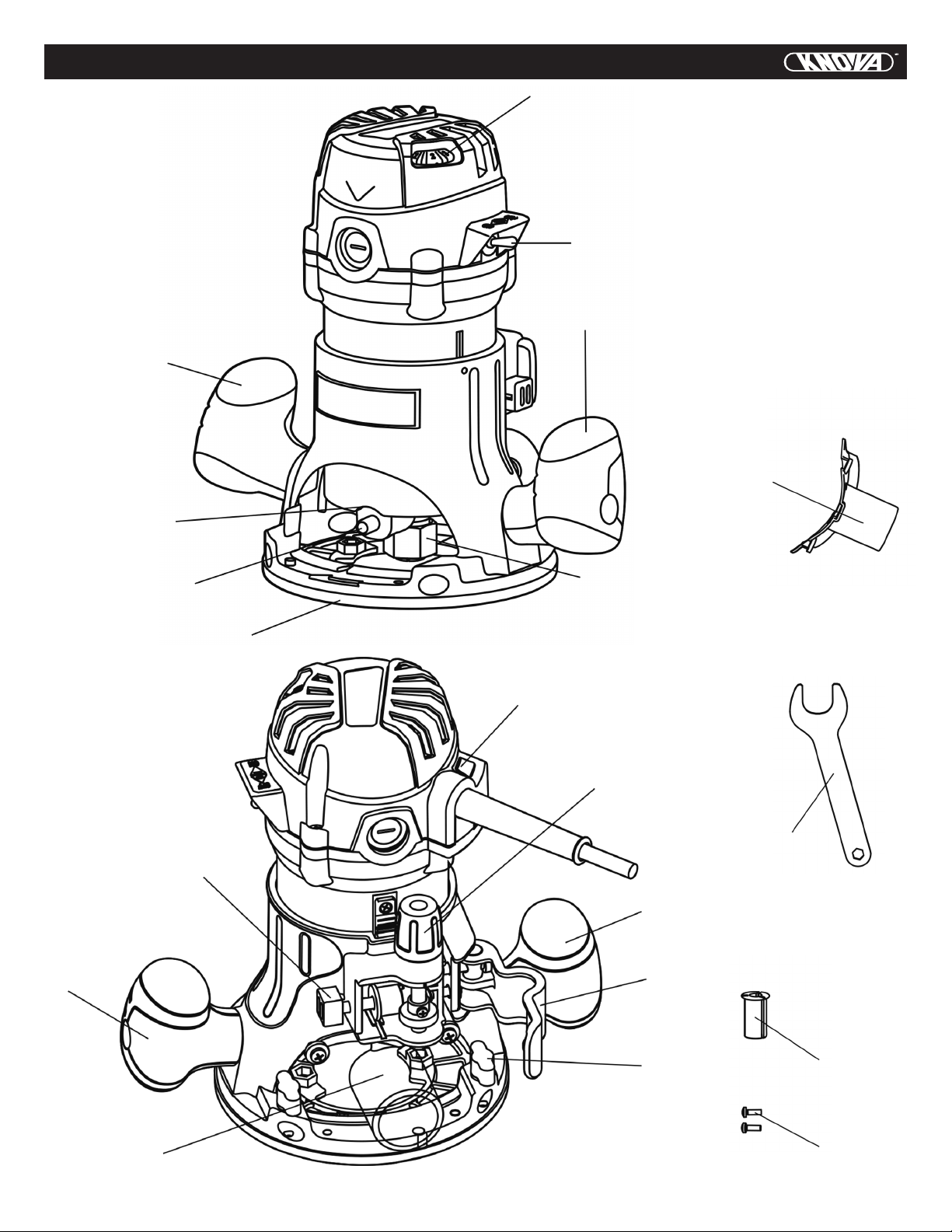
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
1. Stay alert, watch what you are doing and use common
sense when operating a power tool. Do not use a power
tool while you are tired or under the inuence of drugs,
alcohol or medication. A moment of inattention while
operating power tools may result in serious personal injury.
