FA23.............................................................................. 26
10 Wiring example (older) KMS Fuel ...................................................................... 29