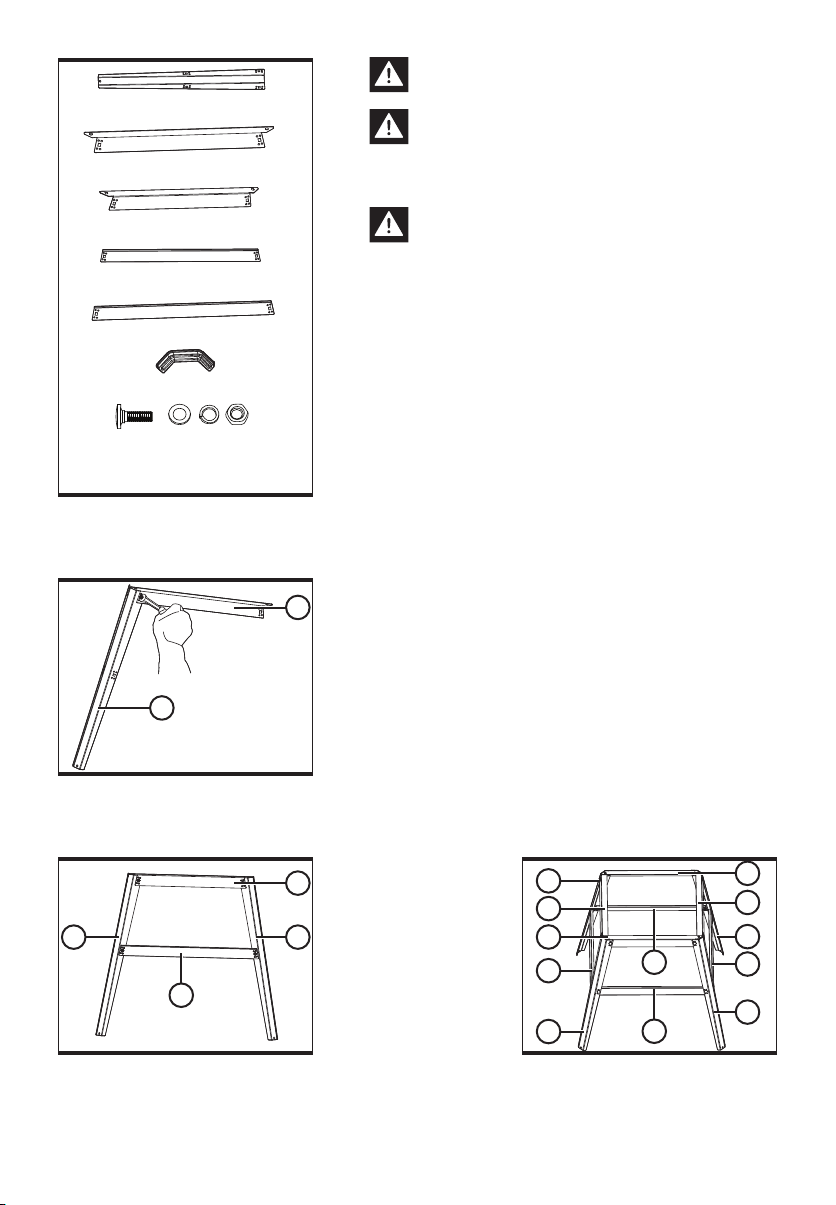
5
- Remove wrenches, cut-off pieces, etc. from the table before the switch is turned on.
- NEVER wear gloves during operation.
- Keep hands out of the line of the saw blade.
- NEVER stand or permit anyone else to stand in line with the path of the saw blade.
- Make sure the blade is not contacting the riving knife or workpiece before the switch
is turned on.
- Before using the tool on an actual workpiece, let it run for a while. Watch for vibration
or wobbling that could indicate poor installation or a poorly balanced blade.
- The tool should not be used for slotting, rabbetting or grooving.
- Replace table insert when worn.
- NEVER make any adjustments while tool is running. Disconnect tool before making
any adjustments.
- Use a push stick when required. Push sticks MUST be used for ripping narrow
workpieces to keep your hands and fingers well away from the blade.
- Always store the push-stick when it is not in use.
- Pay particular attention to instructions for reducing risk of KICKBACK. KICKBACK is
a sudden reaction to a pinched, bound or misaligned saw blade. KICKBACK causes
the ejection of the workpiece from the tool back towards the operator.
KICKBACKS CAN LEAD TO SERIOUS PERSONAL INJURY. Avoid KICKBACKS by
keeping the blade sharp, by keeping the rip fence parallel to the blade, by keeping
the riving knife and blade guard in place and operating properly, by not
releasing the workpiece until you have pushed it all the way past the blade, and by
not ripping a workpiece that is twisted or warped or does not have a straight edge to
guide along the fence.
- Do not perform any operation freehand. Freehand means using your hands to support
or guide the workpiece, in lieu of a rip fence or miter gauge.
- NEVER reach around or over saw blade. NEVER reach for a workpiece until the saw
blade has completely stopped.
- Avoid abrupt, fast feeding. Feed as slowly as possible when cutting hard workpieces.
Do not bend or twist workpiece while feeding. If you stall or jam the blade in
the workpiece, turn the tool off immediately. Unplug the tool.Then clear the jam.
- NEVER remove cut-off pieces near the blade or touch the blade guard while the blade
is running.
- Knock out any loose knots from workpiece BEFORE beginning to cut.
- Do not abuse cord. Never yank cord to disconnect it from the receptacle. Keep cord
away from heat, oil, water and sharp edges.
- Connect the tool to a dust collecting device when sawing.
- The guard can be lifted during workpiece setup and for ease of cleaning. Always
make sure that guard hood is down and flat against sawtable before plugging in the
tool.
Reducing risk of kickback
- Always use the correct blade depth setting. The top of the blade teeth should clear
the workpiece by 1⁄8" (3.2 mm) to 1⁄4" (6.4 mm).
- Inspect the workpiece for knots or nails before beginning a cut. Knock out any loose
knots with a hammer. Never saw into a loose knot or nail.
- Always use the rip fence when rip cutting and the miter gauge when crosscutting.
This helps to prevent twisting the wood in the cut.