2. Use personal protective equipment. Always wear eye
protection. Protective equipment such as dust mask,
non-skid safety shoes, hard hat, or hearing protection used
for appropriate conditions will reduce personal injuries.
3. Prevent unintentional starting. Ensure the switch is in the
off-position before connecting to power source and/or
battery pack, picking up or carrying the tool. Carrying
power tools with your nger on the switch or energising
power tools that have the switch on invites accidents.
4. Remove any adjusting key or wrench before turning the
power tool on. A wrench or a key left attached to a rotating
part of the power tool may result in personal injury.
5. Do not overreach. Keep proper footing and balance at all
times. This enables better control of the power tool in
unexpected situations.
6. Dress properly. Do not wear loose clothing or jewellery.
Keep your hair, clothing and gloves away from moving
parts. Loose clothes, jewellery or long hair can be caught in
moving parts.
7. If devices are provided for the connection of dust
extraction and collection facilities, ensure that these are
connected and properly used. Use of these devices can
reduce dust-related hazards.
PERSONAL SAFETY
1. Have your power tool serviced by a qualied repair person
using only identical replacement parts. This will ensure that
the safety of the power tool is maintained.
SERVICE
1. Hold the power tool by insulated gripping surfaces only,
because the cutter may contact its own cord. Cutting a
“live” wire may make exposed metal parts of the power
tool “live” and could give the operator an electric shock.
2. Use clamps or another practical way to secure and
support the workpiece to a stable platform. Holding
the work by your hand or against the body leaves it
unstable and may lead to loss of control.
SAFETY GUIDELINES FOR ROUTERS
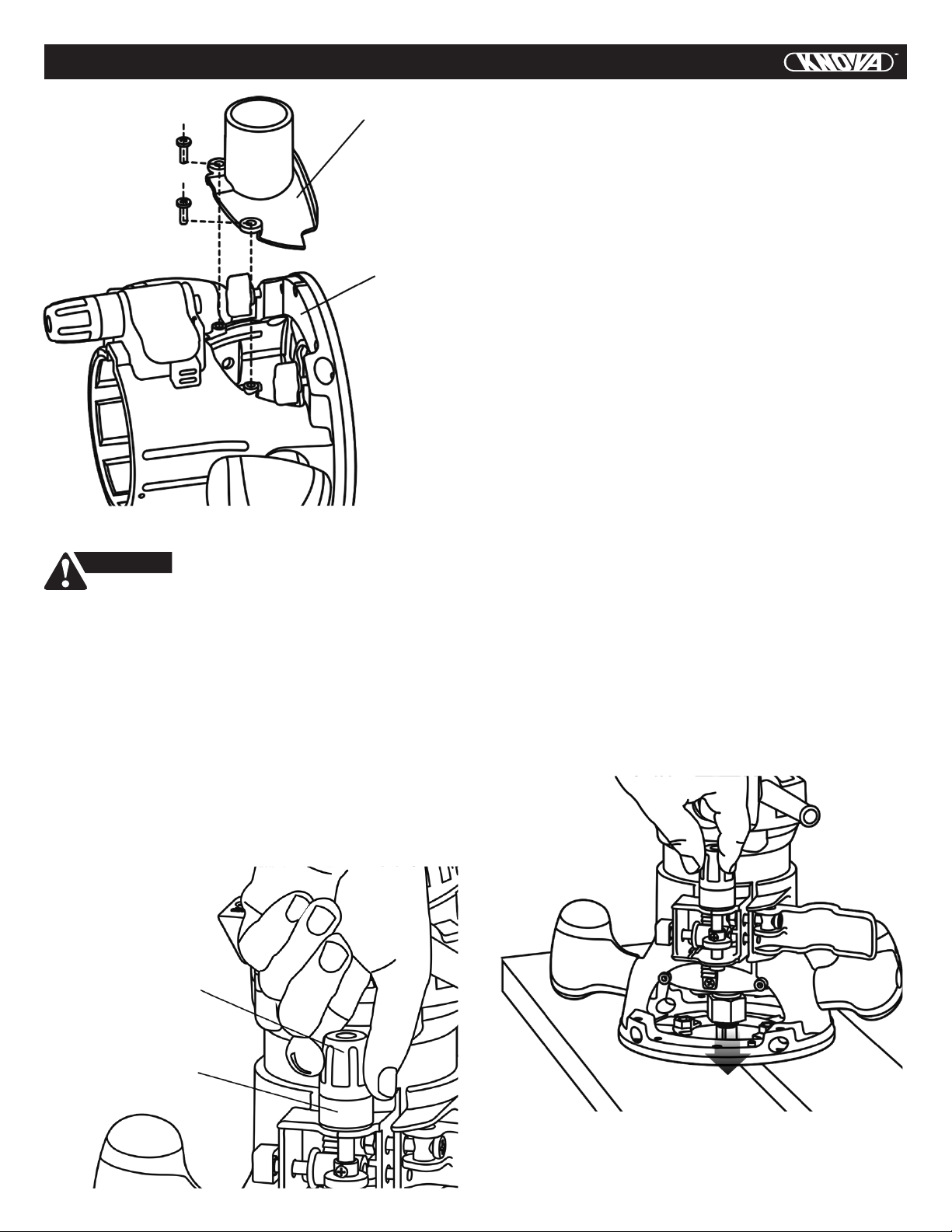
1. Always make sure the work surface is free from nails and
other foreign objects. Cutting into a nail can cause the bit
and the tool to jump and damage the bit.
2. Never hold the workpiece in one hand and the tool in the
other hand when in use. Never place hands near or below
cutting surface. Clamping the material and guiding the tool
with both hands is safer.
3. Never lay workpiece on top of hard surfaces, like concrete,
stone, etc.. Protruding cutting bit may cause tool to jump.
4. Always wear safety goggles and dust mask. Use only in
well ventilated area. Using personal safety devices and
working in safe environment reduces risk of injury.
5. Keep handles dry, clean and free from oil and grease.
Slippery hands cannot safely control the power tool.
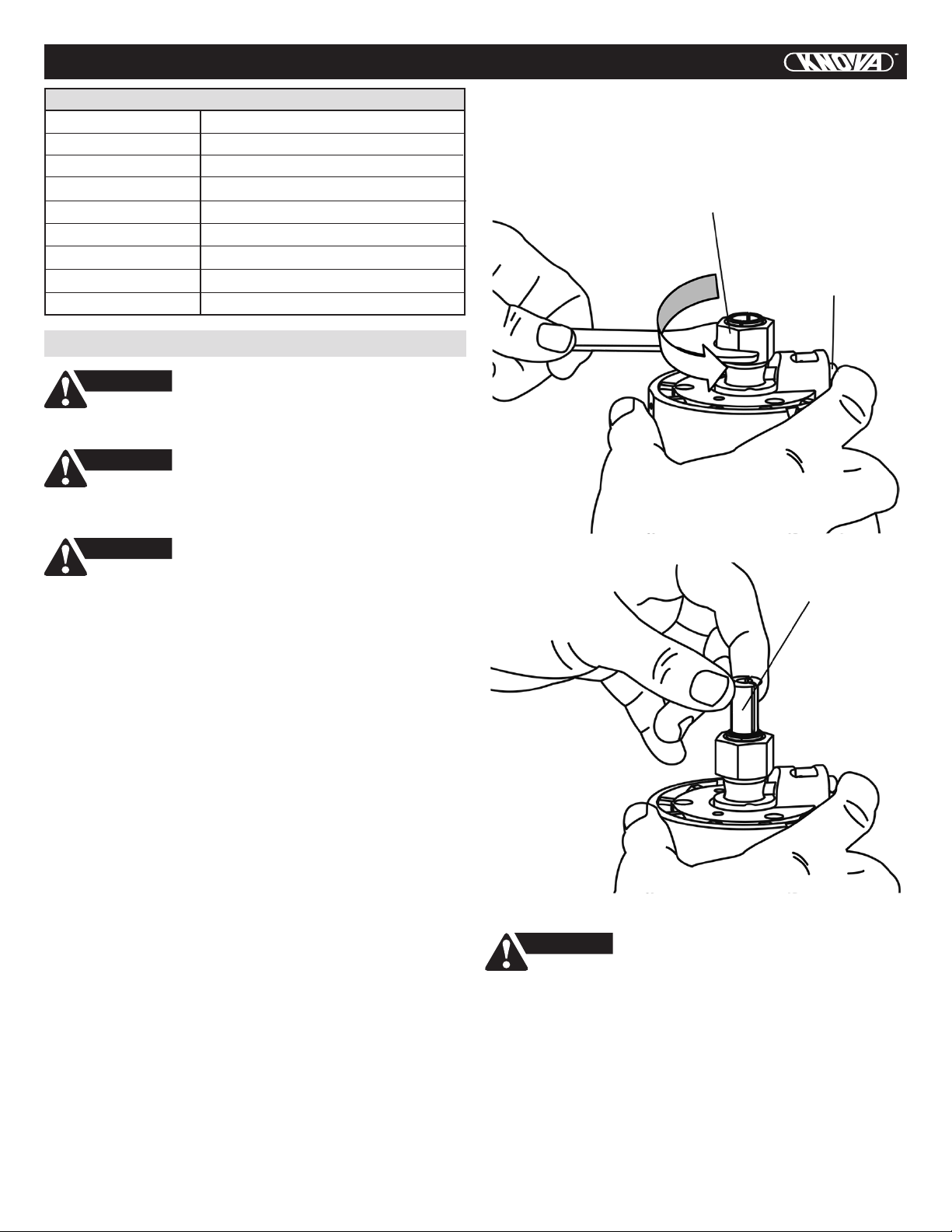
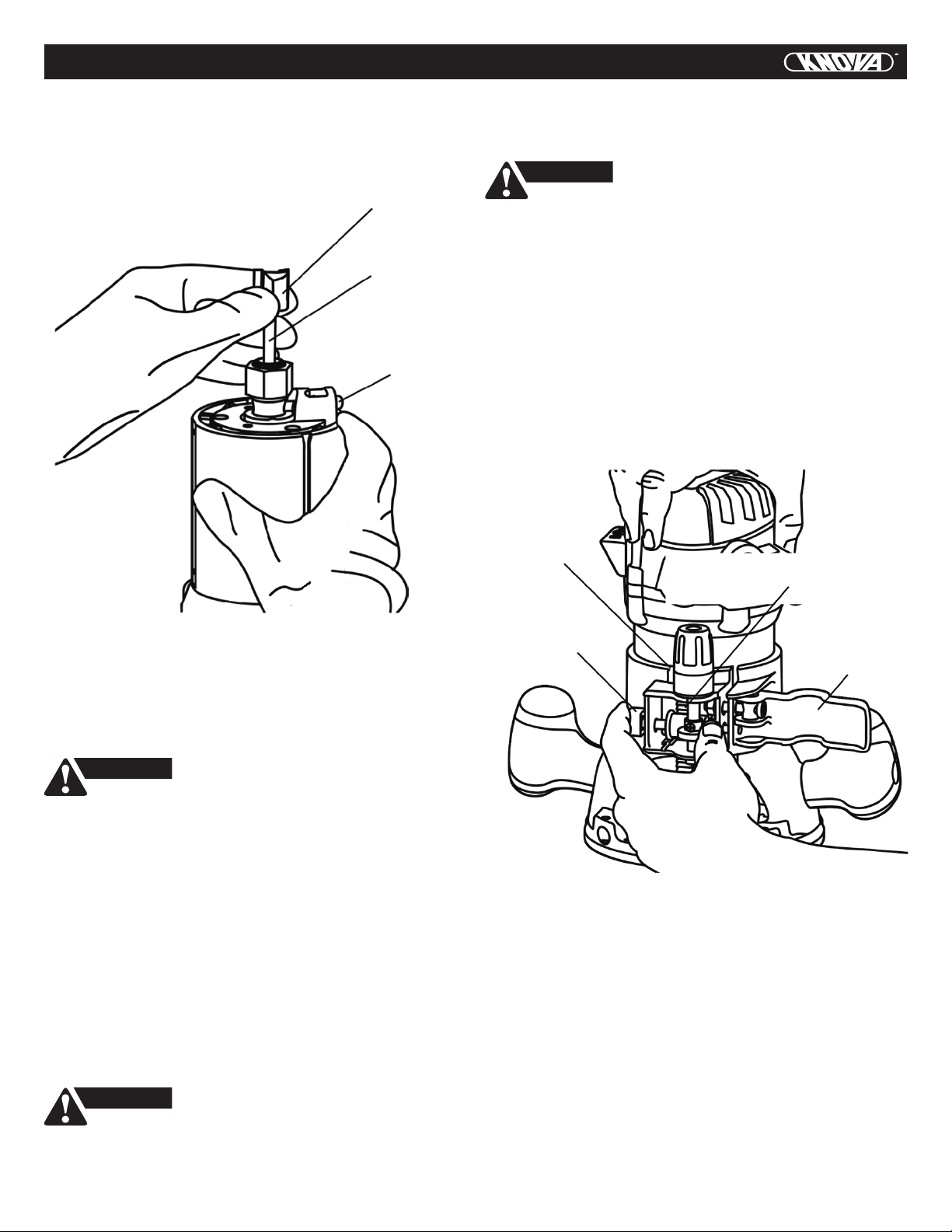
6. After changing the bits or making any adjustments, make
sure the collet nut and any other adjustment devices are
securely tightened. Loose adjustment device can
unexpectedly shift, causing loss of control, loose rotating
components will be violently thrown.
ADDITIONAL SAFETY GUIDELINES FOR ROUTERS
7. Never start the tool when the bit is engaged in
the material. The bit cutting edge may grab the material
causing loss of control of the cutter.
8. Always hold the tool with two hands during start-up. The
reaction torque of the motor can cause the tool to twist.
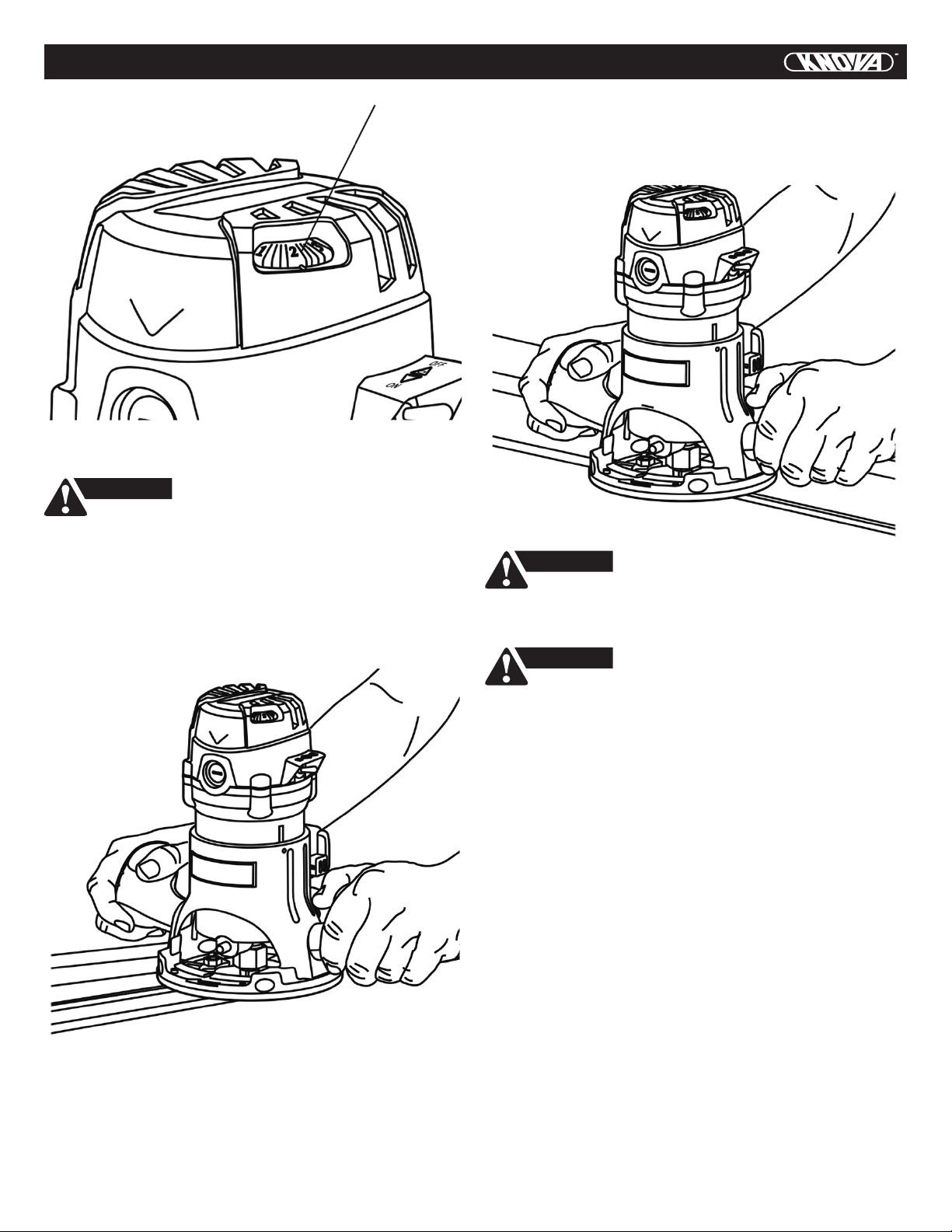
9. The direction of feeding the bit into the material is very
important and it relates to the direction of bit rotation.
When viewing the tool from the top, the bit rotates
clockwise. Feed direction of cutting must be
counter-clockwise. NOTE: inside and outside cuts will
require different feed direction, refer to section on feeding
the router. Feeding the tool in the wrong direction, causes
the cutting edge of the bit to climb out of the work and pull
the tool in the direction of this feed.
10. Never use dull or damaged bits. Sharp bits must be
handled with care. Damaged bits can snap during use.
Dull bits require more force to push the tool, possibly
causing the bit to break.
11. Never touch the bit during or immediately after the use.
After use the bit is too hot to be touched by bare hands.
12. Never lay the tool down until the motor has come to a
complete standstill. The spinning bit can grab the surface
and pull the tool out of your control.
13. Never use bits that have a cutting diameter greater than
the opening in the base.
WARNING
Some dust created by power sanding,
sawing, grinding, drilling and other construction
activities contains chemicals known to the state of
California to cause cancer, birth defects or other
reproductive harm. Some examples of these
chemicals are:
• Lead from lead-based paints
• Crystalline silica from bricks and cement and other
masonry products, and
• Arsenic and chromium from chemicallytreated lumber.
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending on how often
you do this type of work. To reduce your exposure to these
chemical: work in a well ventilated area, and work with
approved safety equipment, such as those dust masks that are
specially designed to lter out microscopic particles.